Personality Rights | 05 Jun 2024
For Prelims: Personality Rights, Rights to Privacy, Article 21, Artificial Intelligence (AI).
For Mains: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology, and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
Why in News?
The recent dispute between Hollywood Actress and OpenAI highlights the importance of personality rights in the context of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models.
- The actress accused OpenAI, the artificial intelligence company behind ChatGPT, of using her voice despite having previously declined licensing requests from the company's CEO.
- Earlier, the New York Times (NYT) took legal action against OpenAI and Microsoft, alleging the unauthorised use of its copyrighted content to train AI models, including ChatGPT.
What are Personality Rights?
- About:
- Personality rights refer to an individual’s right to protect their personality, which is a part of the broader right to privacy or property.
- These rights encompass various aspects of a celebrity’s public persona, including its name, voice, signature, images, distinctive features, mannerisms, poses etc.
- Types:
- Right to Privacy:
- This protects an individual's control over their personal information and affairs.
- It prevents unauthorised disclosure of personal details or intrusion into one's private life
- It is affirmed by the Supreme Court judgement on the Puttaswamy v Union Of India, 2017 Case.
- Right of Publicity:
- This grants individuals control over the commercial use of their name, image, likeness, or other recognisable characteristics.
- They can choose whether and how these aspects of their identity are used for product endorsements or advertising.
- Right to Privacy:
- Importance:
- These rights are important to celebrities as their names, photographs or even voices can easily be misused in various advertisements by different companies to boost their sales.
What is the Status of Personality Rights in India?
- While personality rights are not explicitly mentioned in Indian statutes, they are protected through principles related to privacy and property rights.
- Key legal Provisions include:
- Article 21 of the Indian Constitution:
- While there is no specific statute solely for personality rights, the right to privacy enshrined in Article 21 of the Constitution offers the closest legal protection in India.
- Copyright Act, 1957:
- The Copyright Act of 1957, while not directly addressing personality rights, offers some tangential protection through concepts like "passing off" and "deception" in Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) cases.
- "Passing off" occurs when someone misrepresents their goods or services as belonging to someone else.
- This can be relevant to personality rights if:
- Someone uses a celebrity's name or image to endorse a product without their permission, creating the impression that the celebrity is associated with the product.
- Someone creates a character or image that is so similar to a well-known personality that it deceives the public into thinking it's the real person.
- Deception is when someone uses a person's name or likeness in a way that is deceptive or misleading, it might be possible to argue copyright infringement, especially if the use harms the reputation of the person.
- Indian Trademarks Act, 1999:
- Section 14 restricts the use of individual names and representations.
- Court Judgments:
- Courts have recognized the right of publicity, allowing celebrities to protect their name, likeness, and persona from unauthorised use.
- In Krishna Kishore Singh vs Sarla A Saraogi Case, 2021, the Supreme Court of India held that the right to publicity is distinct from the right to privacy.
- The court emphasised that public figures have a similar right of publicity. It affirmed that publicity rights are inheritable and devisable.
- In its Arun Jaitley vs. Network Solutions Private Limited, 2011, the Delhi High Court observed that an individual's popularity or fame is equally significant on the internet as in real life.
- The court also stated that a name, besides being a personal identifier, can acquire its own distinctive significance.
- Examples:
- In May 2024, the Delhi High Court upheld Jackie Shroff's personality and publicity rights, restraining various e-commerce stores, AI chatbots, and others from using the actor's name, image, voice, and likeness without his consent.
- Similarly, in September 2023, actor Anil Kapoor also received legal protection for his image rights.
- The Delhi High Court placed restrictions on 16 entities, prohibiting them from using his name, image, or likeness for commercial purposes.
- In the 2010 case of D.M. Entertainment Pvt. Ltd. vs. Baby Gift House, Daler Mehndi's company emerged victorious in the Delhi High Court. The case involved shops selling dolls that mimicked Mehndi's appearance and sang his songs.
- The court upheld Mehndi's right to control his public image commercially.
- Article 21 of the Indian Constitution:
What is the Status of AI Regulation in India?
- No Specific Regulation for AI in India:
- Currently, India does not have a specific regulation for artificial intelligence (AI).
- But various advisories, guidelines, and IT rules from time to time have provided legal supervision for the advancement of AI, Generative AI, and large language models (LLM) in India.
- NITI Aayog's Leadership:
- In 2018, NITI Aayog released the "National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence #AIForAll" outlining responsible development and deployment of AI in healthcare, agriculture, education, and smart infrastructure.
- Data Protection & Global Collaboration:
- The recently enacted Digital Personal Data Protection Act (2023) empowers the government to address privacy concerns arising from AI use.
- Additionally, India's membership in the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) fosters collaboration on responsible AI development, data governance, and ethical considerations.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the legal framework for personality rights in India. Analyse the challenges in reconciling them with the right to freedom of speech. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 ‘Right to Privacy’ is protected under which Article of the Constitution of India? (2021)
(a) Article 15
(b) Article 19
(c) Article 21
(d) Article 29
Ans: (c)
Q.2 Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? (2018)
(a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution.
(b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV.
(c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part III.
(d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution.
Ans: c
Q1. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
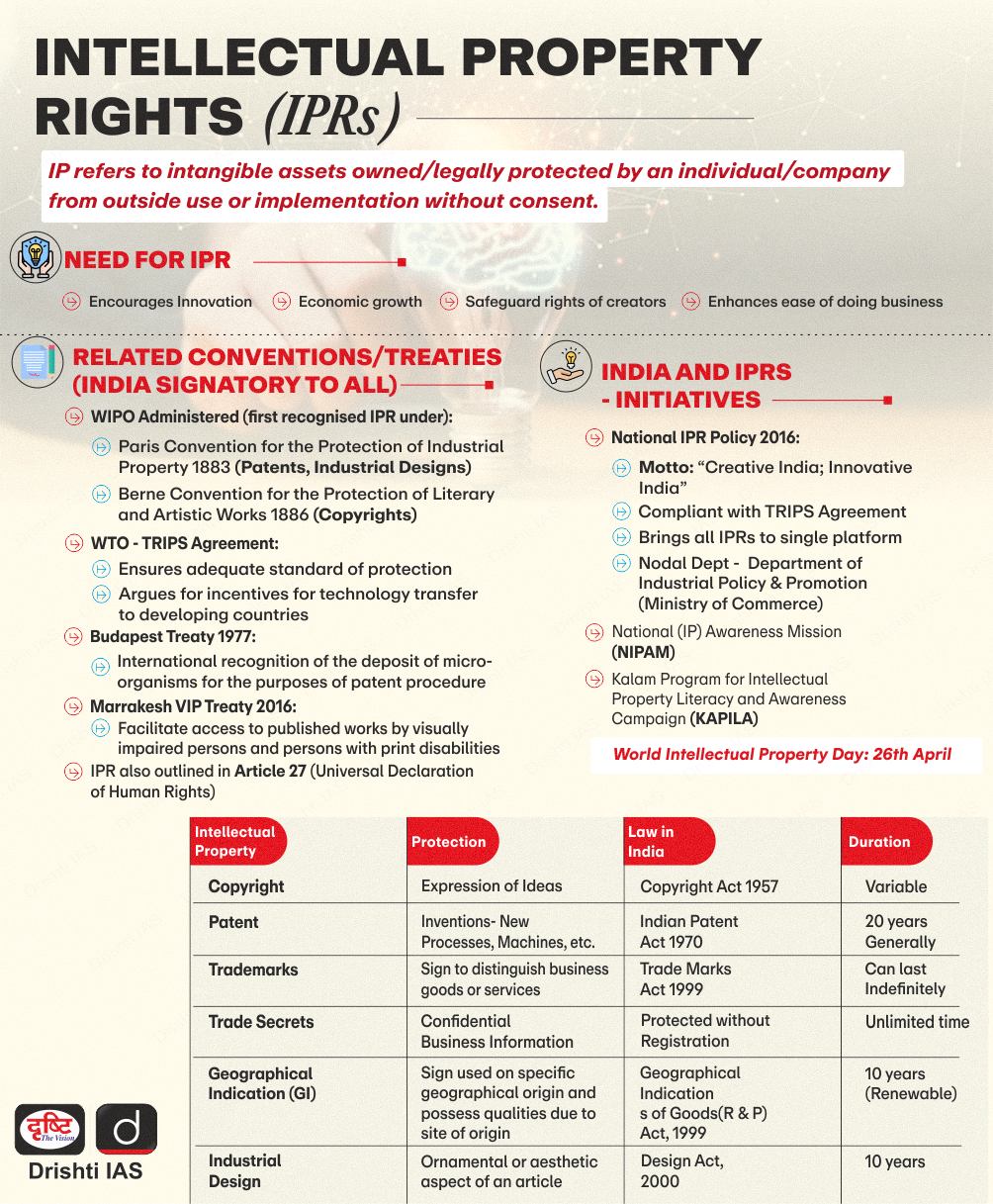
Q. In a globalized world, Intellectual Property Rights assume significance and are a source of litigation. Broadly distinguish between the terms—Copyrights, Patents and Trade Secrets. (2014)