Mount Etna | 18 Nov 2023
Why in News?
Mount Etna, Europe’s most active volcano and one of the largest in the world, has been erupting frequently since February 2023, sending plumes of ash and fountains of lava into the sky.
What are the Key Facts About Mount Etna?
- Mount Etna is a stratovolcano, which means it is composed of layers of lava, ash, and rocks that have accumulated over thousands of years of eruptions.
- It is located on the east coast of Sicily, an island in the Mediterranean Sea that belongs to Italy.
- It stands about 3,300 metres above sea level and covers an area of about 1,200 square kilometres.
- Mount Etna has four summit craters and hundreds of lateral vents that can produce different types of eruptions, such as explosive, effusive, or mixed.
- Mount Etna has been erupting almost continuously since 1500 BC, making it one of the most active volcanoes in the world.
What is a Volcano?
- About:
- Volcanoes are openings or vents where lava, rocks, and steam erupt onto the Earth's surface.
- They result from both their own eruptions and the general formation of the planet through the movement and collision of tectonic plates.
- Types of Volcanoes:
- Based on frequency of Eruption:
- Active volcanoes:
- They erupt frequently and are mostly located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, which includes New Zealand, Southeast Asia, Japan and the western coast of the Americas.
- About 90% of all earthquakes worldwide strike within this region.
- Volcanic activity is linked to the movement and collision of tectonic plates.
- Examples include Kilauea in Hawaii and Santa Maria in Guatemala.
- Dormant Volcano:
- These are not extinct but have not erupted in recent history. The dormant volcanoes may erupt in future.
- Example: Mount Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania, also the highest mountain in Africa, is known to be a dormant Volcano.
- Extinct or inactive volcanoes:
- These have not worked in the distant geological past.
- Example: Dhinodhar hill, Gujarat.
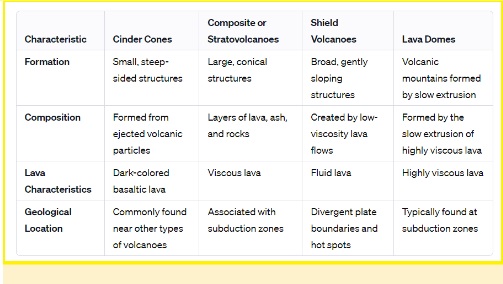
- Based on Geological Formations:
- Based on frequency of Eruption:
- Based on the Type of Eruption:
- Basic:
- The basic magma is dark-coloured like basalt, rich in iron and magnesium but poor in silica. They travel far and generate broad shield volcanoes.
- Acidic:
- These are light-coloured, of low density, and have a high percentage of silica therefore they make a familiar cone volcano shape.
- Basic:
- Tools and Methods to Predict Volcanic Eruptions:
- Seismic Data:
- Monitoring earthquakes and tremors as potential precursors to volcanic eruptions.
- Ground Deformation:
- Observing changes in the ground, indicating magma movement.
- Gas Emissions and Gravity Changes:
- Analyzing volcanic gas emissions, gravity, and magnetic field alterations.
- Seismic Data:
Read more: About the Emergency Alert System during the Earthquake.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Barren Island volcano is an active volcano located in the Indian territory.
- Barren Island lies about 140 km east of Great Nicobar.
- The last time the Barren Island volcano erupted was in 1991 and it has remained inactive since then.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3
C. 3 only
D. 1 and 3
Ans: A
Mains
Q. Mention the global occurrence of volcanic eruptions in 2021 and their impact on regional environment. (2021)