Quantum Nature of Gravity | 01 Mar 2025
Why in News?
Scientists are conducting experiments with nanocrystals to explore if gravity follows quantum principles.
- This effort aims to bridge the gap between General Relativity (explains gravity at macroscopic scales) and Quantum Mechanics (governs atomic and subatomic interactions).
- Since these theories are fundamentally incompatible, the research contributes to the pursuit of a unified theory of quantum gravity.
What is the Experiment Proposed to Test the Quantumness of Gravity?
- About Experiment: Scientists propose an experiment using quantum superposition, where particles exist in multiple states until measured.
- Nanocrystals will test if gravity follows quantum mechanics.
- A test mass crystal will be placed in superposition (existing in two places at once) while another mass interacts with it via gravity.
- After measuring the second crystal, scientists will check if gravity causes the test mass to collapse into a definite state, potentially indicating that gravity follows quantum principles.
- Significance:
- If successful, the experiment may prove that gravity is not just a classical force but also exhibits quantum properties, as current theories suggest that gravity should show quantum effects.
- Most quantum gravity tests rely on strong gravity (e.g., black holes), which is impractical to test.
- This experiment proposes studying weak gravity near small objects, making quantum gravity testing more feasible.
- Challenges:
- The experiment requires extreme precision since even small disturbances (like air molecules or seismic activity) can affect the results.
- Scientists need to create a near-perfect vacuum and measure the results very quickly.
- The technology to perform this experiment is still being developed.
| Read More: What are the Key Features of Quantum Mechanics? |
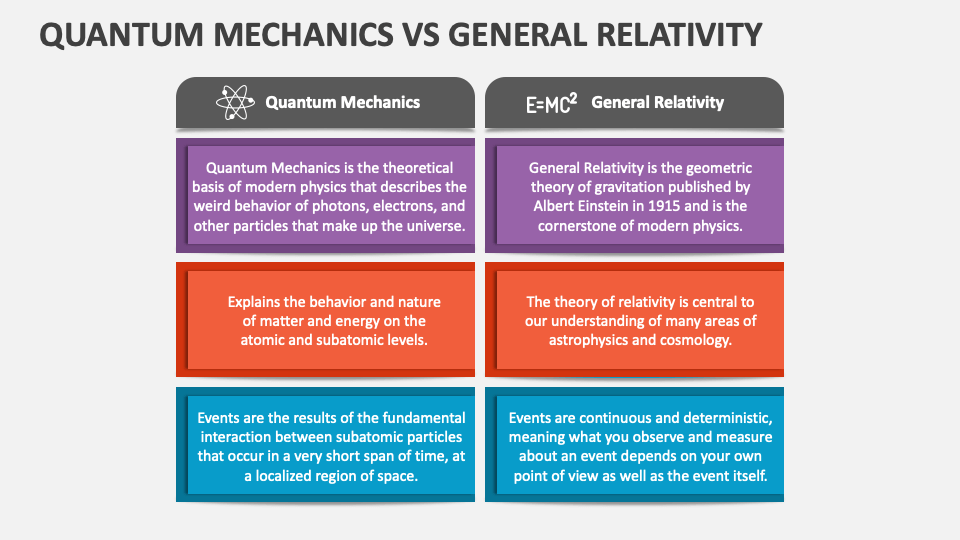
What is Quantum Mechanics and General Relativity?
- Quantum Mechanics:
- About:
- Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that explains how sub-atomic particles, like electrons and photons, can behave both as particles (small bits of matter) and waves (energy disturbances).
- This concept is known as wave-particle duality and is a fundamental principle of quantum physics.
- Key Principles:
- Wave-particle Duality: Particles can behave both as waves and particles.
- Superposition: A particle can exist in multiple states until measured.
- Entanglement: Two particles can be correlated in such a way that the state of one instantly affects the other, even across vast distances.
- Uncertainty Principle: The position and momentum of a particle cannot both be precisely measured at the same time.
- About:
- General Relativity:
- About: It is the modern theory of gravity proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915 as an extension of Newton’s law of universal gravitation.
- It describes gravity not as a force, but as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy.
- Key Principles:
- Space-time curvature: Massive objects like the Sun bend space-time, causing planets to orbit.
- Time Dilation: Time moves slower in stronger gravitational fields (e.g., near black holes).
- Equivalence Principle: Acceleration and gravitational forces are indistinguishable in a closed system.
- About: It is the modern theory of gravity proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915 as an extension of Newton’s law of universal gravitation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following phenomena: (2018)
- Light is affected by gravity.
- The Universe is constantly expanding.
- Matter warps its surrounding space-time.
Which of the above is/are the prediction/predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, often discussed in media?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)