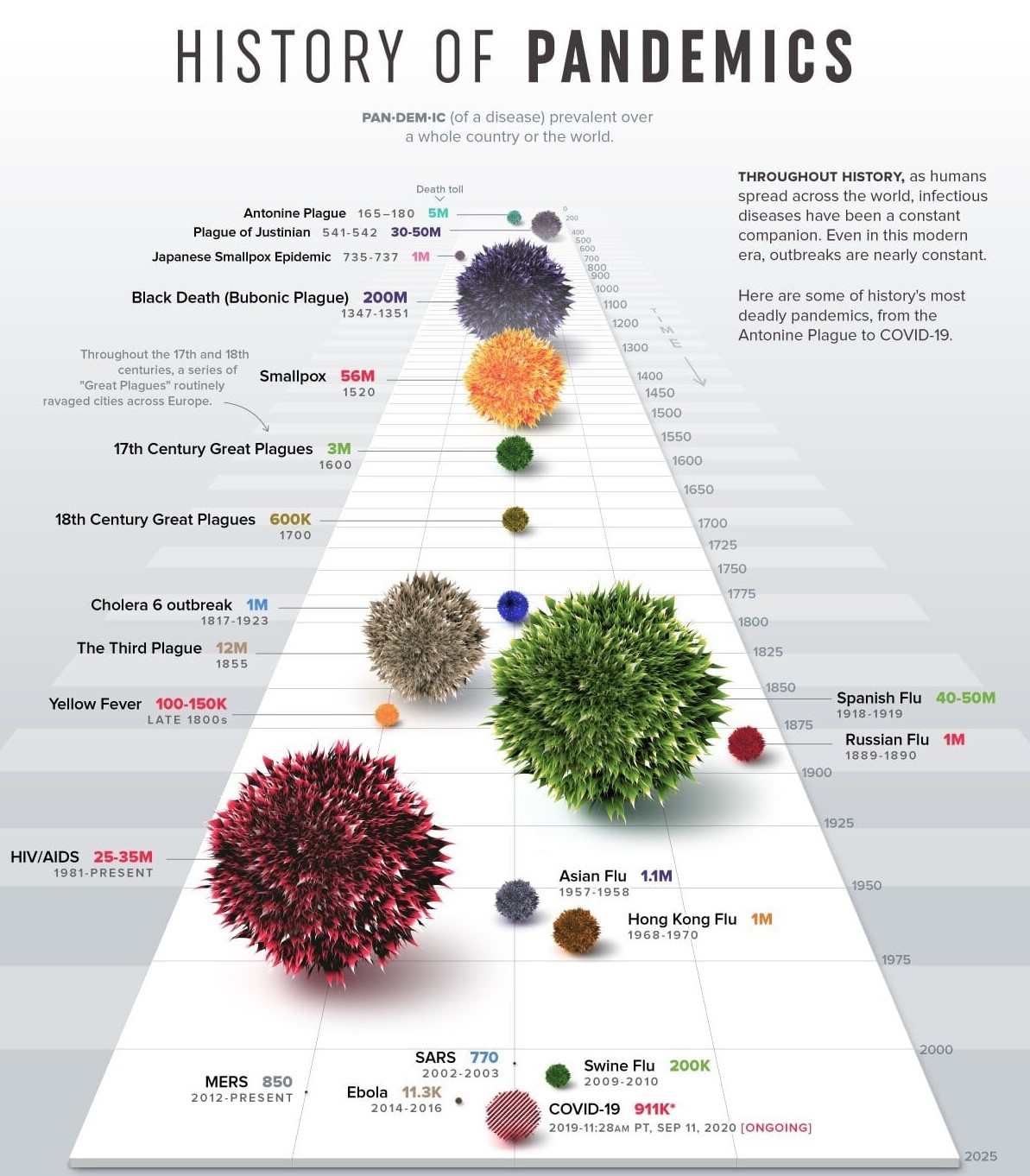
Pandemic Treaty | 03 Jun 2024
For Prelims: World Health Assembly (WHA), genomic sequences, antimicrobial resistance, Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC), International Health Regulations (2005)
For Mains: Key components and developments of the Draft Pandemic Treaty, Existing framework for Global Health Cooperation
Why in News?
Recently, the World Health Assembly (WHA) in the annual meeting, agreed on a set of critical amendments to the International Health Regulations (2005) (IHR), and made concrete commitments to completing negotiations on a global pandemic agreement by 2025.
- These amendments will strengthen global preparedness, surveillance and responses to public health emergencies, including pandemics.
What is the World Health Assembly (WHA)?
- About:
- The World Health Assembly (WHA) is WHO’s decision-making body attended by delegations from all of WHO’s member states.
- It is held yearly at the headquarter of WHO, i.e., Geneva, Switzerland.
- Functions of WHA:
- Deciding on the Organization’s policies.
- Appointment of the Director-General of WHO.
- Administration of financial policies.
- Review and approval of the proposed programme budget.
What are the Key Amendments Agreed to IHR?
- Definition:
- Introduction of a definition of pandemic emergency to enhance international collaboration in response to potential pandemics.
- Definition includes criteria such as wide geographical spread, exceeding health system capacity, causing social and economic disruption, and requiring rapid international action.
- Commitment to Solidarity and Equity:
- It includes establishing a Coordinating Financial Mechanism to support the identification and access to financing needed to address the needs and priorities of developing countries.
- It will also include developing and strengthening core capacities and other pandemic emergency prevention, preparedness and response-related capacities.
- Cooperation for Effective Implementation:
- It involves creation of a States Parties Committee to promote cooperation and effective implementation of the amended regulations
- The creation of National IHR Authorities to improve coordination of implementation within and among countries.
What is the Need for Global Health Cooperation?
- Curbing Infectious Diseases:
- Pandemics like Covid-19 have highlighted the interconnectedness of our world. A disease outbreak in one country can rapidly spread across borders. Global cooperation allows for
- Information Sharing: Early detection and sharing of disease outbreaks enables a faster global response. The World Health Organization (WHO)'s role in identifying and tracking Covid-19 variants is a prime example.
- Coordinated Research & Development: Collaboration facilitates faster development of vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments.
- Pandemics like Covid-19 have highlighted the interconnectedness of our world. A disease outbreak in one country can rapidly spread across borders. Global cooperation allows for
- Addressing Antibiotic Resistance:
- The overuse and misuse of antibiotics in one country can create resistant bacteria that spread globally. Global cooperation helps in
- Standardised Practices: Establishing common guidelines for antibiotic use in humans and animals helps slow resistance.
- According to the WHO, antimicrobial resistance is a global health threat that could lead to millions of deaths each year if not addressed collaboratively.
- Standardised Practices: Establishing common guidelines for antibiotic use in humans and animals helps slow resistance.
- The overuse and misuse of antibiotics in one country can create resistant bacteria that spread globally. Global cooperation helps in
- Chronic Disease Management:
- Non-communicable diseases like heart disease and diabetes are a growing global concern. Cooperation helps in knowledge sharing.
- Sharing best practices in prevention, treatment, and lifestyle interventions allows countries to learn from each other. For example, the Global Alliance for Chronic Diseases (GACD).
- Non-communicable diseases like heart disease and diabetes are a growing global concern. Cooperation helps in knowledge sharing.
- Health Equity and Access:
- Many countries lack the resources to tackle health challenges effectively. Global cooperation promotes technology transfer.
- Sharing knowledge and technology allows developing countries to improve their healthcare systems. Initiatives like the Medicines Patent Pool facilitate access to affordable generic drugs.
- Many countries lack the resources to tackle health challenges effectively. Global cooperation promotes technology transfer.
What is the Existing Framework for Global Health Cooperation?
- Multilateral Agencies:
- Various multilateral organisations like WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, and UNAIDS play crucial roles in specific health areas like child health, reproductive health, and HIV/AIDS.
- The WHO acts as the central coordinating authority on global health within the United Nations system.
- It sets international health standards, provides technical assistance to countries, and monitors and coordinates the global response to health emergencies.
- International Health Regulations (IHR):
- This is a legally binding agreement between 196 countries. It outlines the rights and obligations of countries regarding public health events with international implications.
- Global Health Initiatives:
- These are targeted programs tackling specific health challenges. Examples include the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, and Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance.
- Public-Private Partnerships:
- Collaboration between governments, NGOs, and the private sector allows for leveraging resources and expertise.
- Example, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Collaboration between governments, NGOs, and the private sector allows for leveraging resources and expertise.
- Regional Organizations:
- Regional bodies like the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) for the Americas and the African Union play a role in coordinating health efforts within their regions.
Conclusion
The World Health Assembly's (WHA) recent amendments to the International Health Regulations (IHR) and commitment to a global pandemic agreement by 2025 signify a significant step towards improved global health security.
These changes, including a definition for pandemic emergencies, a focus on equity and financing, and stronger national and international cooperation, aim to equip the world to better detect, prevent, and respond to future health threats.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. What are the recent amendments agreed regarding the pandemic treaty ? Also, highlight the existing framework for Global Health Cooperation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017)
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)
Q. What is the basic principle behind vaccine development? How do vaccines work? What approaches were adopted by the Indian vaccine manufacturers to produce COVID-19 vaccines? (2022)