Negative Leap Second | 04 Apr 2024
A recent study shows that Climate change is causing glaciers and ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica to melt at an accelerating rate, redistributing weight across the planet and slightly slowing down the Earth's rotation on its axis.
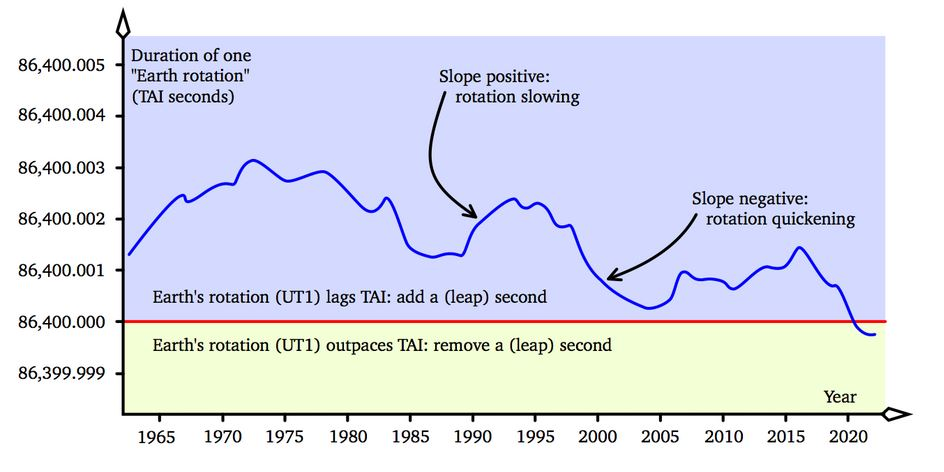
- The Earth has been spinning slightly faster than normal for a few decades.
- Timekeepers have added an extra "leap second" to clocks worldwide to adjust for this increase in speed of Earth’s rotation – they have done this 27 times since the 1970s.
- The plan was to remove this leap second for the first time in 2026, a change they called the "Negative leap second.".
- According to the recent study, the accelerating melt of ice from Antarctica and Greenland has acted like a brake, slowing the rotation back down, and potentially delaying the need for a "negative leap second" adjustment until 2029 or later.
Read More: IPCC Reports and Equity in Climate Change Mitigation