Governance
Polygraph Test
- 21 Aug 2024
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Polygraph Test, Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), Narco-Analysis Test, National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
For Mains: About Polygraph, Narco Test, Legal Implications, Related Court Judgments, Challenges in Implementations and Way Forward
Why in News?
Recently, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has been authorised to perform a polygraph test on the key suspect in the rape and murder case of a postgraduate doctor at Kolkata Medical College.
- The polygraph test will help investigators check the consistency of the suspect's statements and identify potential deception.
What is a Polygraph Test?
- About:
- Polygraph or Lie Detector Test is a procedure that measures and records several physiological indicators such as blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin conductivity while a person is asked and answers a series of questions.
- This test is based on the assumption that physiological responses that are triggered when a person is lying are different from what they would be otherwise.
- A numerical value is assigned to each response to conclude whether the person is telling the truth, is deceiving, or is uncertain.
- A test similar to polygraph was first done in the 19th century by the Italian criminologist Cesare Lombroso, who used a machine to measure changes in the blood pressure of criminal suspects during interrogation.
- Different From Narco-Analysis Test:
- A narco analysis test involves injecting sodium pentothal into the accused, inducing a hypnotic or sedated state that supposedly neutralises their imagination.
- In this state, the individual is considered incapable of lying and is expected to reveal truthful information.
- Accuracy of Tests:
- Polygraph and narco tests are not scientifically proven to be 100% accurate and remain controversial in the medical field.
- Despite this, investigative agencies have recently used these tests as a "softer alternative" to torture to extract the truth from suspects.
Note:
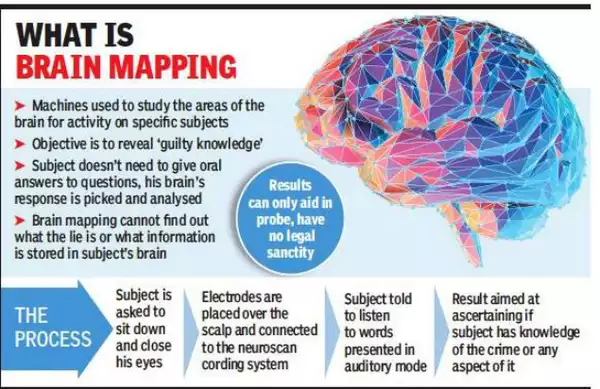
- Brain Mapping: It is a test that uses imaging to study the brain's anatomy and function. It can help doctors determine if brain function is normal, and identify areas of the brain that control movement, speech, and vision.
What is the Legal Admissibility of a Polygraph Test?
- Violation of Article 20(3): Polygraph, narco-analysis, and brain mapping tests conducted without the accused's consent violate Article 20(3) of the Indian Constitution, which protects the right against self-incrimination.
- This article ensures that no person accused of an offence is compelled to be a witness against themselves.
- Necessity of Consent: As these tests involve the accused providing potentially self-incriminating information, obtaining their consent is mandatory to avoid breaching constitutional rights.
- Judicial and Human Rights Concerns: The use of narco-analysis and similar tests raises significant concerns about judicial integrity and human rights, particularly regarding individual rights and freedoms.
- Criticism from Courts: Courts have often criticised these tests as they can constitute mental torture, violating the right to life and privacy guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
What are the Landmark Judgments Related to Polygraph Tests?
- Selvi v. State of Karnataka & Anr Case 2010: The SC ruled on the legality and admissibility of narco tests establishing that the involuntary administration of narco or lie detector tests constitutes an intrusion into an individual's "mental privacy."
- The apex court held that narco tests violate the fundamental right against self-incrimination under Article 20(3) of the Constitution, which states that no person accused of any offence shall be compelled to be a witness against himself.
- Self-incrimination is a legal principle under which a person cannot be compelled to provide information or testify against themselves in a criminal case.
- The apex court held that narco tests violate the fundamental right against self-incrimination under Article 20(3) of the Constitution, which states that no person accused of any offence shall be compelled to be a witness against himself.
- D.K. Basu v. State of West Bengal case, 1997: The SC ruled that involuntary administration of the polygraph and narcos test will amount to cruel, inhuman, and degrading treatment in the context of Article 21 or the Right to Life and Liberty.
- State of Bombay v. Kathi Kalu Oghad, 1961, the Supreme Court of India ruled that the right against self-incrimination under Article 20(3) of the Constitution does not extend to the physical evidence (like fingerprints, handwriting, blood, and voice samples), voluntarily given information and identification procedures (like line-ups and photo arrays).
- Other Observations of the SC: Narco tests are not reliable or conclusive as evidence, as they are based on assumptions and probabilities.
- Any information or material that is subsequently discovered with the help of voluntarily administered test results can be admitted, under Section 27 of the Evidence Act, 1872 ( now Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam).
- Section 27 of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872, allows the admissibility of information provided by an accused in police custody if it leads to the discovery of a fact.
- Only the portion of the information that directly relates to the discovered fact can be proved, regardless of whether it amounts to a confession.
- The court also emphasised that the ‘Guidelines for the Administration of Polygraph Test on an Accused’, published by the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in 2000, must be strictly followed.
- Any information or material that is subsequently discovered with the help of voluntarily administered test results can be admitted, under Section 27 of the Evidence Act, 1872 ( now Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam).
NHRC Guidelines of Polygraph Test
- Voluntary Consent: The accused must willingly agree to undergo the polygraph test, with the option to refuse.
- Informed Consent: Before agreeing, the accused should be fully informed by the police and their lawyer about the test's purpose, procedure, and legal consequences.
- Recorded Consent: The accused's consent must be formally recorded in the presence of a Judicial Magistrate.
- Documentation: During court proceedings, the police must provide evidence that the accused voluntarily agreed to the test, which is documented by the lawyer and presented to the judge.
- Clarification of Statements: The accused should be made aware that any statements made during the polygraph test are treated as statements to the police, not as confessions.
- Judicial Consideration: Judges consider various factors, such as the length of the accused's detention and the nature of the interrogation, when evaluating the results of a polygraph test.
|
Drishti Mains Test: What is a Polygraph Test? Discuss the significance of polygraph tests in criminal investigations |