NATO Suspends CFE Treaty Amid Russian Withdrawal | 18 Nov 2023
For Prelims: Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), Cold War, Warsaw Pact, World War II, The North Atlantic Treaty.
For Mains: Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, World wars, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) has announced the formal suspension of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE), a key Cold War-Era Security Treaty in response to Russia's pullout from the deal.
What is the Background of Russia's Pullout from CFE?
- About CFE Treaty:
- The CFE Treaty, signed in 1990 and fully ratified in 1992, aimed to prevent massing of conventional armed forces by NATO and Warsaw Pact countries near mutual borders during the Cold War.
- It placed limits on the deployment of conventional military forces in Europe and played a significant role in reducing tensions and arms build-up in the region.
- This treaty was one of several Cold War-era agreements involving Russia and the United States.
- Russia's Withdrawal:
- Russia had suspended its participation in the CFE Treaty in 2007 and formally announced its intention to withdraw in 2015.
- The recent move to finalise the withdrawal came after the Russian President signed a bill denouncing the treaty in May 2023.
- Russia has blamed the US and its allies for the withdrawal, citing their "destructive position" on the treaty.
- Ukraine Conflict's Impact:
- Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, which led to a significant military presence in Ukraine, influenced its decision to withdraw from the treaty.
- The conflict has direct implications for NATO member states that share borders with Ukraine, such as Poland, Slovakia, Romania, and Hungary.
What are Russia’s Concerns and NATO’s Position?
- Russia claims CFE is no longer serves its interests because it was signed to restrict the use of conventional weapons and equipment and not other advanced weapons.
- Russia cited that preserving the CFE Treaty has become unacceptable from the standpoint of its fundamental security interests, citing developments in Ukraine and NATO's expansion.
- NATO underlines its commitment to reducing military risk, preventing misperceptions, and maintaining security.
- The suspension of the CFE Treaty underscores the ongoing tensions between Russia and NATO, which have significant implications for global security and regional stability, particularly in Eastern Europe.
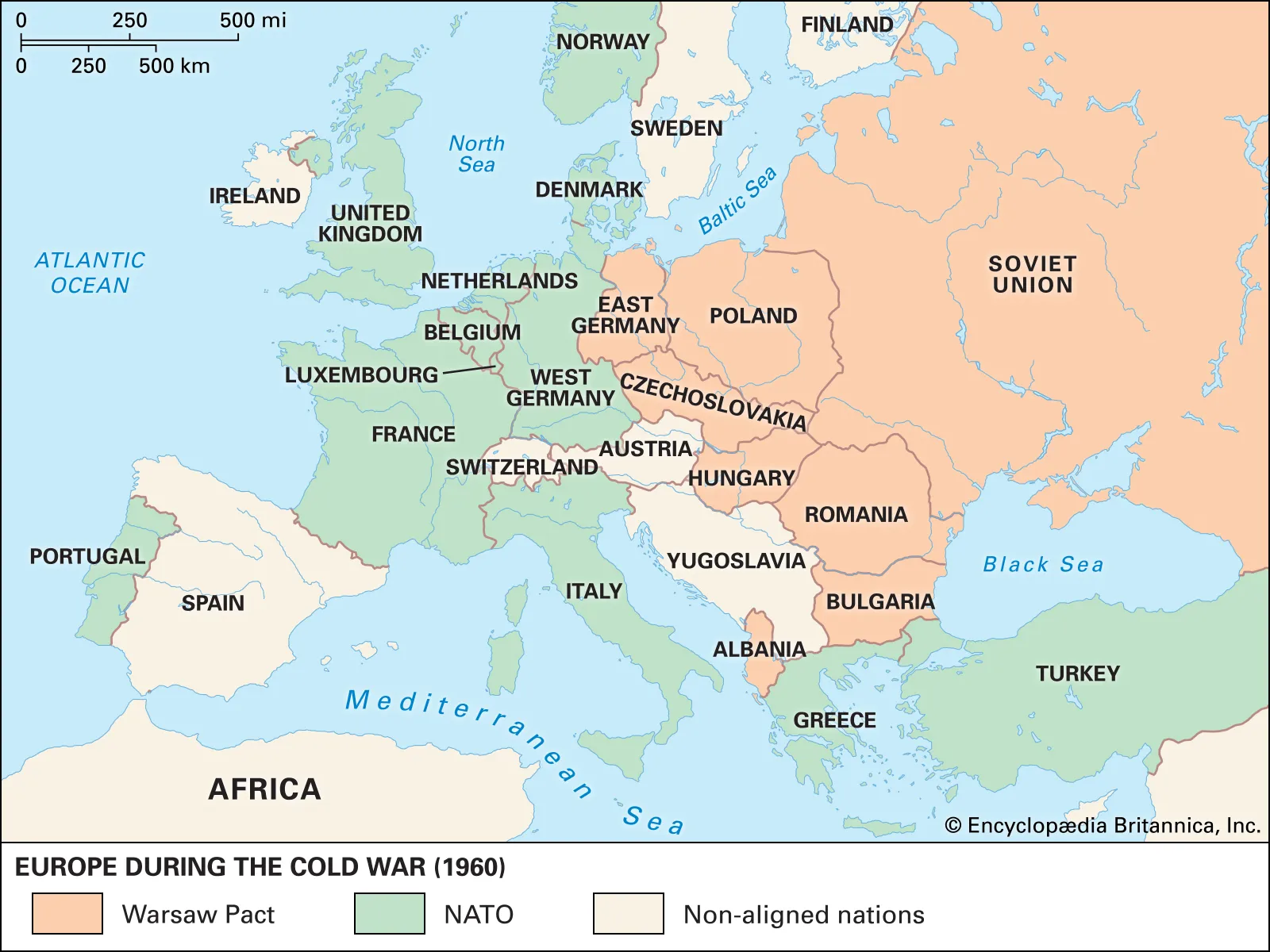
What is the Cold War?
- The Cold War was a period (1945-1991) of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and its satellite states (the Eastern European countries), and the United States with its allies (the Western European countries) after World War II.
- Post World War II, the world got divided into two power blocs dominated by two superpowers viz. the Soviet Union and the US.
- The two superpowers were primarily engaged in an ideological war between the capitalist USA and the communist Soviet Union.
- The term "Cold" is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two sides.
What are Other Cold-War Era NATO and USSR Treaties?
- The North Atlantic Treaty (1949):
- The North Atlantic Treaty, also known as the Washington Treaty, established NATO on 4th April, 1949.
- It was a collective defence alliance formed by Western nations, including the US, Canada, and various European countries.
- The Warsaw Pact (1955):
- The Warsaw Pact, formally known as the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance, was signed on 14th May, 1955.
- It was a response to NATO and established a similar mutual defence alliance among the Eastern Bloc countries, led by the Soviet Union.
- The Warsaw Pact included the Soviet Union, East Germany, Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Bulgaria, and Romania, among others.
- The Four Power Agreement on Berlin (1971):
- This agreement, signed on 3rd September, 1971, between the United States, the United Kingdom, France, and the Soviet Union, addressed the status of Berlin during the Cold War.
- It aimed to improve relations and ease tensions in the divided city.
- The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty (1987):
- It was signed on 8th December, 1987, by the U.S. President and Soviet General Secretary, the INF Treaty eliminated an entire class of intermediate-range nuclear missiles from Europe.
- The treaty marked a significant step in reducing Cold War tensions and nuclear arms.
- The Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) and START Treaties:
- SALT were a series of bilateral conferences and international treaties signed between the United States and the Soviet Union.
- These treaties had the goal of reducing the number of long-range ballistic missiles (strategic arms) that each side could possess and manufacture.
- First treaty, known as SALT I, was signed in 1972.
- By signing SALT I, the US and the USSR agreed to a limited number of ballistic missiles, as well as a limited number of missile deployment sites.
Note: In February 2023, Russia had announced to suspend its participation in the New START Treaty, the last remaining major military agreement with the United States.
- The New START Treaty came into force in February, 2011 between the United States of America and the Russian Federation on measures for the further reduction and limitation of strategic offensive arms.
- The Helsinki Accords (1975):
- The Helsinki Final Act, signed in August, 1975, was not a treaty but a declaration of principles agreed upon by 35 countries, including NATO members and Warsaw Pact countries.
- It aimed to improve relations between East and West and included commitments to respect human rights and territorial integrity.
What is NATO?
- About:
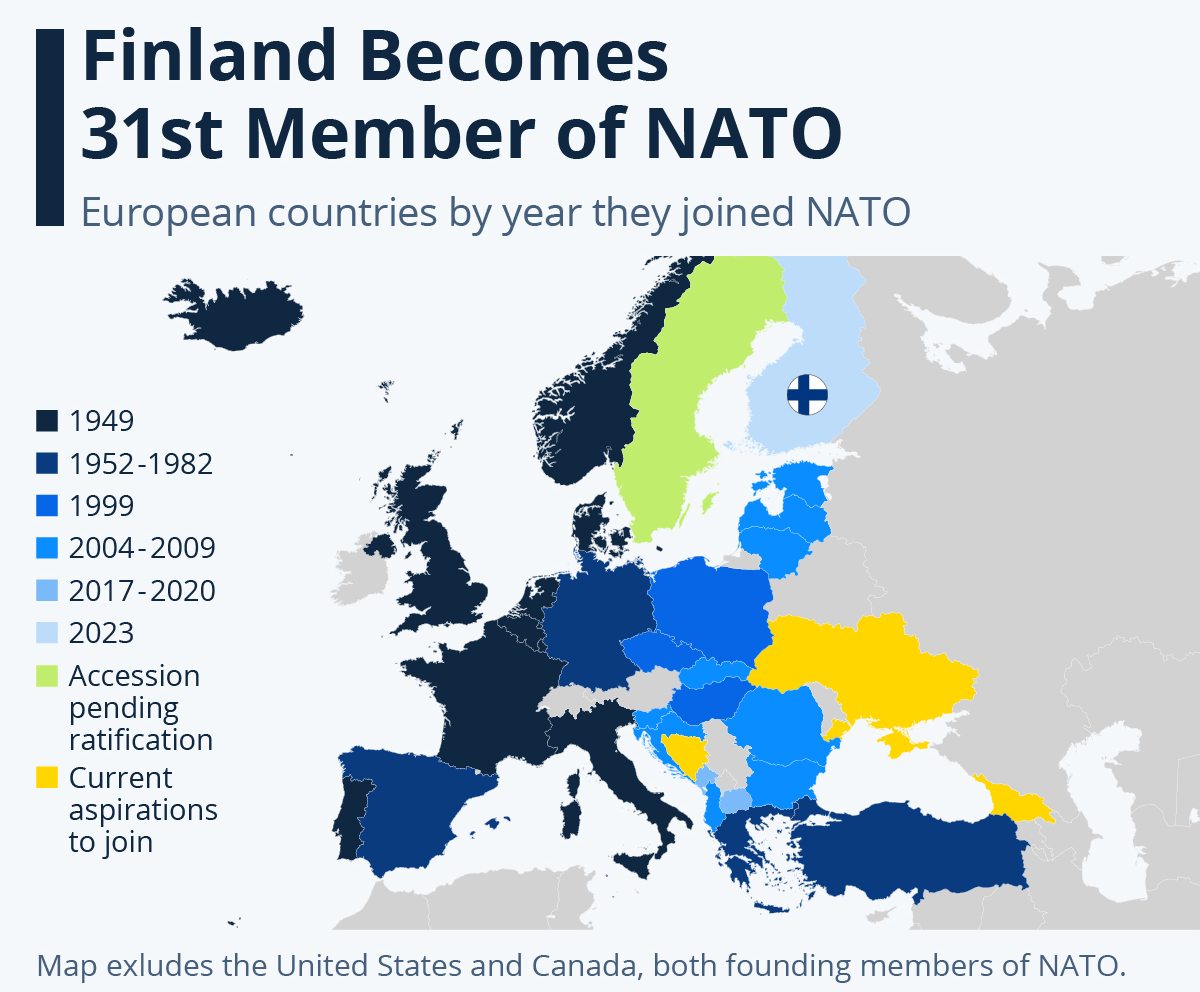
- NATO, or the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is a political and military alliance consisting of 31 member countries.
- It was formed in 1949 to promote mutual defence and collective security among its members.
- Members:
- In 1949, there were 12 founding members of the Alliance: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- Since then, 19 more countries have joined the Alliance: Greece and Turkey (1952); Germany (1955); Spain (1982); Czechia, Hungary and Poland (1999); Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia (2004); Albania and Croatia (2009); Montenegro (2017); North Macedonia (2020); and Finland (2023).
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium:
- Headquarters of Allied Command Operations: Mons, Belgium.
- Special Provision:
- Article 5: Article 5 of the NATO treaty is a key provision that states that an attack on one member is an attack on all members.
- This provision has only been invoked once, after the 9/11 terrorist attacks in the United States.
- However, NATO's protection does not extend to members' civil wars or internal coups.
- Article 5: Article 5 of the NATO treaty is a key provision that states that an attack on one member is an attack on all members.
- Alliances of NATO:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post Cold War international scenario. (2016)