Navigating India's Transition to Sustainability | 14 May 2024
For Prelims: Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting, National Stock Exchange, SEB, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), BRSR
For Mains: Measures to Improve Corporate Governance in India.
Why in News?
Recently, PwC India, a professional services network has published a report called 'Navigating India's Transition to Sustainability'.
- The Report has focused on sustainability initiatives of leading companies in India.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- About:
- The report analyses how companies are adapting to the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) disclosures mandated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- The analysis covers the BRSR reports of the top 100 companies for the financial year ended 31st March 2023.
- The business sector is seen as a critical enabler in achieving India's net zero vision by 2070.
- Net Zero is referred to as carbon neutrality, i.e. achieving an overall balance between greenhouse gas emissions produced and greenhouse gas emissions taken out of the atmosphere.
- Key Findings of the Report:
- 51% of India’s top 100 listed companies by market capitalisation disclosed their data for FY23 despite it being a voluntary disclosure in BRSR.
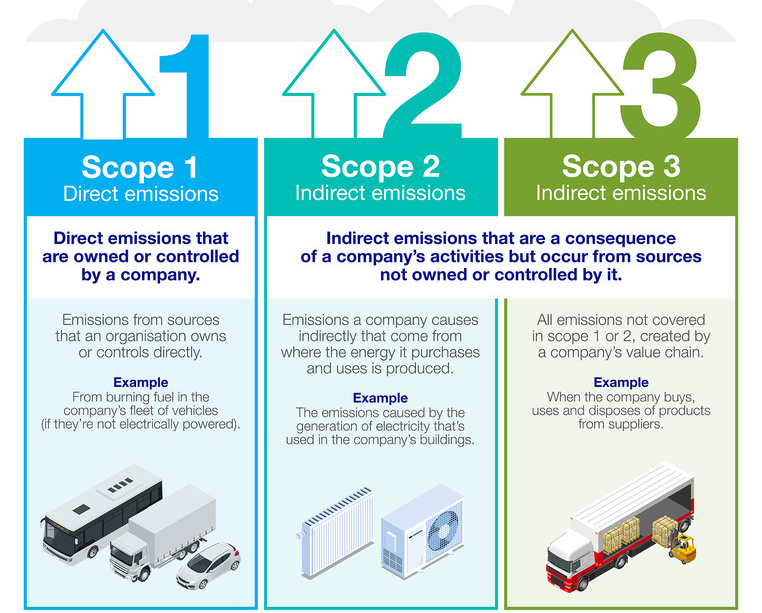
- 34% of the companies have reduced their Scope 1 emissions and 29% have reduced their Scope 2 emissions.
- Scope 1 covers emissions from sources that an organisation owns or controls directly.
- Scope 2 is emissions that a company causes indirectly and come from where the energy it purchases and uses is produced.
- 44% of the top 100 listed companies conducted the life-cycle assessment of their products or services.
- 49% of companies have increased their energy consumption from renewable sources and 31% of companies have disclosed their net-zero targets.
- Key initiatives leading to emission reduction include transitioning to energy-efficient technologies such as LEDs, adopting efficient air-conditioning, ventilation, and heating systems, shifting to renewable sources for energy needs, purchasing carbon offsets, and entering into off-site power purchase agreements.
Note:
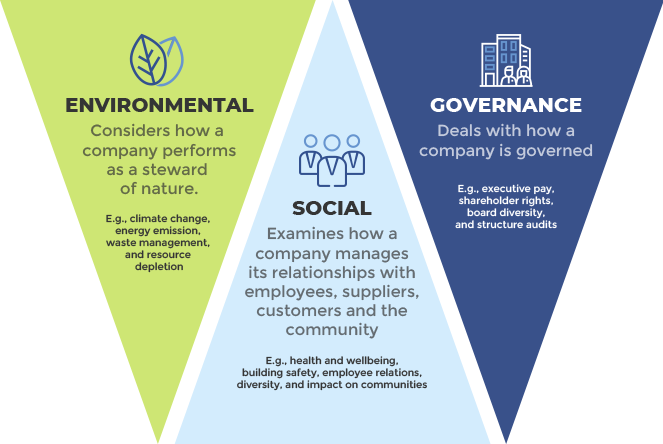
- Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) aims to facilitate more meaningful engagement between businesses and their stakeholders by focusing on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations.
- ESG goals encompass a framework of guidelines that compel companies to adhere to improved governance, ethical conduct, environmentally sustainable practices, and social responsibility in their operations.
- The environmental criteria assess a company's role as a custodian of the environment.
- Social criteria evaluate the company's handling of relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities in which it operates.
- Governance focuses on the leadership, executive compensation, auditing, internal controls, and shareholder rights within a company.
How Significant is the Report for India?
- The report sheds light on India’s journey towards sustainability, emphasising ESG considerations.
- The report encourages companies to be accountable for their sustainability efforts.
- The report aligns with the BRSR framework introduced by the SEBI. The report serves as a guide for compliance and transparent disclosure.
- The report showcases India’s commitment to sustainability, enhancing investor confidence.
- Globally, sustainable practices are becoming a competitive advantage, and this report positions India favourably.
- Policymakers can draw insights from the report to shape regulations and policies that promote sustainable practices.
- The shift towards sustainability in India isn't merely about meeting regulations but it's also about fostering growth in a responsible manner.
- The report emphasises the need to balance economic development with environmental and social well-being.
What are the Initiatives taken to Ensure ESG Compliance in India?
- In 2011, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) released the National Voluntary Guidelines (NVGs) on Social, Environmental and Economic Responsibilities of Business, marking an early step in defining ESG disclosure standards for companies.
- The SEBI introduced the Business Responsibility Reports (BRR) in 2012, requiring the top 100 listed entities by market capitalisation to include BRR in their annual reports. This was later extended to the top 500 listed entities in 2015.
- In 2021, SEBI replaced the BRR reporting requirement with the more comprehensive Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR).
- The BRSR seeks disclosures from listed entities on their performance against the nine principles of the ‘National Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct’ (NGBRCs).
- Companies have the opportunity to use different reporting frameworks in order to show their commitment to ESG practices like Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
SEBI
- SEBI is a Statutory Body established in 1992 in accordance with the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
- The basic functions of SEBI is to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote and regulate the securities market.
- The headquarters of SEBI is situated in Mumbai. The regional offices of SEBI are located in Ahmedabad, Kolkata, Chennai and Delhi.
|
Drishti Mains Question: The Securities and Exchange Board of India plays a vital role in overseeing and regulating the securities market in the country. Discuss its significance and the obstacles it encounters. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following is issued by registered foreign portfolio investors to overseas investors who want to be part of the Indian stock market without registering themselves directly? (2019)
(a) Certificate of Deposit
(b) Commercial Paper
(c) Promissory Note
(d) Participatory Note
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Economic growth in the recent past has been led by an increase in labor activity.” Explain this statement. Suggest the growth pattern that will lead to creation of more jobs without compromising labor productivity. (2022)