Nanoplastics Causing Antibiotic Resistance | 21 Dec 2024
Why in News?
Recently, a study revealed that nanoplastics derived from single-use plastic bottles (SUPBs) contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance (AR), presenting an overlooked public health risk.
- Antibiotic resistance, a type of antimicrobial resistance, occurs when bacteria evolve to resist the effects of drugs that once killed them or inhibited their growth.
What are Key Highlights of the Study?
- Risk to Gut Microbiome: Nanoplastics could transform Lactobacillus acidophilus (gut microbiota) into a carrier of AR genes, which may then be transferred to pathogenic bacteria during infections, thus worsening the AR crisis.
- Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT): Polyethylene terephthalate bottle-derived nanoplastics (PBNPs) facilitate the transfer of AR genes from E. coli to Lactobacillus acidophilus through horizontal gene transfer (HGT).
- In HGT, genes are passed directly from one organism to another, potentially across different species. (Vertical gene transfer, from parent to offspring).
- Two Mechanisms of AR Gene Transfer:
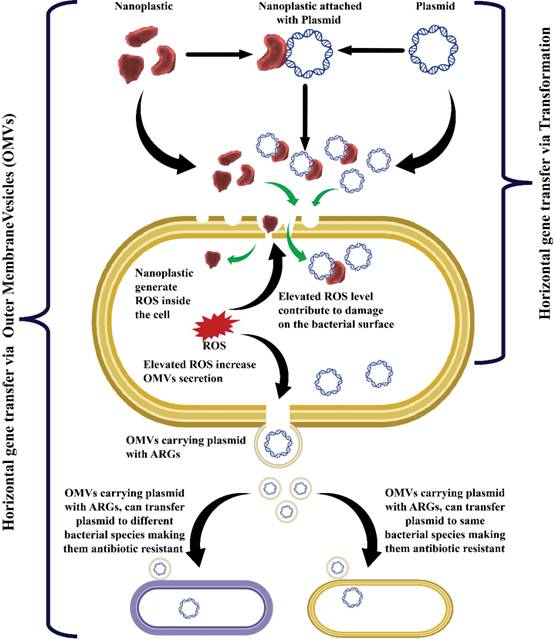
- Direct Transformation Pathway: PBNPs act as physical carriers, transporting AR plasmids across bacterial membranes and promoting direct gene transfer.
- OMV-Induced Transfer Pathway: PBNPs induce oxidative stress, triggering increased outer membrane vesicle (OMV) secretion.
- These OMVs, carrying AR genes, facilitate gene transfer between bacterial species, including between beneficial and pathogenic bacteria.
- AR Gene Transfer Mechanism:
What Are Nanoplastics?
- Definition: Nanoplastics are solid particles of synthetic or heavily modified natural polymers with sizes ranging between 1 nm and 1000 nm.
- Types:
- Primary Nanoplastics: These are intentionally produced nanoplastics, typically for specific applications.
- Secondary Nanoplastics: The majority of nanoplastics in the environment are secondary, meaning they result from the fragmentation of larger plastic items released unintentionally into the environment.
- Concerns with Nanoplastics:
- Environmental Presence: Disrupts marine food chains and ecosystems.
- Bioaccumulation: Harmful effects on health.
- Toxicity: Inflammation, and disruptions in normal cellular processes.
- Gut Microbiome Disruption: Digestive problems, immune dysfunction, or an increased risk of infections.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? (2019)
- Genetic predisposition of some people
- Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases
- Using antibiotics in livestock farming
- Multiple chronic diseases in some people
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)