Important Facts For Prelims
Pushpak, ISRO’s Reusable Launch Vehicle
- 25 Jun 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully completed the third and final Reusable Launch Vehicle Landing Experiment (RLV LEX-03) for the Pushpak vehicle.
- This demonstrated the autonomous landing capability of the RLV under more challenging release conditions and severe wind conditions.
What is RLV LEX-03 Mission?
- About:
- During the RLV LEX-03 mission, the Pushpak vehicle was released from an Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter at an altitude of 4.5 km.
- From this point, the winged vehicle autonomously executed cross-range correction manoeuvres approached the runway and performed a precise horizontal landing at the runway centerline.
- The high-speed landing, exceeding 320 km/h, was successfully slowed to around 100 km/h using the vehicle's brake parachute and landing gear brakes.
- Technologies and Capabilities Demonstrated:
- Precise Landing: LEX-03 used multisensor fusion to guide the vehicle for a controlled landing.
- Autonomous Flight: The Pushpak vehicle demonstrated its ability to land itself, including correcting its course during descent.
- Reusable Design: The mission reused key parts from a previous flight, highlighting the cost-saving potential of RLVs.
- Significance:
- This mission simulated the approach and landing interface, as well as the high-speed landing conditions, for a vehicle returning from space.
- It validated ISRO's advanced guidance algorithm for longitudinal and lateral error corrections, which is essential for future Orbital Re-entry Missions.
- By testing key technologies like autonomous landing and reusable parts, it paves the way for a fully reusable launch vehicle. This could cut launch costs and make space missions more efficient.
- This mission simulated the approach and landing interface, as well as the high-speed landing conditions, for a vehicle returning from space.
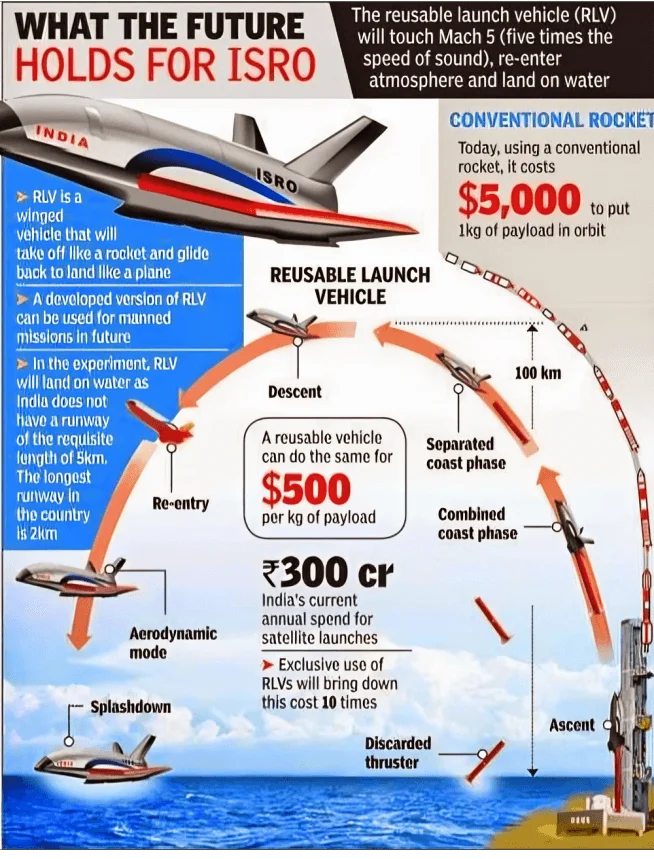
What are Reusable Launch Vehicles?
- About:
- Reusable launch vehicles (RLVs) are rockets that can be used multiple times for space missions, unlike traditional expendable rockets where each stage is discarded after use.
- Different from Multi-Stage Rocket:
- In a typical multi-stage rocket, the first stage is jettisoned (discarded to lighten the load) after its fuel is consumed, while the remaining stages continue to propel the payload into orbit.
- RLVs recover and reuse the first stage. After detaching from the upper stages, the first stage uses engines or parachutes to descend and land back on Earth.
- It can then be refurbished for future launches, significantly reducing costs.
- Space Agencies Currently Using or Developing RLVs.
- SpaceX (USA): Falcon 9, with over 220 launches, 178 landings, and 155 re-flights as of May 2023.
- Blue Origin (USA): New Shepard performs suborbital flights and lands vertically.
- JAXA (Japan) and ESA (Europe): Researching reusable launch systems to reduce space access costs.
- ISRO (India): Developed the Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstration (RLV-TD) and conducted a successful landing.
Read More: Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)