Indian History
Pythagorean Geometry in Vedic-Era
- 20 Jul 2022
- 4 min read
For Prelims: Indian Ancient History, Vedic Age, Veda System
For Mains: Significance of Veda System, Significance of Vedic Age
Why in News?
Recently, a position paper by the Karnataka government on the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has described Pythagoras’s theorem as “fake news”.
- It has referred to a text called the Baudhayana Sulbasutra, in which a specific shloka refers to the theorem.
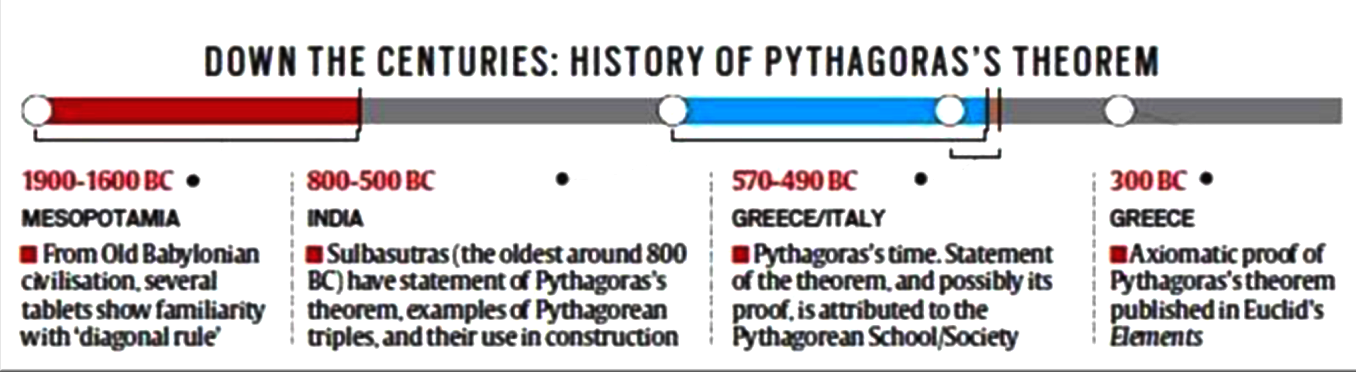
What do we need to know about Pythagoras?
- About Pythagoras:
- Evidence suggests that the Greek philosopher (around 570–490 BC) did exist.
- There is an element of mystery around him, largely because of the secretive nature of the school/society he founded in Italy.
- Relatively little is known about his mathematical achievements, because there is nothing today of his own writings.
- About Pythagoras Theorem:
- The Pythagoras theorem describes the relationship connecting the three sides of a right triangle (one in which one of the angles is 90°).
- a2 + b2 = c2
- If any two sides of a right triangle are known, the theorem allows you to calculate the third side.
- a2 + b2 = c2
- The Pythagoras theorem describes the relationship connecting the three sides of a right triangle (one in which one of the angles is 90°).
How do we know that Vedic Indian Mathematicians knew this?
- There are references of Pythagoras in the Sulbasutras, which are texts pertaining to fire rituals (yajanas) performed by Vedic Indians.
- The oldest of these is the Baudhayana Sulbasutra.
- The period of Baudhayana Sulbasutra is uncertain. It is estimated based on linguistic and other secondary historical considerations.
- In recent literature, Baudhayana Sulbasutra is taken to be from around 800 BCE.
- Baudhayana Sulbasutra contains a statement of what is called Pythagoras theorem (it was known rather as a geometric fact, and not as a ‘theorem’).
- The yajna rituals involved construction of altars (vedi) and fireplaces (agni) in a variety of shapes such as isosceles triangles, symmetric trapezia, and rectangles.
- The sulbasutras describe steps towards construction of these figures with prescribed sizes.
How did the Knowledge of Equation Evolve?
- The earliest evidence is from the Old Babylonian civilisation (1900-1600 BCE).
- They referred to it as the Diagonal Rule.
- The earliest evidence of a proof comes from a period after the sulbasutras.
- The oldest surviving axiomatic proof of the theorem is in the Elements of Euclid from around 300 BCE.
What are Vedas?
- The word Veda signifies knowledge and the texts are actually about providing mankind knowledge to conduct their entire life on earth and beyond.
- There are four major vedas:
- Rig Veda:
- Oldest existing veda among the four.
- Focus is on worldly prosperity and natural beauty.
- Text is organised in 10 books known as Mandalas.
- Prominent gods mentioned in Rig Veda:
- Lord Indra, Agni, Varuna, Rudra, Aditya etc.
- Yajur Veda:
- The name Yaju signifies Sacrifice.
- It concentrates on rites and mantras of the different types of sacrifices.
- Two major recensions (samhita) are:
- Shukla, also called Vajasaneyi Samhita.
- Krishna, also called Taittiriya Samhita.
- Sama Veda:
- It has been named after Saman (melody).
- It concentrates on Melody or Songs.
- It is also called the Book of Chants.
- Atharva Veda:
- It is also known as Brahma Veda and has been attributed to two rishis called Atharban and Angiras.
- It concentrates on Peace and Prosperity of human society.
- Two major recensions (sakhas) are:
- Paippalada
- Saunakiya
- Rig Veda: