Important Facts For Prelims
Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2024
- 27 Mar 2024
- 6 min read
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has notified the Patents Amendment Rules, 2024 making significant changes to Indian patent practice and procedure.
What are the Key Changes Introduced Under Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2024?
- Reduced timeline for filing a Request for Examination (RFE): The timeline for filing the RFE is now reduced from 48 months to 31 months from the priority date.
- The reduced timeline for filing a Request for Examination (RFE) will accelerate the patent examination process.
- Simplified Submission of Form 3: Applicants can simply file a single updated Form 3 after receiving the First Examination Report (FER).
- The Patent office issues an examination report to the applicant which is generally known as FER.
- Introduction of ‘Certificate of Inventorship’: To recognise inventors’ contributions to patented inventions.
- As the Indian patent certificate does not identify the inventors, this provision will allow inventors to be identified for their inventions.
- Frequency of filing statements: The frequency of filing working patents was reduced from once in a financial year to once in every three financial years.
- Amendments in Pre-grant and Post-grant Opposition Procedures: The time frame for submission of recommendations by an Opposition Board and the response time for applicants have been adjusted.
- A divisional application can be filed in respect of an invention disclosed in the provisional or complete application or a further divisional application.
- This amendment is in alignment with the recent decision of the Delhi High Court in Syngenta Limited v. Controller of Patents and Designs Case, 2023.
- In this the court clarified that divisional applications may be filed in respect of parent applications where the complete or provisional specification (and not necessarily the claims) of the parent application disclose a plurality of inventions.
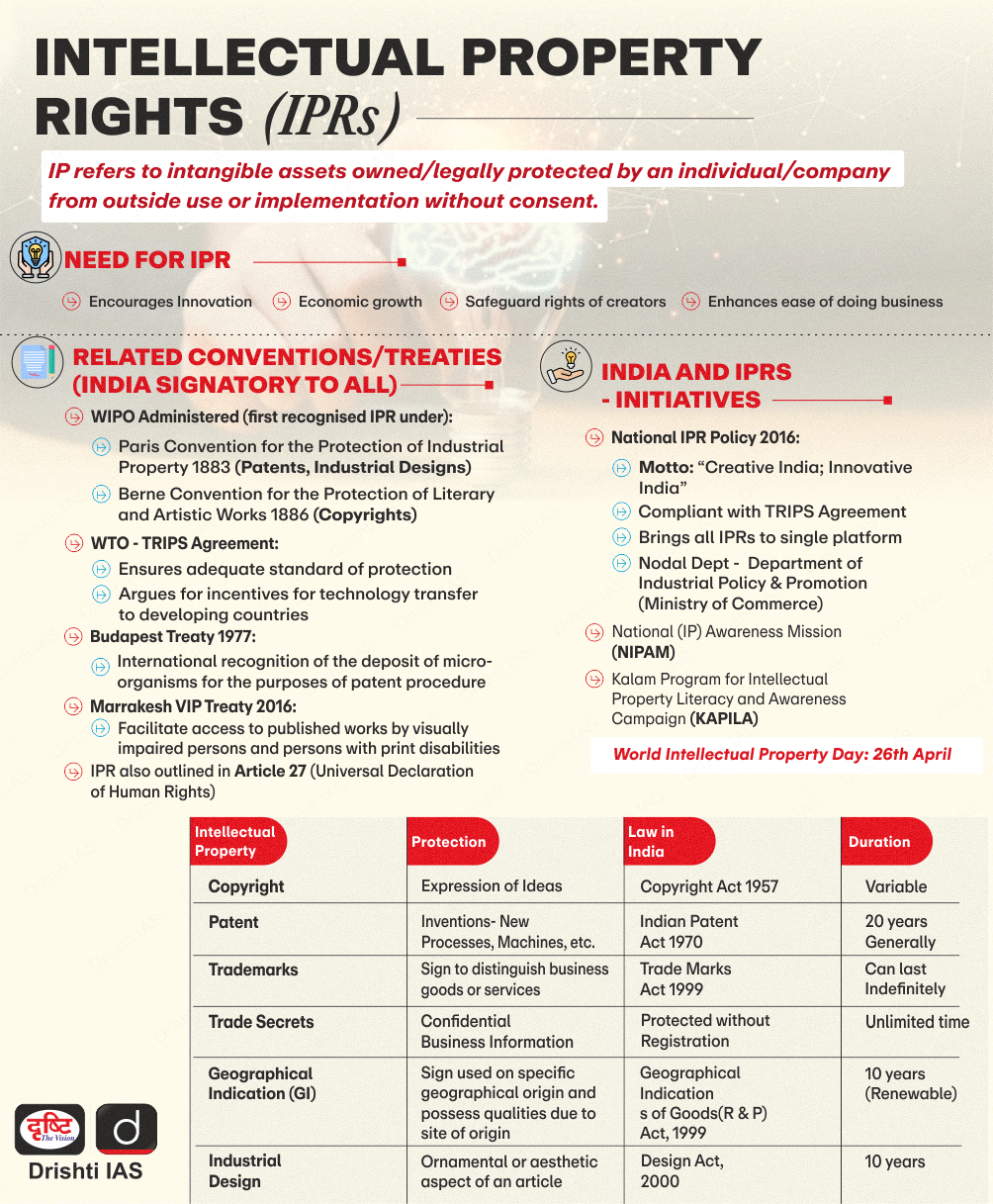
What is a Patent?
- About:
- A Patent is a statutory right for an invention granted for a limited period to the patentee by the Government, in exchange of full disclosure of his invention for excluding others, from making, using, selling, importing the patented product or process for producing that product for those purposes without his consent.
- The patent system in India is governed by the Patents Act, 1970 which was amended in 2003 and 2005.
- The Patent Rules are regularly amended in consonance with the changing environment, the most recent being Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2024.
- Term of a Patent:
- The term of every patent granted is 20 years from the date of filing of the application.
- However, for applications filed under the national phase of the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), the accorded term will be 20 years from the international filing date.
- PCT is an international treaty with more than 150 contracting states, making it possible to seek patent protection for an invention simultaneously in each of a large number of countries by filing an international patent application.
- Such an application may be filed by anyone who is a national or resident of a PCT contracting State, and generally be filed with the national patent office of the contracting State with the International Bureau of World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO) in Geneva.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q With reference to the ‘National Intellectual Property Rights Policy’, consider the following statements:
- It reiterates India’s commitment to the Doha Development Agenda and the TRIPS Agreement.
- Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion is the nodal agency for regulating intellectual property rights in India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q How does the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) help in protecting Indian agriculture?
- NBA checks the biopiracy and protects the indigenous and traditional genetic resources.
- NBA directly monitors and supervises the scientific research on genetic modification of crop plants.
- Application for Intellectual Property Rights related to genetic/biological resources cannot be made without the approval of NBA
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. In a globalized world, Intellectual Property Rights assume significance and are a source of litigation. Broadly distinguish between the terms—Copyrights, Patents and Trade Secrets. (2014)