Monsoon, El Nino And Their Impact on Agriculture | 03 Aug 2023
For Prelims: Monsoon, Kharif crop, El Nino, Groundwater, Droughts, Food inflation, Oceanic Nino Index.
For Mains: Impact of Monsoon and El Nino on Indian Agriculture
Why in News?
The 2023 southwest monsoon season in India started late, with the initial two weeks experiencing a significant rainfall deficiency of 52.6% below the normal long-period average(LPA).
- However, as of July 30, 2023 there was an overall 6% surplus rainfall. This turnaround has positively impacted kharif crop plantings. However, concerns persist regarding the potential impact of the approaching El Nino phenomenon on rabi crops.
What is the Long-Period Average (LPA) of Rainfall?
- The IMD defines the "LPA of rainfall" as the average rainfall recorded over a specific region for a long period, like 30 or 50 years. Based on this, the IMD classifies rainfall into five categories on an all-India scale:
- Normal or near normal: Rainfall between 96-104% of LPA.
- Below normal: Rainfall between 90-96% of LPA.
- Above normal: Rainfall between 104-110% of LPA.
- Deficient: Rainfall less than 90% of LPA.
- Excess: Rainfall more than 110% of LPA.
What are Kharif and Rabi Crops?
- Kharif crops:
- Kharif crops are sown during the monsoon season, from June to October, and harvested in the late summer or early autumn.
- They depend on the southwest monsoon for irrigation and growth.
- Major Kharif crops include rice, maize, sorghum, pearl millet (bajra), finger millet (ragi), groundnut and pulses like pigeon pea (arhar) and green gram (moong).
- They account for about 55% of the total foodgrain production in India.
- Rabi Crops:
- These crops are sown around the Retreating Monsoon and Northeast monsoon season, which begins in October and are called rabi or winter crops.
- The harvest for these crops happens typically during April and May, during the summer season.
- Major Rabi crops are wheat, gram, peas, barley etc.
- A warm climate is required for seed germination and cold climate for the growth of crops.
What is the Impact of Monsoon on Indian Agriculture?
- Positive Impacts:
- Increased Crop Production: A major portion of the country's crop area is completely dependent on Monsoon rains as they're not equipped with methods of manual irrigation.
- Adequate rainfall during the monsoon season leads to increased soil moisture and promotes the growth of crops, resulting in higher agricultural output.
- The availability of water supports the cultivation of a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, millets, and pulses.
- Economic Boost: Successful monsoon seasons contribute to rural prosperity by providing income to farmers and laborers, which, in turn, stimulates demand for goods and services in the rural economy.
- This increased economic activity has a positive impact on overall national growth.
- Recharge of Groundwater: The monsoon helps recharge groundwater resources, which is crucial for sustainable agricultural practices in regions where water scarcity is a challenge.
- Increased Crop Production: A major portion of the country's crop area is completely dependent on Monsoon rains as they're not equipped with methods of manual irrigation.
- Negative Impacts:
- Erratic Monsoon Patterns: The monsoon's timing, intensity, and distribution are unpredictable, leading to uncertainties in agricultural planning and crop management.
- Delayed or early monsoons can disrupt planting schedules and affect crop yields.
- Droughts and Floods: Monsoon failure or excess rainfall can lead to droughts or floods, respectively.
- Both scenarios can be disastrous for agriculture. Droughts result in water shortages, crop failures, and reduced yields, while floods can damage crops, wash away fertile topsoil, and lead to livestock losses.
- Crop Losses: Prolonged and excessive monsoon rains can cause crop diseases, reducing crop quality and yield. These conditions also hinder farmers' ability to conduct agricultural operations effectively.
- Soil Erosion: Heavy rainfall can lead to soil erosion, which depletes soil fertility and affects agricultural productivity in the long run.
- Soil erosion also impacts water bodies and can lead to siltation in reservoirs, reducing their storage capacity.
- Food Price Inflation: Inconsistent monsoon patterns can affect crop production and lead to shortages, resulting in food price inflation.
- This can have adverse effects on the economy, especially for low-income households that spend a significant portion of their income on food.
- Erratic Monsoon Patterns: The monsoon's timing, intensity, and distribution are unpredictable, leading to uncertainties in agricultural planning and crop management.
What is El Nino and Its Implications on Agriculture?
- About:
- El Nino is a climate phenomenon that occurs irregularly in the tropical Pacific Ocean, characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures.
- It can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world, including India.
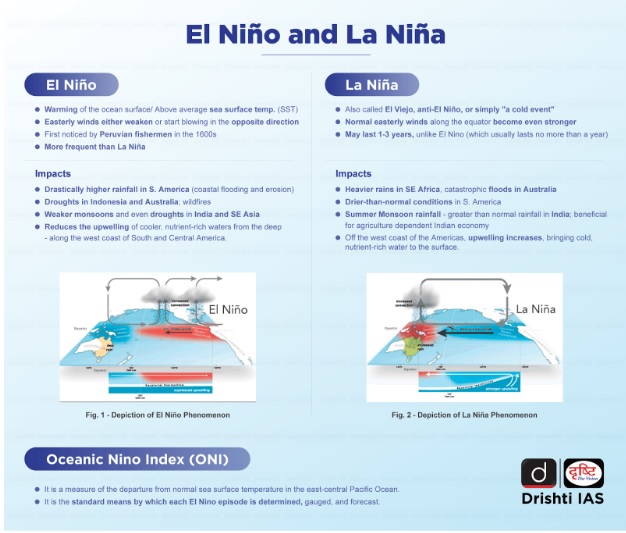
- The Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) reached 0.8 degrees Celsius in June, 2023 surpassing the El Nino threshold of 0.5 degrees.
- Global weather agencies forecast El Nino to persist and strengthen through the 2023-24 winter.
- It can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world, including India.
- El Nino is a climate phenomenon that occurs irregularly in the tropical Pacific Ocean, characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures.
- Impacts:
- Temperature Extremes: El Nino is often associated with higher temperatures in some parts of India.
- Elevated temperatures can adversely impact crops, leading to heat stress and reduced yields, especially for sensitive crops like fruits and vegetables.
- Pest and Disease Outbreaks: El Nino conditions can create a conducive environment for certain pests and diseases that affect crops.
- Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can lead to increased pest populations, posing additional challenges to farmers.
- Impact on Livestock: Reduced availability of fodder and water scarcity during El Nino can affect livestock and animal husbandry, leading to lower milk and meat production.
- Temperature Extremes: El Nino is often associated with higher temperatures in some parts of India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. How far do you agree that the behaviour of the Indian monsoon has been changing due to humanizing landscape? Discuss.(2015)
Q. Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014)
