Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle Technology | 12 Mar 2024
Why in News?
India has recently made a significant advancement in missile technology, joining the select group of nations possessing Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) capabilities.
- This milestone was achieved through the successful flight test named Mission Divyastra, conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). It marked the first time the indigenously developed Agni-5 missile integrated MIRV technology.
What are the Key Facts About MIRV Technology?
- Inception:
- MIRV technology originated in the United States, with the deployment of a MIRVed Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) in 1970.
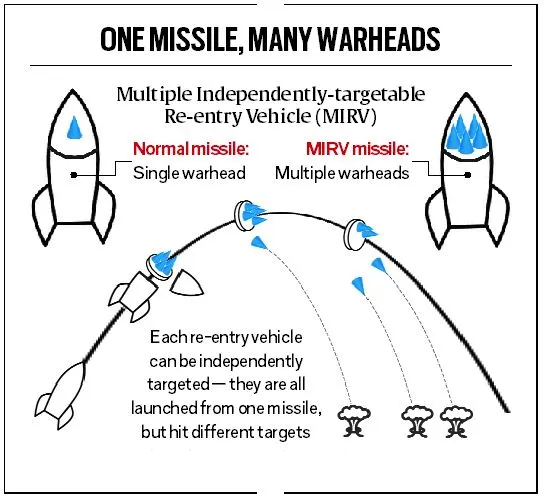
- MIRV allows a single missile to carry multiple warheads (3-4), each capable of targeting different locations independently.
- MIRV technology enhances the missile’s effectiveness by increasing the number of potential targets it can engage.
- MIRVs can be launched from both land-based platforms and sea-based platforms, such as submarines, expanding their operational flexibility and range.
- Global Adoption and Proliferation:
- Nations possessing MIRV technology include major nuclear powers such as the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Russia, China, and India, while Pakistan tested the technology (Ababeel Missile) in 2017.
- The test flight of Agni-5 marked the first time that the MIRV technology was tested in India, which aims to deploy multiple warheads at different locations in a single launch.
- The Agni-5 weapon system is equipped with indigenous avionics systems and high-accuracy sensor packages, which ensured that the re-entry vehicles reached the target points within the desired accuracy.
- Strategic Significance:
- MIRVs were initially designed to enhance offensive capabilities rather than to defeat ballistic missile defences.
- Their ability to deploy multiple warheads independently makes them significantly more challenging to defend against compared to traditional missiles.
- Challenges:
- Deploying MIRV technology presents complex challenges, including the miniaturisation of warheads, the development of advanced guidance systems, and ensuring the reliability of individual re-entry vehicles.
- Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness and reliability of MIRV systems in strategic operations.
- Deploying MIRV technology presents complex challenges, including the miniaturisation of warheads, the development of advanced guidance systems, and ensuring the reliability of individual re-entry vehicles.
Agni-5 Missile
- Agni is an Inter-continental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed indigenously by the DRDO.
- It is capable of carrying nuclear warheads and has a target range of more than 5,000 km. It uses a three-stage solid-fuelled engine.
- Agni-5 has been successfully tested several times since 2012. In December 2022, DRDO also tested the night-time capabilities of Agni-5.
- Missiles in Agni Family:
- Agni I: Short-range ballistic missile (Range more than 700 km).
- Agni II: Medium-range ballistic missile (Range more than 2000 to 3500 km).
- Agni III: Intermediate-range ballistic missile (Range more than 3000 km).
- Agni IV: Intermediate-range ballistic missile (Range more than 3500 km).
- Agni-P (Agni Prime): A nuclear-capable, two-stage canisterised solid propellant ballistic missile (Range 1,000 to 2,000 km).
- The next upgrade of the Agni missile, Agni-6, is expected to be a full-fledged intercontinental ballistic missile with a range well over 7,000 km.
Read more: Agni-5 Ballistic Missile
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news? (2018)
(a) An Israeli radar system
(b) India’s indigenous anti-missile programme
(c) An American anti-missile system
(d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea
Ans: (c)
Q2. With reference to Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. How is S-400 air defence system technically superior to any other system presently available in the world? (2021)