Pandavula Gutta and Ramgarh Crater as Geo-Heritage Sites | 19 Mar 2024
Why in News?
Pandavula Gutta, an ancient geological marvel predating the Himalayan hills, has been officially designated as the sole Geo-heritage site in Telangana.
- Also, the Rajasthan government designates Ramgarh Crater in Baran district as a geo-heritage site.
- The recognition marks a significant milestone in preserving the region's geological legacy.
What are the Key Facts About Pandavula Gutta?
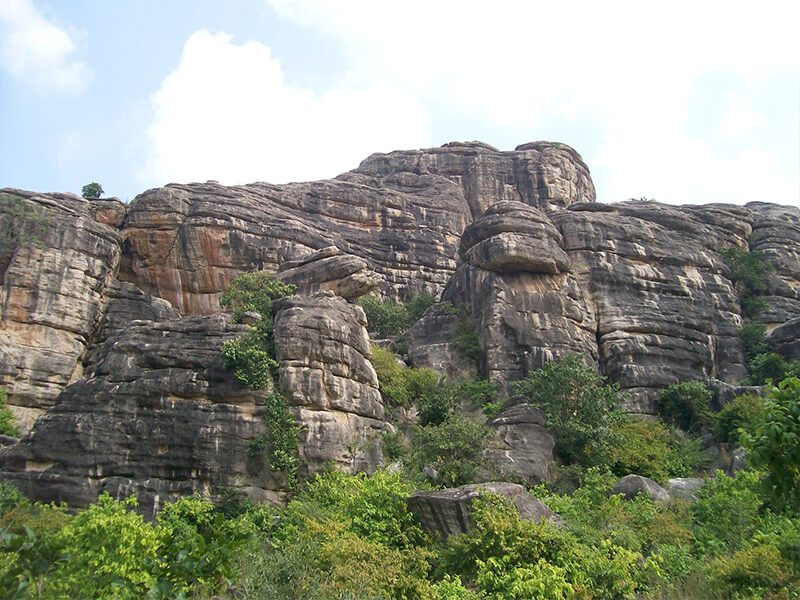
- Pandavula Konda (Pandavula Gutta) is a geological marvel situated in the Jayashankar Bhupalpally district of Telangana.
- Pandavula Gutta is rich in terms of rock shelters, and habitation from the Mesolithic period (about 10,000 B.C. to 8,000 B.C.) to mediaeval times.
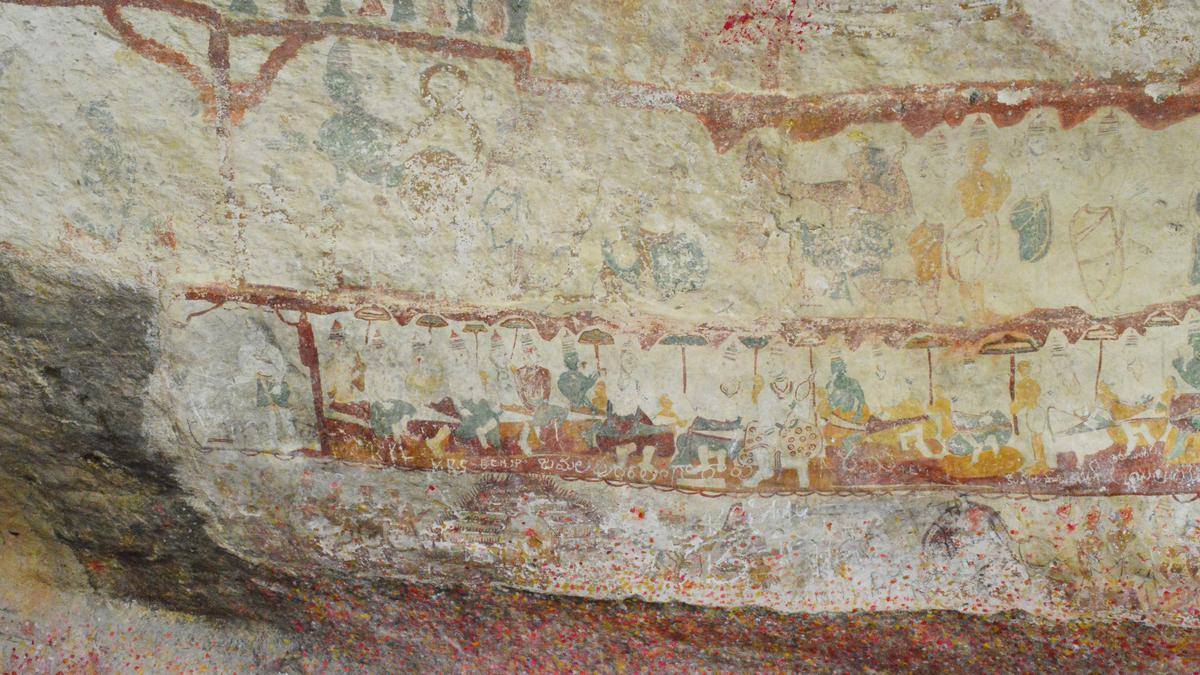
- Pandavula Gutta boasts Palaeolithic (500,000 BCE–10,000 BCE) cave paintings offering a glimpse into prehistoric life.
- The cave paintings depict wildlife like Bison, Antelope, Tiger, and Leopard, as well as shapes like swastika symbols, circles, squares, and weapons.
- The paintings also feature geometrical designs and impressions in green, red, yellow, and white pigment colours.
- The topography of Pandavula Gutta makes it a popular destination for rock climbing enthusiasts.
What are the Key Facts About Ramgarh Crater?
- Ramgarh Crater, Rajasthan formed around 165 million years ago due to a meteor impact, this 3-km diameter crater provides essential ecosystem services, contributing to the region's ecological balance and biodiversity.
- Recognised as a Ramgarh Conservation Reserve under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, the Ramgarh Crater is protected to preserve its unique ecological and cultural heritage.
- It is declared as the Ramgarh Conservation Reserve under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 and the presence of Pushkar Talab complex within the crater, recognised as wetlands under Wetland (Conservation & Management) Rules, 2017.
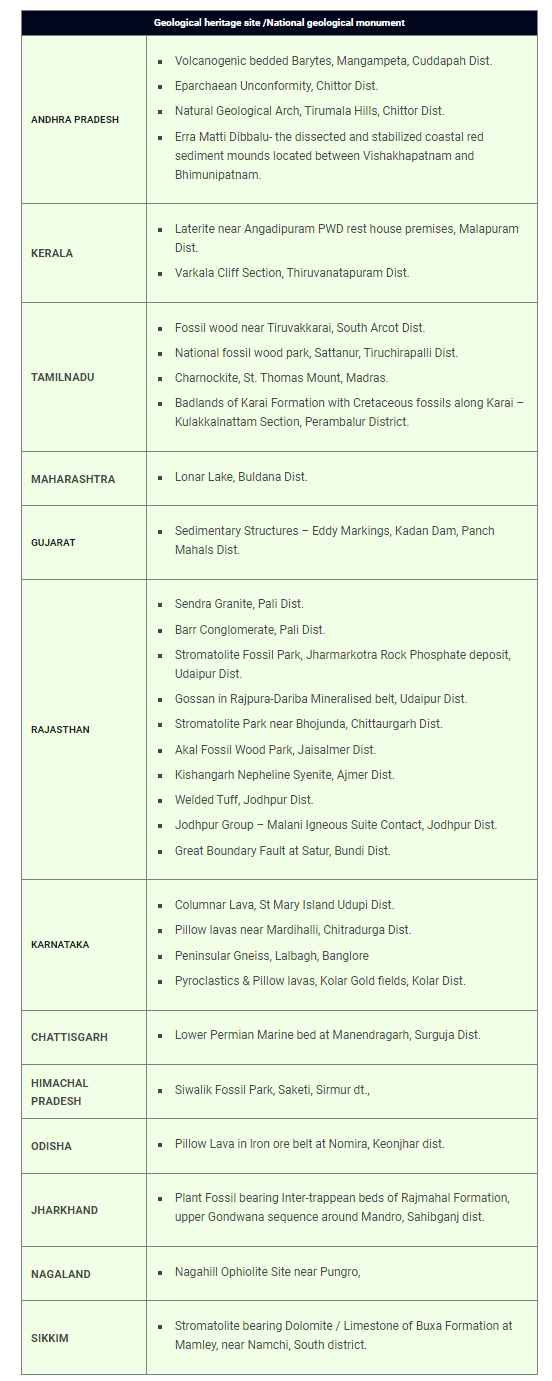
Geo-Heritage Site/National Geological Monuments
- Geoheritage refers to sites or areas with significant scientific, educational, cultural, or aesthetic value due to their geological features.
- These sites may have unique rock formations, fossils, or landscapes that are important for education, research, cultural significance, or visual appeal. They can also contribute to local and regional economies as tourist destinations.
- GSI or the respective State governments take necessary measures to protect these sites.
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) declares geo-heritage sites/national geological monuments for protection and maintenance.
- GSI is a scientific agency that was founded in 1851 to find coal deposits for the Railways. The GSI is headquartered in Kolkata, and is an attached office to the Ministry of Mines. Its main functions include creating and updating national geoscientific information, and assessing mineral resources.
Read more: Draft Geo-heritage Sites and Geo-relics Bill, 2022
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following historical places:
- Ajanta Caves
- Lepakshi Temple
- Sanchi Stupa
Which of the above places is/are also known for mural paintings?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (b)
Q. Where is the famous Virupaksha temple located? (2009)
(a) Bhadrachalam
(b) Srikalahasti
(c) Hampi
(d) Chidambaram
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 Safeguarding the Indian Art Heritage is the need of the moment. Discuss. (2018)
Q.2 Indian Philosophy and tradition played a significant role in conceiving and shaping the monuments and their art in India. Discuss. (2020)