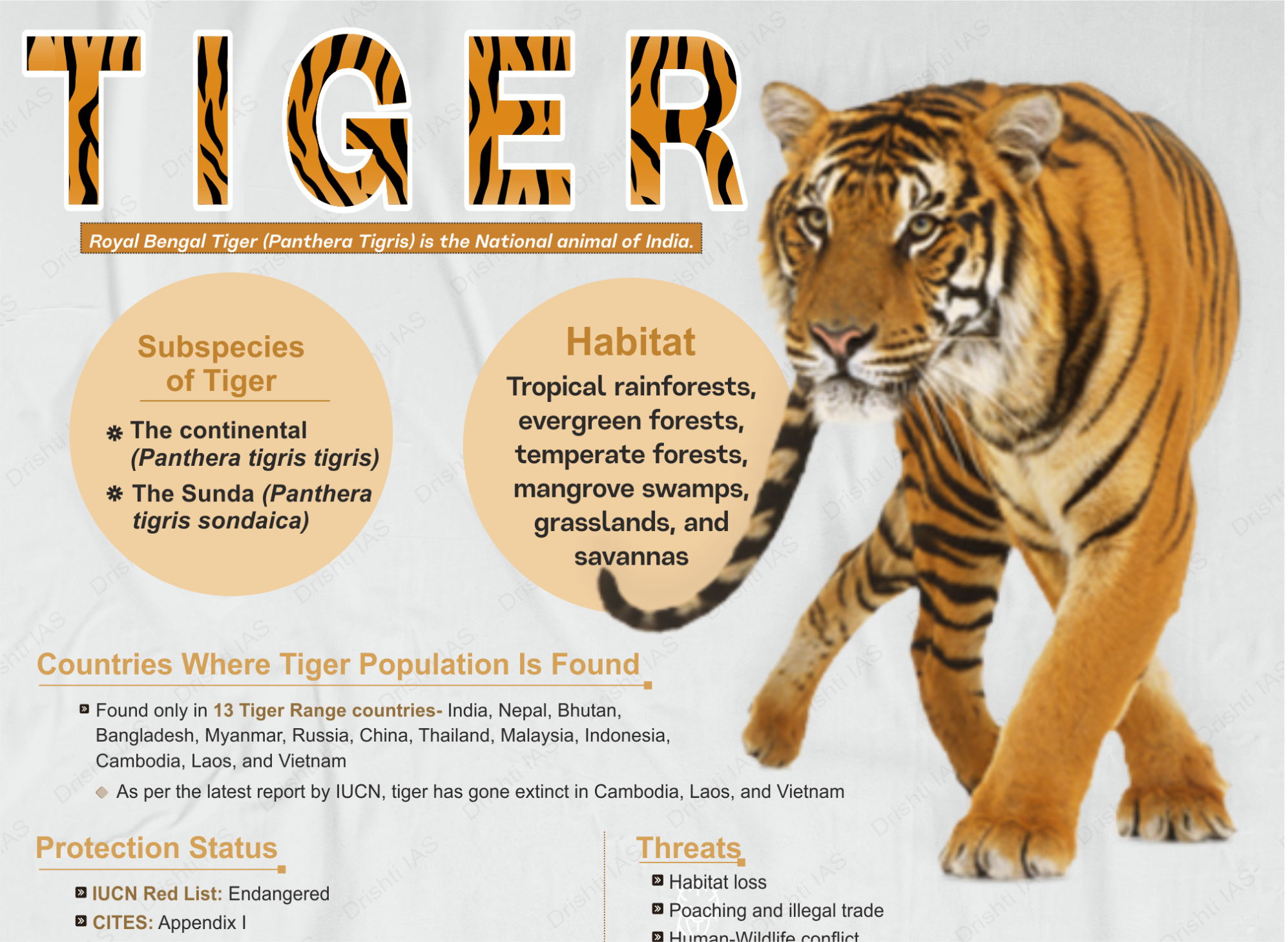
Project Tiger | 13 Jan 2024
For Prelims: Project Tiger, Tiger Reserves, Pug-mark method, Tiger Census, Camera-trap method, The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH), National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Tiger Task Force, The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH), IAS, UPSC.
For Mains: Project tiger and its contribution in conservation of tiger population.
Why in News?
Over time, the tiger conservation initiative has evolved, establishing Tiger Reserves (55) and implementing crucial wildlife protection laws.
- However, conflicts in Tiger Reserves between the forest bureaucracy and forest dwellers have intensified due to violations of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, and the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change announced the merger of the two flagship programmes Project Tiger (PT) and Project Elephant as Project Tiger and Elephant (PTE).
What are the Shortcomings in Tiger Conservation?
- The Wildlife Protection (Amendment) Act, 2006 didn’t prohibit the diversion of a “tiger’s forest” for development projects and allowed wildlife to be killed as a last resort if they threatened human lives.
- The government planned to notify the FRA Rules in 2009 and operationalise the Act.
- But in November 2007, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) passed an order that gave the Chief Wildlife Wardens 13 days’ time to submit a proposal to delineate Critical Tiger Habitats (CTHs), each with an area of 800-1,000 sq. km.
- As a result, the government ended up notifying 26 Tiger Reserves in 12 States Section 38 (V) of WLPA, and without complying with its provisions.
- Tiger Reserves in Similipal, Odisha, the Critical Tiger Habitats (CTHs) lacked a Buffer Area.
- It was only in 2012 that they were included following a directive from the Supreme Court, which gave the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) a three-month ultimatum.
- The Tiger Task Force found the approach of using guns, guards, and fences wasn’t protecting tigers, and that the increasing conflict between the forest/wildlife bureaucracy and those who coexist with the tigers was a recipe for disaster.
What are Initiatives Taken for Tiger Conservation?
Project Tiger:
- About:
- Project Tiger is a wildlife conservation initiative in India that was launched in 1973.
- The primary objective of Project Tiger is to ensure the survival and maintenance of the tiger population in their natural habitats by creating dedicated Tiger Reserves.
- Starting with only nine reserves covering 9,115 sq. km, the project marked a paradigm shift in wildlife conservation efforts.
- Method of Tiger Census:
- The unreliable pug-mark method of the first tiger census in 1972 gave way to more accurate techniques like the camera-trap method.
- Growth Rate in Tiger Population:
- The first tiger census, in 1972, used the unreliable pug-mark method to count 1,827 tigers.
- As of 2022, the tiger population is estimated at 3,167-3,925, showcasing a growth rate of 6.1% per year.
- India is now home to three-quarters of the world’s tigers.
- Tiger Reserve:
- In 1973, Project Tiger began with nine reserves covering 9,115 sq. km. By 2018, it had grown to 55 reserves in different states, totalling 78,135.956 sq. km or 2.38% of India's land area.
Wildlife (Protection) Act,1972:
- The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 provides a legal framework for the protection of various species of wild animals and plants, management of their habitats, regulation, and control of trade in wild animals, plants, and products made from them.
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act (WLPA), 1972 laid the groundwork for tiger conservation. It established National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries, segregating rights in favour of State governments and introducing the concept of Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH).
- The amendment to WLPA in 2006 led to the creation of the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and a comprehensive tiger conservation plan.
- This marked a departure from the earlier fortress conservation approach, acknowledging the inseparable link between tiger protection, forest conservation, and the well-being of local communities.
Tiger Task Force:
- In 2005, the formation of the Tiger Task Force, prompted by concerns about tiger conservation, emphasized the necessity for a reassessment. The task force pointed out flaws in the existing strategy that heavily depended on weapons, guards, and fences.
What is the Recognition of Forest Rights Act, 2006?
- The enactment of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 recognized the customary and traditional forest rights in communities.
- This empowered Gram Sabhas to democratically manage forest resources and biodiversity within their boundaries.
- Critical Wildlife Habitat (CWH):
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA) introduced a 'Critical Wildlife Habitat' (CWH), similar to the Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH) under the Wildlife Protection Act (WLPA).
- However, a key difference was that once a CWH was notified, it couldn't be redirected for non-forestry purposes. This particular clause was insisted upon by Adivasi movements during negotiations.
- Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH) cover 42,913.37 sq. km, or 26% of the area under National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries.
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA) introduced a 'Critical Wildlife Habitat' (CWH), similar to the Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH) under the Wildlife Protection Act (WLPA).
- The Gram Sabhas were given the authority to safeguard, preserve, and oversee the forest, wildlife, and biodiversity within their customary boundaries.
Conclusion
The journey from Project Tiger in 1973 to creation of the NTCA by 2006 amendments reflects India's commitment to tiger conservation and sustainable coexistence. The integration of community empowerment, recognition of forest rights, and a nuanced approach to wildlife protection showcase a holistic paradigm in wildlife conservation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006? (2021)
(a) Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
(b) Ministry of Panchayati Raj
(c) Ministry of Rural Development
(d) Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The definition of “Critical Wildlife Habitat” is incorporated in the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
- For the first time in India, Baigas have been given Habitat Rights.
- Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change officially decides and declares Habitat Rights for Primitive and Vulnerable Tribal Groups in any part of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)