Post-Quantum Encryption Cryptography | 31 Jan 2025
Virtual Private Network (VPN) companies are adapting to the potential threats posed by quantum computing through the implementation of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC).
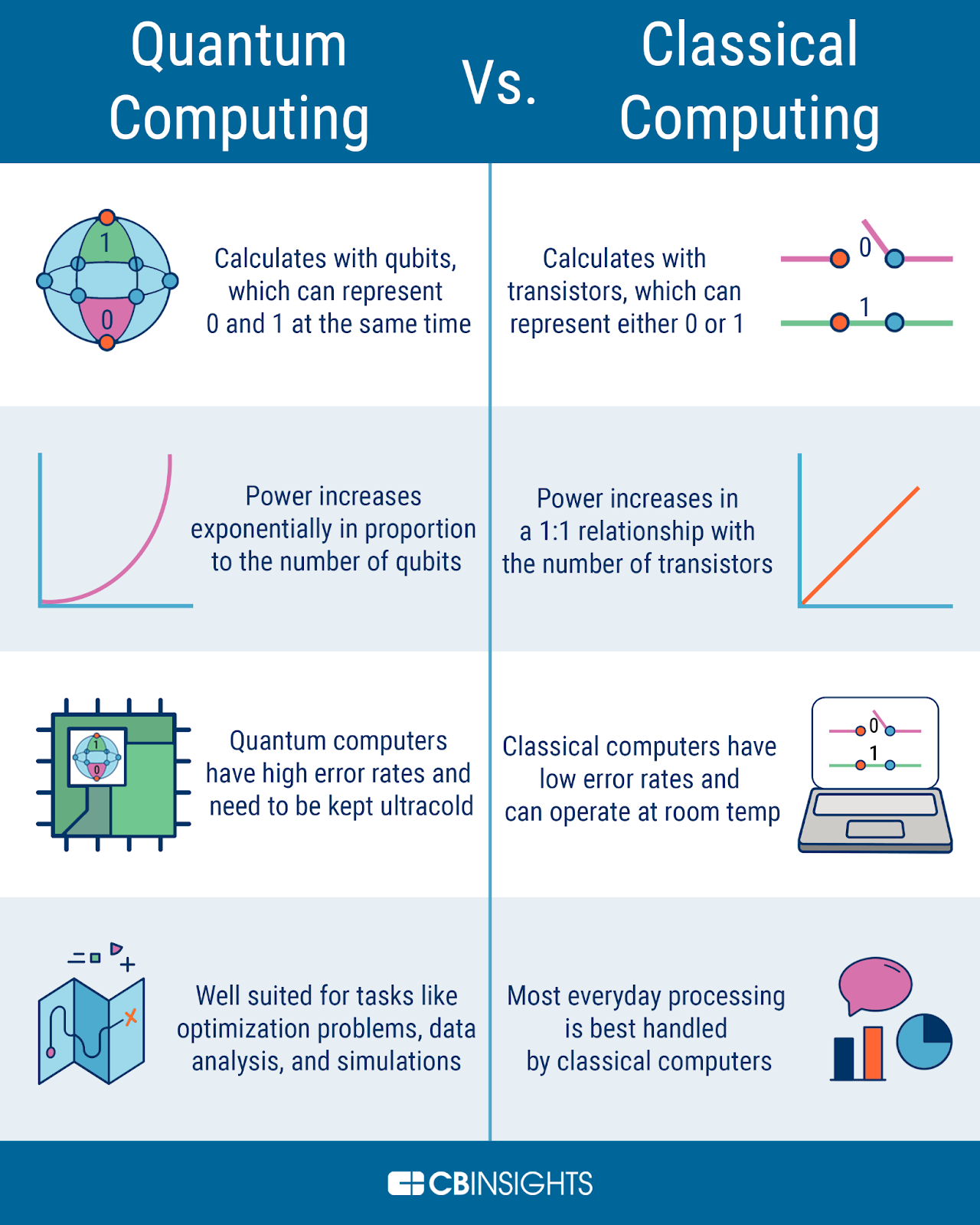
- Quantum computing poses several threats to current encryption methods due to its ability to perform extremely fast calculations.
- Breaking Asymmetric Encryption: Quantum computers can solve complex mathematical problems like factoring large numbers and solving discrete logarithms.
- This could compromise encryption methods like Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), which are widely used for secure communication.
- Store Now, Decrypt Later (SNDL) Attacks: Cybercriminals may store encrypted data instantly and decrypt it later when quantum computers become powerful enough, endangering sensitive information.
- Industry-Wide Data Security Risks: Sectors like finance, healthcare, and government communications face risks of data breaches and financial losses if quantum computers break encryption standards.
- Breaking Asymmetric Encryption: Quantum computers can solve complex mathematical problems like factoring large numbers and solving discrete logarithms.
- Post-Quantum Encryption/ Cryptography (PQC):
- PQC refers to cryptographic methods that do not rely on mathematical problems easily solvable by quantum computers.
- It is also known as quantum-resistant, quantum-safe, or quantum-proof cryptography.
- These methods are designed to remain secure against attacks from both classical and quantum computing systems.
- A VPN technology encrypts data and hides a user's IP address to ensure secure communication between devices to protect data privacy and security.
Read More: Post-Quantum Cryptography, Virtual Private Network