Governance
National Electricity Plan for 2022-27
- 05 Apr 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Central Electricity Authority, Electricity Act, 2003, Battery Energy Storage Systems, Lithium-ion batteries.
For Mains: National Electricity Plan for 2022-27.
Why in News?
The latest draft of the National Electricity Plan (NEP), which covers the period 2022-27, marks a significant departure from its previous edition, which had focused primarily on renewable energy.
What is the National Electricity Plan?
- About:
- The NEP is a crucial document that guides the development of the power sector in India. It is formulated by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) every five years under the Electricity Act, 2003.
- The CEA formulates short-term (5-year) and prospective plans (15-year) to assess the demand for planning capacity addition and coordinate the activities of various planning agencies for the optimal utilization of resources.
- The NEP provides a review of the last five years (2017-22), capacity addition requirements for 2022-27, and projections for the period 2027-2032.
- The first NEP was notified in 2007, the Second Plan in December 2013, and the third plan which covers the detailed Plan for 2017-22 and the perspective Plan for 2022-27 was notified in 2018.
- New Draft:
- It recognizes the need for additional coal-based capacity, ranging from 17 GW to nearly 28 GW, till 2031-32, over and above the 25 GW of coal-based capacity that is currently under construction.
- The draft Plan also highlights the need for significant investments in battery storage, with an estimated requirement of between 51 GW to 84 GW by 2031-32.
- It projects an increase in the Plant Load Factor (PLF) of coal-fired power plants from 55% up to 2026-27 to 62 % in 2031-32.
- It also emphasizes the challenges posed by the increasing reliance on renewables, which will require careful management and planning in the years ahead.
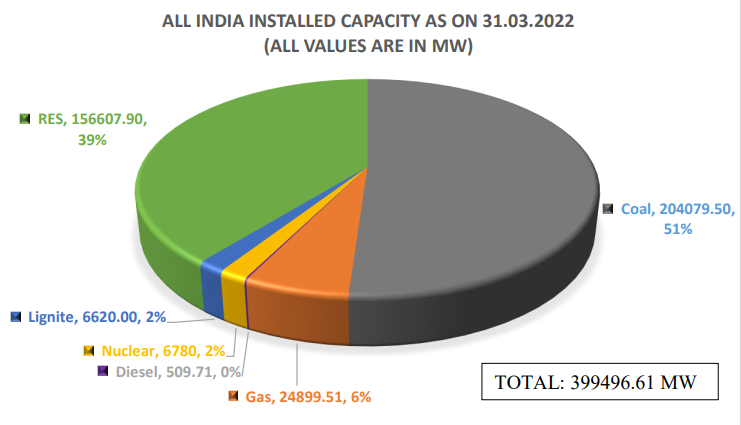
What is the Power Scenario of India?
What are the Related Challenges?
- Reliance on Old Plants:
- India's fleet of coal-fired thermal power plants is over 25 years old and runs on outdated technology, which raises concerns about grid stability and power interruptions.
- Difficult to Manage the Renewables-Dominated Grid:
- While there has been a pronounced reliance on renewable generation for meeting capacity additions, there is a lack of clarity on how the grid will be managed. The slow development of hydropower and zero-inertia solar generators has resulted in a decrease in inertia, which provides stability to the grid.
- Inadequate Funding:
- If battery storage is to be relied on to back up renewable generation, it requires significant investments.
- The CEA report estimates that the total fund requirement for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) between 2022-27 is approximately 14.30 lakh crore. However, the CEA has only allocated a budget of 8 lakh crore for BESS development for a 10-year period.
- If battery storage is to be relied on to back up renewable generation, it requires significant investments.
- Lack of Evaluation:
- There is no evaluation of the ramping rate for thermal plants under different solar generation scenarios.
- The ramping rate is the rate at which a power plant can increase or decrease its output.
- Without proper assessment, it could lead to issues such as overloading, underloading, or power interruptions.
- There is no evaluation of the ramping rate for thermal plants under different solar generation scenarios.
How can the Related Challenges be Addressed?
- BESS based on Lithium-ion batteries offer a cost-effective solution to balance the grid against load fluctuations and intermittency in generation. The energy storage can provide energy time-shifting, allowing power to be used when it is needed rather than being wasted when it is generated.
- It is important to continue investing in the development of battery storage technology, as well as exploring new solutions such as water-based systems. This will help address the challenges outlined in the National Electricity Plan for 2022-27 and ensure a stable and reliable power supply in India.
- Additionally, increasing the use of hybrid generation models will help to transition to renewable energy sources while ensuring backup power is available when needed.