Particulate Matter & SO2 Control | 29 Oct 2024
Why in News?
Recently, CSIR-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) advised against further Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) installations in Indian thermal power plants (TPPs), stating that Sulphur Dioxide (SO₂) emissions have minimal impact on ambient air quality.
- The report of the institute indicated that the focus should shift to controlling Particulate Matter (PM) rather than solely on SO₂ emissions.
Note:
- CSIR-NEERI is a research institute created and funded by the Government of India. It functions under the Ministry of Science & Technology.
- It was established in Nagpur in 1958 with focus on water supply, sewage disposal,communicable diseases and to some extent on industrial pollution and occupational diseases found common in post-independent India.
What is Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD)?
- About:
- FGD is the process of removing sulphur compounds from the exhaust emissions of fossil-fueled power stations.
- This is done through the addition of absorbents, which can remove up to 95% of the sulphur dioxide from the flue gas.
- Flue gas is the material emitted when fossil fuels such as coal, oil, natural gas, or wood are burned for heat or power.
- Categorisation:
| Category | Location/Area | Timelines for Compliance |
| A |
Within 10 km radius of NCR or cities with million-plus population (2011 Census) |
Up to 31st December 2024 |
| B | Within 10 km radius of Critically Polluted Areas or Non-attainment cities (as defined by CPCB) | Up to 31st December 2025 |
| C | Areas not included in Categories A and B | Up to 31st December 2026 |
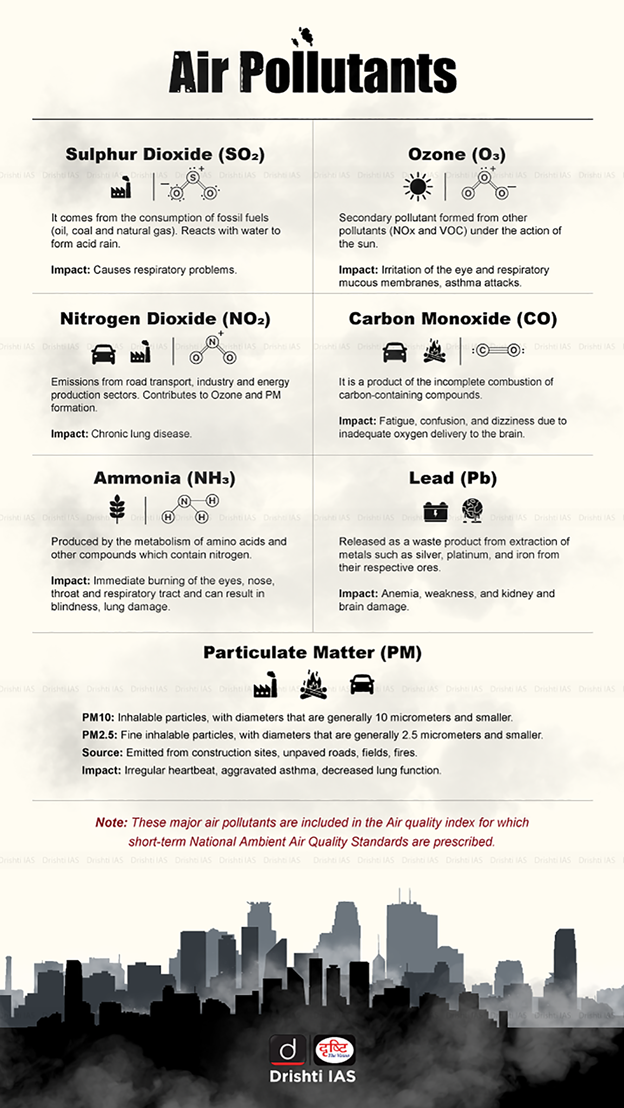
What is Air Pollution?
- About:
- Air pollution encompasses the presence of solids, liquids, gases, noise, and radioactive radiation in the atmosphere, at concentrations harmful to humans, living organisms, property, or environmental processes.
- These substances, known as pollutants, can be either natural or human-made and can originate from various sources such as industrial processes, vehicle emissions, agricultural activities, and natural events like wildfires and volcanic eruptions.
- Air pollution encompasses the presence of solids, liquids, gases, noise, and radioactive radiation in the atmosphere, at concentrations harmful to humans, living organisms, property, or environmental processes.
- Particulate Matter (PM):
- PM refers to a complex mixture of extremely small particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. These particles come in a wide range of sizes and can be made up of hundreds of different compounds.
- PM10 (coarse particles) - Particles with a diameter of 10 micrometres or less.
- PM2.5 (fine particles) - Particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometres or less.
- PM refers to a complex mixture of extremely small particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. These particles come in a wide range of sizes and can be made up of hundreds of different compounds.
- Sulphur Dioxide:
- SO2 emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution. It can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form small particles.
- These particles contribute to PM pollution.
- The greatest source of SO2 in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels in power plants and other industrial facilities.
- Other sources include industrial processes such as extracting metal from ore, natural sources such as volcanoes, and locomotives, ships and other vehicles and heavy equipment that burn fuel with high sulphur content.
- SO2 emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution. It can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form small particles.
- Government Initiatives for Controlling Air Pollution:
Note: In M.C. Mehta vs. Union of India (1986), the Supreme Court treated the right to live in pollution free environment as a part of fundamental right to life under Article 21 of the Constitution.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Why is there a concern about copper smelting plants? (2021)
- They may release lethal quantities of carbon monoxide into environment.
- The copper slag can cause the leaching of some heavy metals into environment.
- They may release sulphur dioxide as a pollutant.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to furnace oil, consider the following statements: (2021)
- It is a product of oil refineries.
- Some industries use it to generate power.
- Its use causes sulphur emissions into the environment.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)