Open Network for Digital Commerce | 07 Jun 2024
For Prelims: Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), Micro, Small and Medium enterprises (MSMEs), Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
For Mains: Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), its potential, challenges and way forward
Why in News?
Recently, Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) recorded an all-time high of 8.9 million transactions across retail and ride-hailing segments in May 2024, representing a 23% month-on-month increase in total transaction volume.
What is ONDC?
- About:
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is a network of interconnected e-marketplaces through which sellers, including brands, can list and sell their products directly to customers bypassing any middlemen or intermediaries.
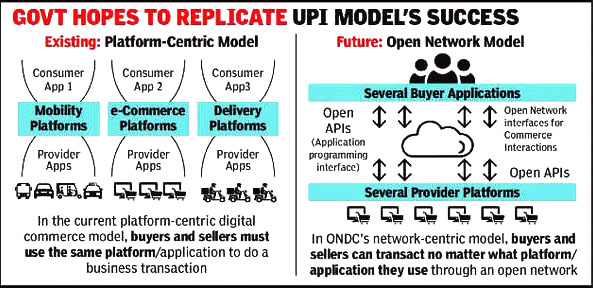
- It allows transitioning from a platform-centric model to an open source network for buying and selling goods and services.
- It was launched in 2021 under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) by the Ministry of Commerce as part of the Digital India initiative.
- It offers delivery services for groceries, home decor, cleaning essentials, food delivery and other products.
- It is a not-for-profit organisation that provides a network enabling local digital commerce stores across various industries to be discovered and engaged by any network-enabled applications.
- Similar to the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), ONDC aims to level the operational playing field among e-commerce platforms.
- The Quality Council of India has been tasked with integrating e-commerce platforms through this open-source technology network, allowing users to modify, enhance, or improve the original code.
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is a network of interconnected e-marketplaces through which sellers, including brands, can list and sell their products directly to customers bypassing any middlemen or intermediaries.
- Objectives:
- Democratisation and decentralisation of e-Commerce
- Inclusivity and access for sellers, especially small and medium enterprises as well as local businesses
- Increased choices and independency for consumers
- Making goods and services cheaper.
- Working Mechanism:
- ONDC functions on the basis of an open network where it will not be a single platform similar to Amazon or Flipkart but rather in the form of a gateway where buyers and sellers across different platforms will be able to connect.
What is Open Source?
- Open source implies that the technology or code deployed for the process is freely made available for everyone to use, redistribute, and modify.
- For instance, the operating system of iOS is closed source, it cannot be legally modified or used.
- Whereas, the android operating system is open source, making it possible for smartphone manufacturers, such as Samsung, Nokia, Xiaomi, etc., to modify it for their respective hardware.
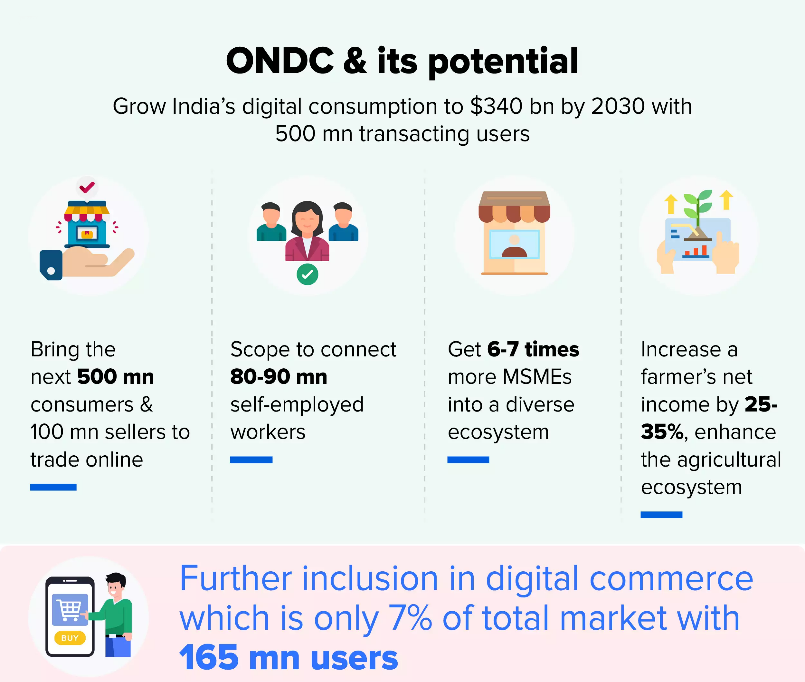
What are the Potential Advantages of ONDC?
- Empowering Consumers: ONDC fosters a more transparent environment by potentially increasing access to information.
- This empowers consumers to make informed choices and benefit from a wider array of sellers, potentially leading to lower prices.
- Boosting Competition: By breaking down the dominance of existing platforms, ONDC creates a level playing field. This incentivizes competition among sellers, ultimately translating into a wider variety of products and potentially lower prices for consumers.
- Innovation: The open-source architecture of ONDC fosters innovation.
- Cost Efficiency: ONDC's decentralised structure has the potential to streamline operations and reduce redundancies and lead to significant cost savings.
- Boosting Small Businesses: ONDC removes entry barriers for small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) and local vendors. This paves the way for greater participation in the digital marketplace, fostering a more inclusive e-commerce ecosystem.
What are the Challenges to ONDC?
- Complexity Factor: Compared to user-friendly systems like UPI, ONDC's underlying mechanisms are intricate. The ease of adoption witnessed with UPI might not be easily replicated with ONDC.
- Breaking Established Habits: Consumers are accustomed to the existing e-commerce platforms' user interfaces and functionalities. ONDC will need to provide a seamless and user-friendly experience to compete effectively.
- Dispute Resolution Concerns: Unlike traditional platforms that manage the entire transaction lifecycle, ONDC focuses solely on online buying and selling.
- This separation might lead to an increase in disputes related to deliveries, product quality, or after-sales service, as ONDC doesn't function as a direct intermediary.
- Lack of a Robust Grievance Redressal Mechanism: The lack of clarity on responsibility for customer service and handling complaints may deter people from joining the platform.
- Challenges from Existing E-commerce Platforms: Existing e-commerce giants have fostered strong relationships with consumers through loyalty programs, bundled services, and other incentives.
- ONDC will need to develop compelling strategies to attract and retain customers in this competitive landscape.
- Price Advantage Uncertainty: As a facilitator, ONDC might not be able to directly influence product pricing or offer discounts on the scale of established players who leverage bulk deals and partnerships.
Note
The Nandan Nilekani committee, formed by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), recommended the following for the ONDC:
- Open Network Protocols: Establish open protocols for digital commerce operations.
- Interoperability: Ensure seamless interaction across different platforms.
- Standardisation: Develop uniform standards for e-commerce.
- Decentralisation: Reduce reliance on a few large platforms to foster competition.
- Inclusivity: Make the network accessible to small and medium enterprises.
- Transparency and Security: Ensure data privacy and fair operations.
- Regulatory Framework: Create robust regulations for compliance and consumer protection.
- Capacity Building: Train small businesses to participate effectively.
- Consumer Choice: Expand product and service options through competition.
- Tech-Driven Innovations: Utilize advanced technologies to improve digital commerce.
Way Forward
- Enhancing Digital Infrastructure: The government can play a crucial role in fostering a robust digital infrastructure that supports ONDC.
- This may involve investments in broadband connectivity and initiatives to bridge the digital divide in rural and remote areas.
- Promoting Digital Literacy: A comprehensive digital education policy that caters to diverse regional languages is crucial.
- This will empower both consumers and sellers, particularly small businesses and local vendors, to navigate the ONDC platform effectively. User-friendly interfaces that prioritise ease of use will further enhance adoption.
- Targeted Outreach Programs: Extensive outreach programs with adequate funding are necessary to attract and onboard small sellers, especially micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) and kirana stores.
- Incentives and handholding support can be instrumental in overcoming initial hurdles and promoting platform adoption.
- Dispute Resolution Framework: Establishing a secure and efficient single window mechanism for addressing issues like information asymmetry, opaque pricing, quality concerns, and buyer-seller disputes is essential.
- This will build trust and confidence among stakeholders in the ONDC ecosystem.
Conclusion
The success of ONDC hinges on a collaborative effort between the government, industry players, and civil society.
By prioritising digital infrastructure development, promoting digital literacy, facilitating seller onboarding, and establishing a robust grievance redressal mechanism, ONDC can usher in a new era of inclusivity, transparency, and competition in the Indian e-commerce landscape.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the potential of Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in the Indian e-commerce landscape. Discuss the key challenges it faces and suggest a roadmap for its successful implementation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to ‘Quality Council of India (QCI)’, consider the following statements: (2017)
- QCI was set up jointly by the Government of India and the Indian Industry.
- Chairman of QCI is appointed by the Prime Minister on the recommendations of the industry to the Government.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans c
Q. Consider the following: (2022)
- Aarogya Setu
- CoWIN
- DigiLocker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)

.png)