Programme on Science of Natural Farming | 22 Jul 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the "Regional Consultation Program on the Science of Natural Farming” emphasised the importance of natural farming as a sustainable agricultural practice.
- It was announced that farmers who practise natural farming on a portion of their land for 3 years will be eligible for government subsidies.
What is Natural Farming?
- About:
- Natural farming is an agricultural practice that emphasises minimal intervention and the use of natural resources to cultivate crops.
- It seeks to enhance soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem balance without relying on synthetic fertilisers, pesticides, or herbicides.
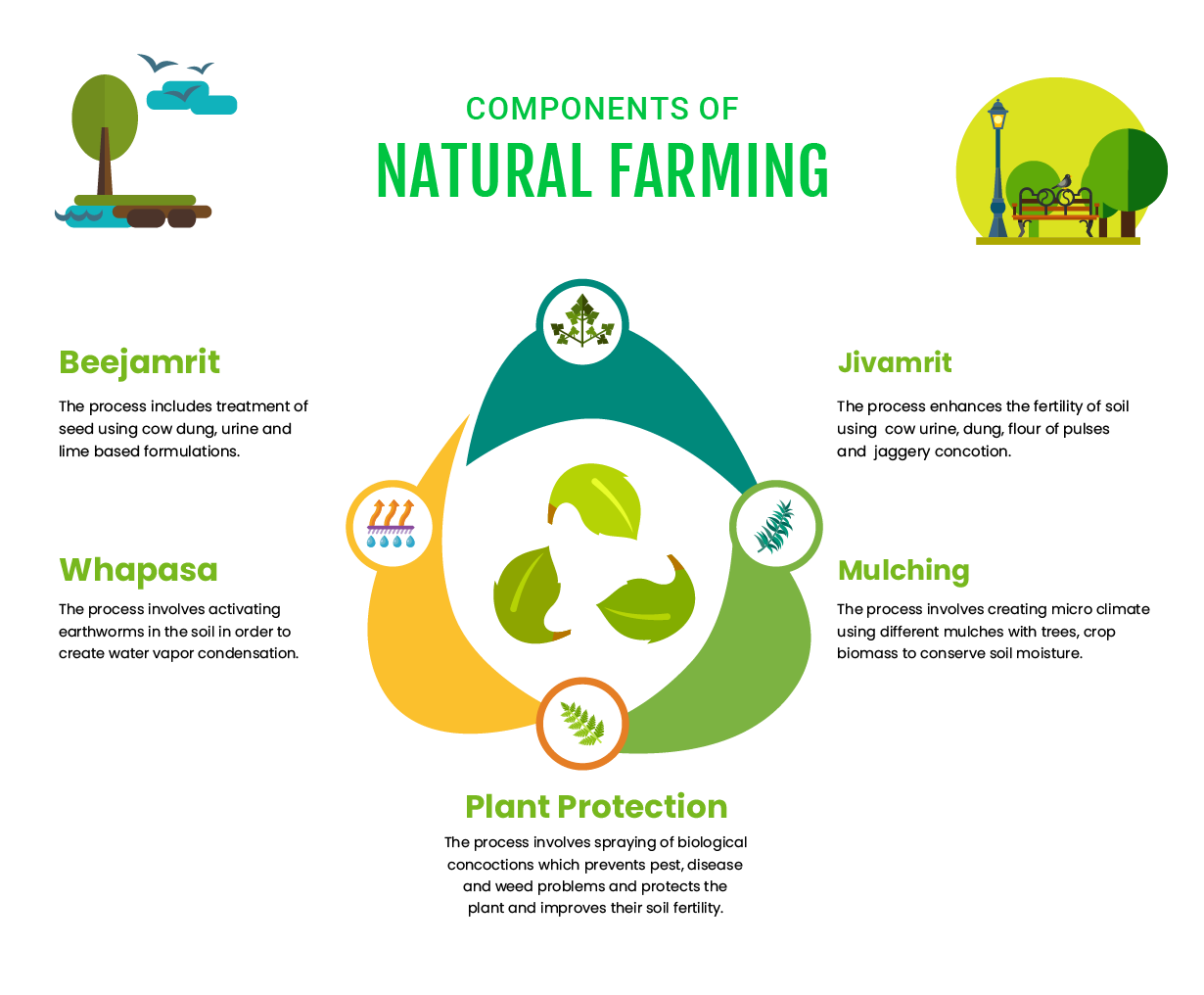
- It is largely based on on-farm biomass recycling with major stress on biomass mulching, use of on-farm cow dung-urine formulations; maintaining soil aeration and exclusion of all synthetic chemical inputs.
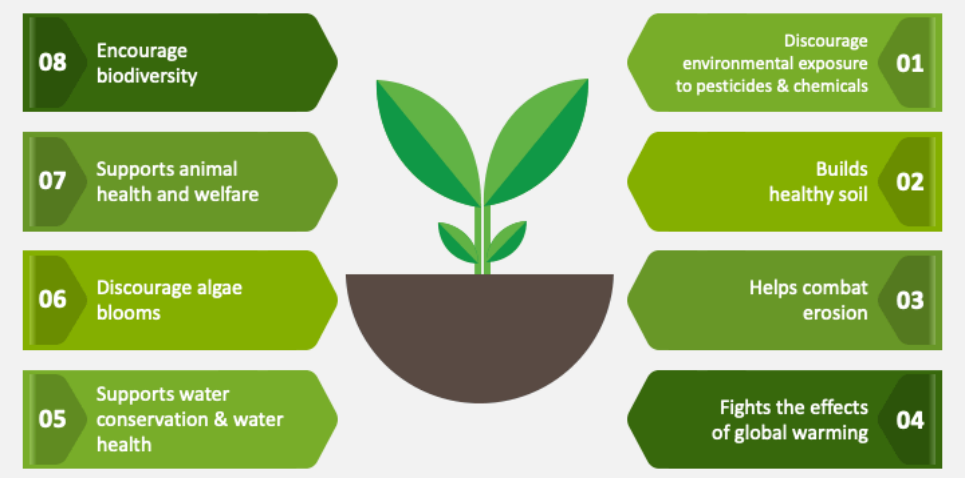
- Aims and Objectives:
- Preserve natural flora and fauna
- Restore soil health and fertility
- Maintain diversity in crop production
- Efficient utilisation of land and natural resources
- Promote natural beneficial insects, animals, and microbes
- Promotion of local breeds for livestock integration
- Use of natural/local resource-based inputs
- Reduce input cost of agricultural production
- Improve economics of farmers
- Components:
- Current Scenario:
- Several states, including Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu, have initiated programs to promote natural farming.
- Currently, over 10 lakh hectares of land in India are being used for natural farming.
- Government Schemes:
- Bharatiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhati (BPKP): It is a sub-mission under the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY), which falls within the umbrella of the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- National Mission on Natural Farming
Read more: Plough to Plate: Natural Farming Unleashed, Natural Farming
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 How is permaculture farming different from conventional chemical farming? (2021)
- Permaculture farming discourages monocultural practices but in conventional chemical farming, monoculture practices are predominant.
- Conventional chemical farming can cause an increase in soil salinity but the occurrence of such phenomenon is not observed in permaculture farming.
- Conventional chemical farming is easily possible in semi-arid regions but permaculture farming is not so easily possible in such regions.
- Practice of mulching is very important in permaculture farming but not necessarily so in conventional chemical farming.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 4 only
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q.2 Which of the following is the chief characteristic of ‘mixed farming’? (2012)
(a) Cultivation of both cash crops and food crops
(b) Cultivation of two or more crops in the same field
(c) Rearing of animals and cultivation of crops together
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What are the present challenges before crop diversification? How do emerging technologies provide an opportunity for crop diversification? (2021)
Q.2 How has India benefited from the contributions of Sir M. Visvesvaraya and Dr. M. S. Swaminathan in the fields of water engineering and agricultural science respectively? (2019)