Biodiversity & Environment
Planetary Boundaries
- 20 Sep 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Planetary Boundaries, Climate change
For Mains: Importance of Planetary Boundaries in maintaining Earth's stability and biodiversity.
Why in News?
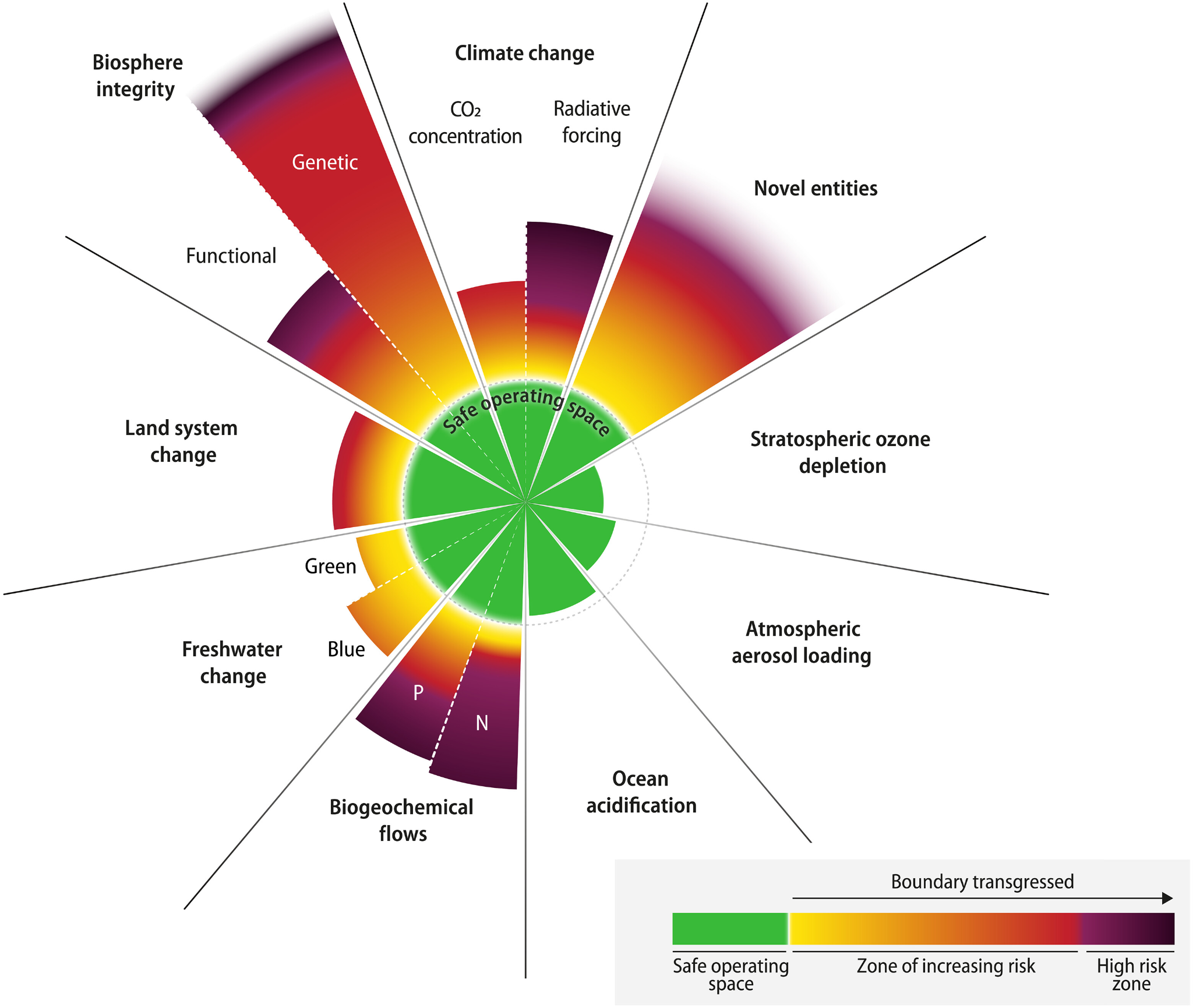
According to a new study, published in the journal Science Advances. The world has breached six out of nine planetary boundaries necessary to maintain Earth's stability and resilience.
- Scientists have investigated the processes within Earth's ecosystem that have played a crucial role in maintaining favorable conditions for human existence over the last 12,000 years.
What Are Planetary Boundaries?
- About:
- The planetary boundaries framework was first proposed by Johan Rockström and a group of 28 internationally renowned scientists in 2009 to define the environmental limits within which humanity can safely operate to maintain Earth's stability and biodiversity.
- Nine Planetary Boundaries:
- Climate change.
- Change in biosphere integrity (biodiversity loss and species extinction)
- Stratospheric ozone depletion.
- Ocean acidification.
- Biogeochemical flows (phosphorus and nitrogen cycles).
- Land-system change (for example deforestation).
- Freshwater use (alterations across the entire water cycle over land).
- Atmospheric aerosol loading (microscopic particles in the atmosphere that affect climate and living organisms).
- Introduction of novel entities(consisting of microplastics, endocrine disruptors, and organic pollutants).
- Breaching Planetary Boundaries:
- Breaching of these boundaries doesn't indicate an immediate catastrophe but raises the risk of irreversible environmental changes.
- This situation could lead to conditions on Earth that no longer support our current way of life.
- Breaching of these boundaries doesn't indicate an immediate catastrophe but raises the risk of irreversible environmental changes.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Impacted Boundaries:
- Climate Change:
- The researchers set the planetary boundary for atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration and radiative forcing (represents the size of the energy imbalance in the atmosphere) contributing to climate change at 350 parts per million (ppm) and 1 Watts per square meter (Wm−2), respectively. Currently, this has reached 417 ppm and is 2.91 W m−2.
- Biosphere Integrity:
- As for biosphere integrity, the researchers kept a limit of less than 10 extinctions per million species-years. Human-induced species extinctions have far exceeded the safe limit.
- The study estimated the extinction rate was greater than 100 extinctions per million species-years.
- It is estimated that around one million of the 8 million plant and animal species are threatened with extinction.
- Over 10% of the genetic diversity of plants and animals may have been wiped out over the last 150 years.
- Land System Change:
- The global forested land area has dropped below the safe limit of 75%, currently standing at only 60%.
- Freshwater Change:
- Both blue water (surface and groundwater) and green water (available water for plants) have experienced impacts beyond their safe thresholds of 10.2% and 11.1%, respectively in 1905 and 1929, currently at 18.2 % and 15.8 %, respectively.
- Biogeochemical Flows:
- Flows of nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen in the environment have surged beyond safe limits.
- The boundary was fixed at 11 teragrams (Tg) for Phosphorus and 62 Tg for Nitrogen. This is now 22.6 Tg and 190 Tg, respectively.
- Flows of nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen in the environment have surged beyond safe limits.
- Novel Entities:
- The planetary boundary of novel entities was calculated to be zero.
- Human influence on novel entities, including microplastics, endocrine disruptors, and organic pollutants, has transgressed the zero boundary. This means humans have transgressed this limit as well.
- Climate Change:
- Safe Boundaries:
- Stratospheric ozone depletion, aerosol loading and ocean acidification were found to be within the planetary boundary.
Way Forward
- Implement conservation programs targeting biodiversity preservation, restoration of ecosystems, and the protection of endangered species and genetic diversity.
- Embracing circularity promotes resource regeneration, minimizing waste and ensuring that valuable materials are continually repurposed rather than discarded.
- Implement strict regulations on waste disposal, encouraging recycling and reducing pollution of novel entities like microplastics.
- Empower communities to actively participate in sustainable practices, cultivating a collective sense of responsibility for environmental stewardship.
- Prioritize climate mitigation strategies to limit temperature rise and prevent further breaches of the planetary boundary related to climate change.
- Promote zero-emission technologies and reduce carbon footprints through incentives for clean energy adoption and sustainable transportation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Discuss global warming and mention its effects on the global climate. Explain the control measures to bring down the level of greenhouse gases that cause global warming, in the light of the Kyoto Protocol, 1997. (2022)