National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations | 07 Aug 2023
For Prelims: NIDHI, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE 2.0)
For Mains: Significance of NIDHI, Major Challenges Related to Startups in India, Recent Government Initiatives Related to Startups.
Why in News?
Recently, in a written reply in the Rajya Sabha, the Union Minister of State for Science and Technology highlighted achievement in India's innovation landscape through the NIDHI (National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations).
- The Department of Science & Technology (DST) launched the NIDHI program in 2016. NIDHI also involves collaboration with other key entities to encourage startups.
What is the National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI)?
- About:
- The NIDHI is a groundbreaking initiative designed to drive innovation, support startups, and create a thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem in India.
- NIDHI comprises various components that provide a comprehensive framework for promoting and accelerating innovation-driven enterprises across the nation.
- Components of NIDHI Program:
- NIDHI-PRAYAS (Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups):
- Focuses on converting innovative ideas into tangible prototypes.
- Offers mentoring and financial support at the Proof-of-Concept level.
- NIDHI Entrepreneurs-In-Residence (EIR) Program:
- Provides fellowships to students pursuing entrepreneurship.
- Aims to nurture and encourage young entrepreneurs.
- NIDHI Seed Support Program:
- Offers early-stage seed funding to startups.
- Enables startups to embark on their innovation journey.
- NIDHI Accelerator Program:
- Speeds up the investment readiness of startups.
- Equips startups with the resources needed for growth and scaling.
- Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) and Centres of Excellence (CoE):
- Establishes state-of-the-art infrastructure for incubating startups.
- Fosters innovation in technology sectors.
- NIDHI-Inclusive Technology Business Incubators (iTBI) program:
- Strengthens the innovation and startup incubation ecosystem in Tier II and Tier III cities.
- The iTBI program has helped increase entrepreneurial inclusiveness in terms of geographies, gender and persons with special abilities.
- NIDHI-PRAYAS (Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups):
- Key Players and Collaborators:
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR):
- NIDHI collaborates closely with CSIR to shape and develop cutting-edge incubation facilities.
- Plays an active role in conceptualizing and developing advanced incubation facilities.
- Supports translating technology and products, benefiting society, industry, and the country.
- NIDHI collaborates closely with CSIR to shape and develop cutting-edge incubation facilities.
- Department of Biotechnology (DBT) through Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC):
- NIDHI joins hands with DBT and BIRAC to encourage startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators in the biotechnology domain.
- Through strategic collaboration, they drive translational research and facilitate the creation of affordable biotech solutions.
- Supports startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators in developing affordable products and technologies.
- The progress made through BIRACs incubation program include setting up of 75 Incubation Centers supported through BIRAC’s BioNEST and E-YUVA (Empowering Youth for Undertaking Value Added Innovative Translational Research) schemes of BIRAC across the country, around 900 innovative projects supported under Biotech Ignition Grant (BIG).
- Ministry of Defence (MoD):
- Collaborating with MoD's Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX), NIDHI contributes to a dynamic ecosystem for innovation.
- This partnership engages industries, startups, and R&D institutes to drive advancements in defence and aerospace technologies.
- Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY):
- NIDHI's partnership with MeitY in the Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE 2.0) Scheme empowers tech-driven startups.
- Together, they provide financial and technical support to foster technology-based entrepreneurship.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR):
- Collaborating with ICAR's National Agriculture Innovation Fund, NIDHI empowers agri-tech startups.
- Their joint efforts establish Agri-business Incubator (ABIs) centres, driving innovative solutions in agriculture.
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR):
Department of Science and Technology:
- The foundation of DST was laid on 3rd May 1971 along the model of National Science Foundation (NSF), USA.
- It provides funding and also makes policies and co-ordinates scientific work with other countries.
- It empowers scientists and scientific institutions and also works with a highly distributed system permeating stakeholders ranging from school college, PhD, Postdoc students, young scientists, startups and NGOs working in Science & Technology.
What is the Status of India’s Innovation and Startup Ecosystem?
- India is ranked 40th out of 132 among the top innovative economies globally as per the Global Innovation Index (GII) 2022.
- India has emerged as the 3rd largest ecosystem for startups globally as of 31st May 2023.
- As of June 2023, India is home to 108 Unicorns with a total valuation of USD 340.80 Bn.
- Out of the total number of unicorns, 44 unicorns were born in 2021 and 21 unicorns were born in 2022.
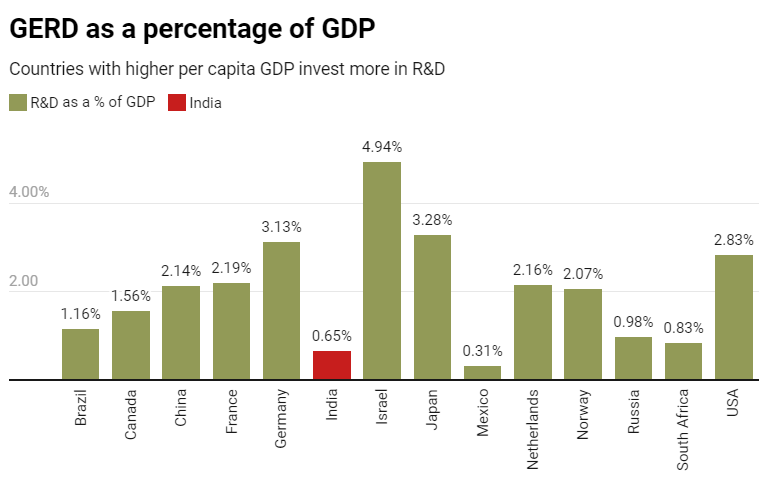
- India’s Gross Domestic Expenditure on R&D (GERD) as a percentage of GDP was 0.65% in 2017-18, which is lower than the global average of 2.2% and much lower than the leading innovators such as Israel (4.9%), South Korea (4.5%), and Japan (3.2%).
- India faces issues such as funding, revenue generation, and supportive infrastructure in its innovation and startup journey.
- India’s public sector accounts for about three-fourths of the total R&D expenditure in the country, while the private sector contributes only about one-fourth. This is in contrast to the global trend, where the private sector plays a dominant role in R&D spending.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Encourage Startup and Innovation in India?
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Startup India Hub.
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Centres of Excellence.
- Startup India Action Plan (SIAP).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What does venture capital mean? (2014)
(a) A short-term capital provided to industries
(b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
(c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
(d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- Venture capital is a form of fund for a new or growing business. It usually comes from venture capital firms that specialize in building high risk financial portfolios.
- With venture capital, the venture capital firm gives funding to the startup company in exchange for equity in the startup.
- The people who invest this money are called venture capitalists (VCs). Venture capital investment is also referred to as risk capital or patient risk capital, as it includes the risk of losing the money if the venture does not succeed and takes a medium to long-term period for the investments to fructify.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.