Oncolytic Virotherapy for Treating Cancer | 11 Jul 2022
Why in News?
Researchers in the US have developed a novel strategy in Oncolytic Virotherapy (OV) to improve a cancer therapy that can kill tumour cells while leaving nearby healthy tissues intact.
- Earlier a Monoclonal Antibody trial was held in the USA, where 12 patients were completely cured of rectal cancer without requiring any surgery or chemotherapy.
What is Oncolytic Virotherapy?
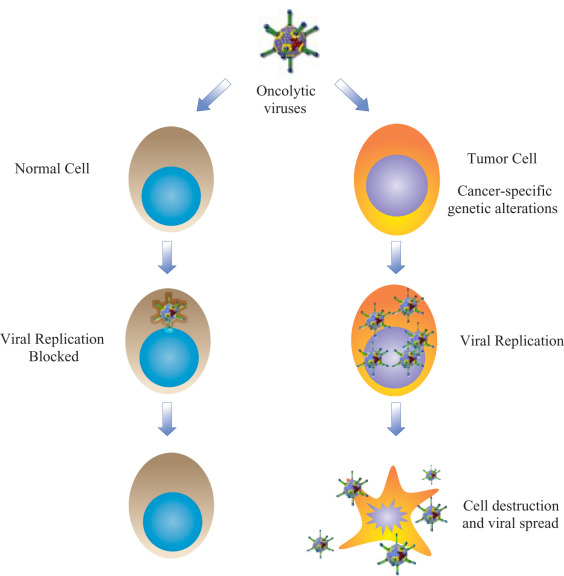
- Oncolytic viruses can kill cancer cells while leaving nearby healthy cells and tissues intact.
- In oncolytic virotherapy, the treatment also exerts its influence by activating an antitumor immune response made of immune cells such as Natural Killer (NK) cells.
- However, sometimes those natural killers limit the oncolytic viruses, and so despite the exciting development in the OV field in recent years, there is room for improvement to tackle some limitations, including the relatively weak therapeutic activity and lack of means for effective systemic delivery.
What is the Novel Approach?
- A region of the gene is deleted which shows to activate the signaling pathway that enables the virus to replicate in normal cells.
- It consists of a new oncolytic virus called FusOn-H2, based on the Herpes simplex 2 virus, (HSV-2), commonly known as genital herpes.
- Arming FusOn-H2 with a chimeric NK engager that can engage the infiltrated natural killer cells with tumour cells can significantly enhance the effectiveness of this virotherapy.
What is Cancer?
- About:
- It is a large group of diseases that can start in almost any organ or tissue of the body when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, go beyond their usual boundaries to invade adjoining parts of the body and/or spread to other organs. The latter process is called metastasizing and is a major cause of death from cancer.
- A neoplasm and malignant tumor are other common names for cancer.
- Lung, prostate, colorectal, stomach and liver cancer are the most common types of cancer in men, while breast, colorectal, lung, cervical and thyroid cancer are the most common among women.
- Cancer Burden:
- Cancer remains as one of the leading causes of adult illness and death due to chronic and Non-Communicable Diseases (NCD) world-over including in India.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), cancer is the second leading cause of death globally and in 2018, there were approximately 18 million cases globally, of which 1.5 million were in India alone.
- Prevention:
- Between 30% and 50% of cancer deaths could be prevented by modifying or avoiding the key risk factors.
- Key risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol use, diet, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, pollution, chronic infections, etc.
- Treatment:
- Options include surgery, cancer medicines and/or radiotherapy, administered alone or in combination.
- Palliative care, which focuses on improving the quality of life of patients and their families, is an essential component of cancer care.