Multimodal Transport Hub | 19 Mar 2024
Why in News?
Indian Railways plans to develop a Multi-Modal Transport Hub (MMTH) in Aspirational cities with a population of more than 10 lakh across the country.
- The programme is part of the infrastructure being developed for India’s ‘Viksit Bharat’ initiative.
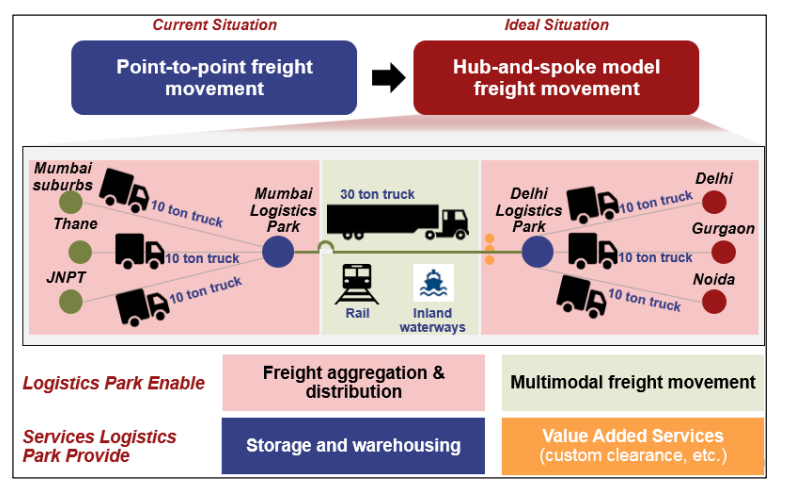
What is a Multimodal Transport Hub?
- About:
- An MMTH is a transportation facility designed to integrate various modes of transportation such as rail, road, and mass transit systems in a single location.
- The primary objective of an MMTH is to provide seamless connectivity and efficient transfer of passengers and goods between different modes of transportation.
- Key Features:
- Railway Station: The railway station serves as a terminus for train services connecting different regions.
- It is equipped with modern facilities for passengers including waiting areas, ticketing counters, platforms, and amenities.
- Interstate Bus Terminus (ISBT): The ISBT facilitates interstate and intrastate bus services, providing connectivity to various destinations.
- Mass Rapid Transit System (MRTS) Station: The MRTS station accommodates rapid transit services such as metro, light rail, or other forms of urban mass transit.
- It connects the hub to the wider urban transit network and offers convenient transportation options for commuters.
- Transportation Catchment Zone: The surrounding area of the MMTH serves as a catchment zone, attracting travellers from nearby regions and facilitating improved transport connectivity for the surrounding areas.
- This enhances accessibility and contributes to the economic development of the region.
- Railway Station: The railway station serves as a terminus for train services connecting different regions.
What are the Aspects of Viksit Bharat?
- Structural transformation: This refers to the shift of resources from low-productivity sectors (such as agriculture) to high-productivity sectors (such as manufacturing and services).
- Organising Labour Markets: This involves improving the quality and quantity of labour supply, enhancing the skills and employability of workers, and ensuring fair and efficient labour regulations.
- Increasing Competitiveness: This entails enhancing the efficiency and innovation of firms, improving the quality and diversity of products and services, and expanding the domestic and international markets..
- Improving Financial and Social Inclusion: This implies expanding the access and affordability of financial services and social welfare schemes for the poor and marginalised groups.
- Governance Reforms: This involves strengthening the institutions and processes of governance, such as the rule of law, accountability, transparency, and participation.
- Seizing Opportunities in the Green Revolution: This refers to adopting and promoting green technologies and practices, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and climate resilience.
What are the Government Initiatives for Railways and Transportation?
- The Gati Shakti Terminal (GCT) policy
- National Logistics Policy (NLP)
- Sagarmala’ and ‘Bharatmala for Investment in railway infrastructure
- Dedicated Freight Corridors
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to bio-toilets used by the Indian Railways, consider the following statements: (2015)
- The decomposition of human waste in the biotoilets is initiated by a fungal inoculum.
- Ammonia and water vapour are the only end products in this decomposition which are released into the atmosphere.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. The Gati-Shakti Yojana needs meticulous coordination between the government and the private sector to achieve the goal of connectivity. Discuss. (2022)