Neuroscience of Addiction | 18 Mar 2025
Why in News?
During the Brain Awareness Week (March 10-16), a study revealed that addiction involves a complex neural circuit in the brain affecting craving, emotional regulation, and decision-making.
- It underscores addiction as a chronic brain condition rather than a moral failing, paving the way for more effective treatment strategies.
How Does Neuroscience Explain Addiction?
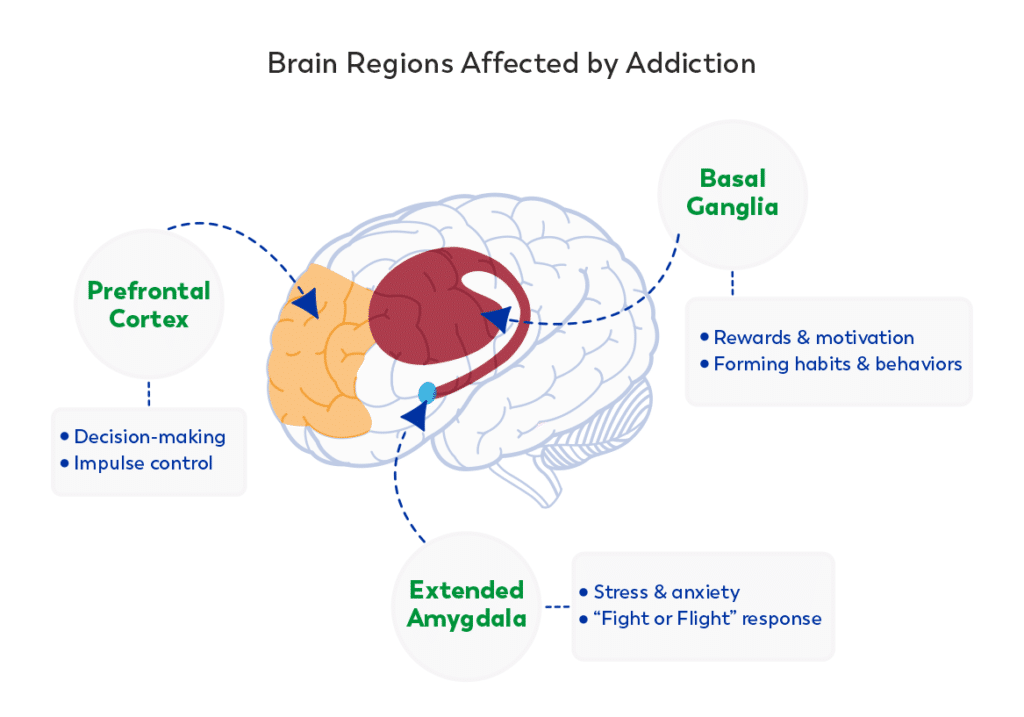
- Role of Brain in Addiction: The study highlights 3 key brain regions involved in addiction i.e., basal ganglia, extended amygdala, and prefrontal cortex.
- Basal Ganglia: It teaches the brain to repeat pleasurable activities, whether from food, social interaction, or addictive substances.
- It works with neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin to reinforce pleasurable behaviors.
- Extended Amygdala: It triggers anxiety, irritability, and unease when substance use stops, pushing continued use despite harm.
- Prefrontal Cortex: It explains why substance use continues despite knowing its harmful effects, a key trait of addiction.
- The prefrontal cortex, which handles decision-making, time management, and prioritization, completes the triad.
- Basal Ganglia: It teaches the brain to repeat pleasurable activities, whether from food, social interaction, or addictive substances.
- Vulnerability to Adolescents: Adolescence represents a critical “at-risk period” for substance use because the brain is still developing.
- The prefrontal cortex, which controls impulses and decision-making, matures last. This makes teens more vulnerable to addiction.
- Other Reasons of Addiction:
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are biologically more prone to addiction.
- Psychological Factors: Trauma, stress, and mental health disorders increase vulnerability.
- Environmental Influences: Family history, peer pressure, and socioeconomic conditions play a significant role.
- Age of First Use: Earlier exposure increases the risk of long-term dependency.
Note:
- Brain imaging (E.g., MRI) has helped in identifying structural and biochemical changes caused by addiction.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT) and neurofeedback techniques are helping in rewiring the brain for recovery.
What is Brain Awareness Week (BAW)?
- About: It is celebrated annually in the third week of March highlighting the role of brain science in understanding biology, preventing diseases, and improving healthcare.
- It is organised annually by Dana Foundation, a private philanthropic organization in New York that is dedicated to advancing neurosciences.
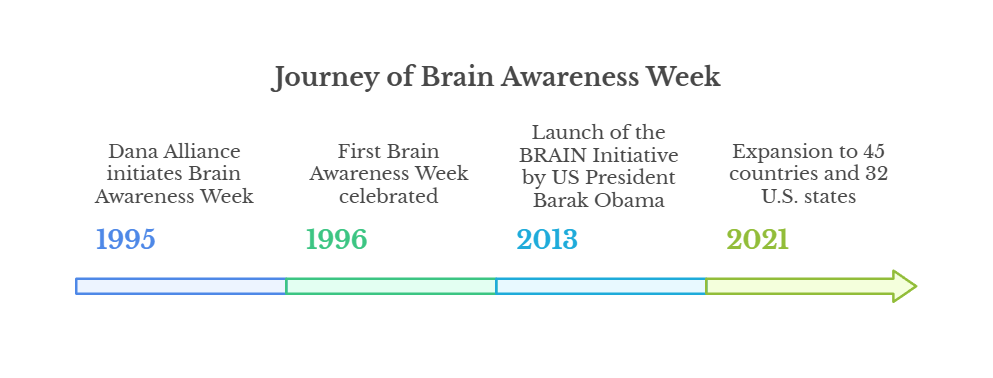
- Journey:
- Purpose and Participation: Educates the public on brain functions, disorders, and research advancements.
| Read More: Working of Anaesthetic Drugs in the Brain |