Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
- 16 Jun 2023
- 6 min read
Julley Ladakh (Hello Ladakh)
The Indian Navy initiated the “Julley Ladakh” (Hello Ladakh), outreach program to foster awareness about the Navy and engage with the youth and civil society in Ladakh. This initiative, following the Navy's successful efforts in the Northeast and coastal states, aims to achieve several objectives. Firstly, it seeks to celebrate the 75th anniversary of Indian Independence through the "Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav." Secondly, it aims to create awareness about the career opportunities in the Indian Navy, including the Agnipath Scheme, among students and colleges in Ladakh. Moreover, the program endeavors to motivate the youth to join the Indian Navy and showcase Nari Shakti by involving women officers and spouses.
Read more: Agnipath Scheme
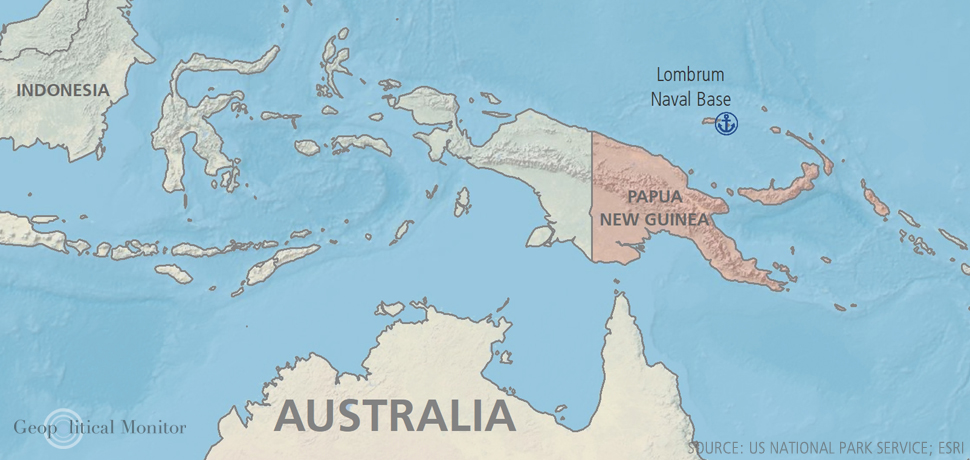
U.S. and Papua New Guinea Security Pact
In a significant move aimed at countering China's influence in the Pacific region, the United States has entered into a landmark security pact with Papua New Guinea. The agreement, which allows the U.S. military to develop and operate bases in Papua New Guinea, grants access to strategic ports and airports, including the Lombrum Naval Base on Manus Island and facilities in Port Moresby. Lombrum Naval Base has historical significance as a former garrison for various countries during World War II and provides deep-water port capabilities. By securing this foothold, the U.S. aims to outflank China's growing presence in the region and reinforce its defense capabilities in the Pacific.
The security pact has faced both support and criticism within Papua New Guinea. Concerns have been raised about potential compromises to Papua New Guinea's autonomy and the target it might paint on the nation. As the country finds itself at the center of a diplomatic tug-of-war between Washington and Beijing, its rich natural resources and strategic location make it a valuable asset for both powers. This agreement is part of Washington's broader strategy to counter China's military foothold in the South Pacific, particularly concerning the defense of Taiwan.
Read more: China's Expansion in the Pacific Island Countries
Bio-Stimulants
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India issues draft guidelines for the registration of bio-stimulants. It is mandatory for a person who wants to manufacture or import any bio-stimulant to list such bio-stimulant under Schedule VI of the Fertiliser (inorganic, organic or mixed) Control Amendment Order 2021, also called the FCO Amendment order.
Bio-stimulants are substances, microorganisms, or combinations thereof that enhance the physiological processes in plants, leading to improved nutrient uptake, growth, yield, nutrition efficiency, crop quality, and stress tolerance. They serve to stimulate plant processes without directly providing nutrients. Bio-stimulants are different from pesticides or plant growth regulators which fall under the Insecticides Act, 1968.
Some examples of bio-stimulants include plant hormones, vitamins, enzymes, humic acid, sugars, sea kelp, fish emulsion, protein hydrolysates, seaweed and plant extracts, chitosan and other biopolymers, inorganic compounds and beneficial microbes.
The key difference between bio-stimulants and fertilizers is the use and the mechanism of action, and the fact that living microbes are involved in the bio-stimulants. While bio-stimulants help to improve plant growth and health, fertilizers are primarily used to replenish the soil with essential nutrients that plants need to grow.
Phosphorus on Saturn’s Moon Enceladus
Scientists have discovered phosphorus, a key element for life, on Saturn’s moon Enceladus. Previous studies had found minerals and organic compounds in Enceladus' ice grains but had not detected phosphorus until now. The discovery was based on a review of data collected by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft during its 13-year exploration of the giant planet, its rings and its moons from 2004 to 2017.
Phosphorus is a fundamental unit of the structure of DNA and RNA and is a vital part of cell membranes and energy-carrying molecules existing in all forms of life on Earth. This new discovery makes Enceladus a potential option as a habitable place in the solar system beyond Earth, if only to microbes.
Over the past 25 years, scientists have discovered habitable places with oceans beneath a surface layer of ice in the solar system, including Jupiter’s moon Europa, Saturn’s largest moon Titan, and Pluto.