Mekong - Lancang Cooperation | 05 Jul 2022
For Prelims: Mekong - Lancang Cooperation, Mekong River, Myanmar Neighbouring Countries
For Mains: India and its neighbourhood, Presence of China in Neighbouring Countries, Significance of International Groupings
Why in News?
Recently, Myanmar’s military government hosted the first high - level regional meeting since the Army took power in 2021.
What Do We Know About the Meeting?
- China’s Foreign Minister and counterparts from Mekong Delta nations attended the meeting.
- Foreign Minister of China along with his colleagues from Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam at the Mekong - Lancang Cooperation group meeting.
- It was held in the central city of Bagan, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- The theme of the meeting was “Solidarity for Peace and Prosperity”.
What Do We Mean by Mekong - Lancang Cooperation?
- About:
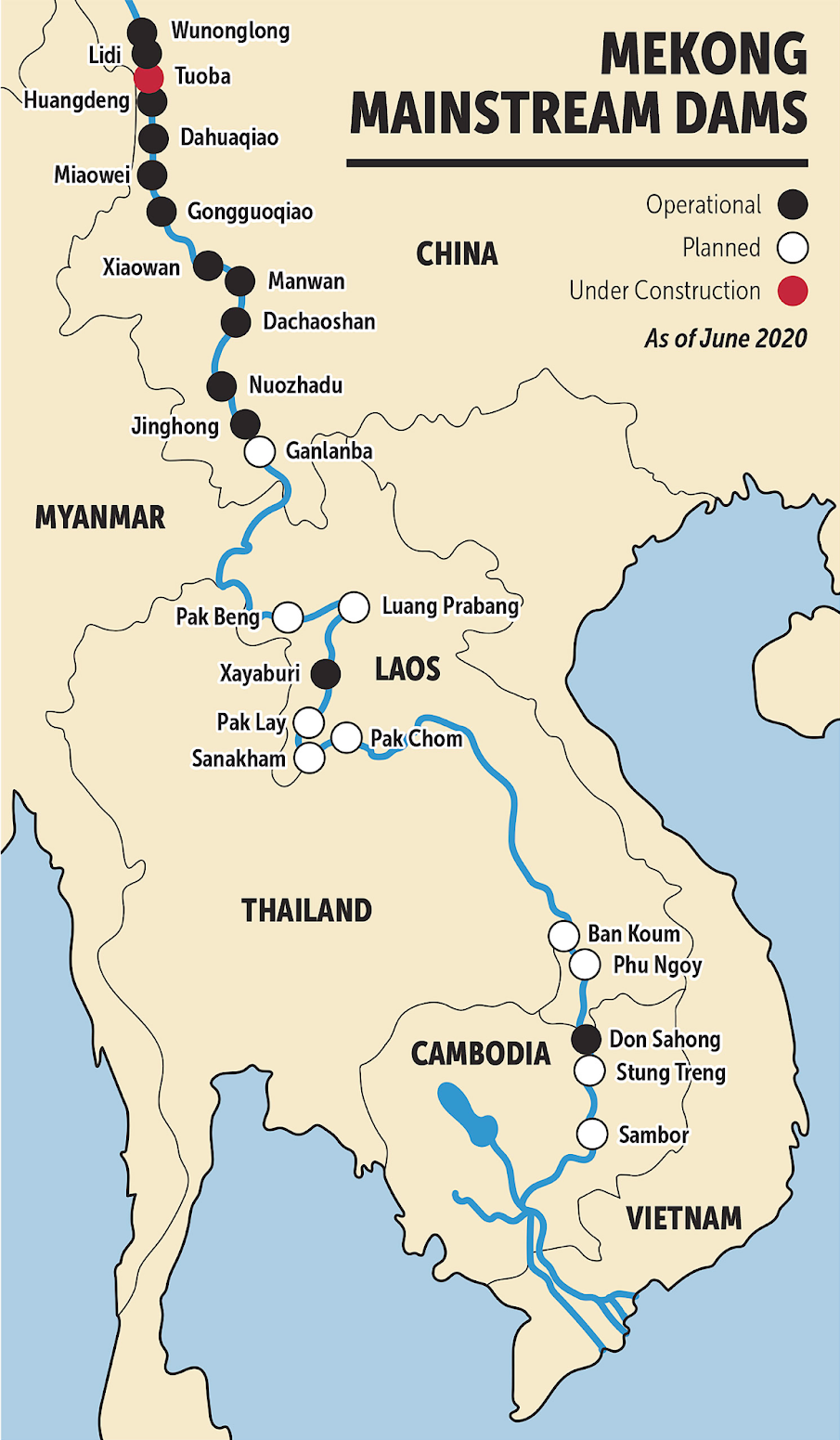
- The grouping is a Chinese led initiative that includes the countries of the Mekong Delta, a potential source of regional tensions due to an increasing number of hydroelectric projects that are altering the flow and raising concerns of ecological damage.
- Issues:
- China has built 10 dams along the upper stretch of the Mekong, the part it calls the Lancang.
- China has been criticized for the dams upstream on the Mekong river which affect water levels and downstream fisheries that are important to several Southeast Asian nations’ economies.
What is there to Know about Myanmar’s Military Coup?
- About:
- In the November 2020 parliamentary election, Suu Kyi’s party National League for Democracy (NLD) secured the majority of the seats.
- In the Myanmar's’ Parliament, the military holds 25% of the total seats according to the 2008 military-drafted constitution and several key ministerial positions are also reserved for military appointees.
- When the newly elected Myanmar lawmakers were to hold the first session of Parliament in 2021, the military imposed a state of emergency for one year citing massive voting fraud in the parliamentary elections.
- India’s reaction to the Coup:
- India supports the process of democratic transition in Myanmar.
- Though India has expressed deep concern over developments in Myanmar, cutting off from the Myanmar military is not a viable option as India has significant economic and strategic interests in Myanmar and its neighbourhood.
How has India’s Relations with Myanmar Been?
- Importance of Myanmar for India:
- Myanmar is geopolitically significant to India as it stands at the center of the India-Southeast Asia geography.
- Myanmar is the only Southeast Asian country that shares a land border with north-eastern India.
- Myanmar is the only country that sits at the intersection of India’s “Neighborhood First” policy and its “Act East” policy.
- As part of India’s SAGAR Vision, India developed the Sittwe port in Myanmar’s Rakhine state.
- The port is meant to be India’s answer to the Chinese-fronted Kyaukpyu port, which is intended to cement China’s geostrategic footprint in Rakhine.
- Projects in which India is involved Includes:
- Upgradation and resurfacing of the 160 km. long Tamu-Kalewa-Kalemyo road.
- An Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) project for high-speed data link in 32 Myanmar cities has been completed.
- ONGC Videsh Ltd. (OVL), Gas Authority of India Limited (GAIL) and ESSAR are participants in the energy sector in Myanmar.
- India and Myanmar 's Groupings:
- ASEAN:
- Myanmar became a member of ASEAN in July 1997.
- As the only ASEAN country which shares a land border with India, Myanmar is a bridge between India and ASEAN.
- BIMSTEC:
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a regional organization that was established on 6th June 1997 with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
- Representatives of the Governments of Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand came together in Bangkok, and signed the ‘Declaration on the Establishment of the Bangladesh–India–Sri Lanka–Thailand Economic Cooperation (BIST-EC)’.
- Myanmar became a member of BIMSTEC in December 1997.
- Myanmar is a signatory to the BIMSTEC Free Trade Agreement.
- Myanmar is the lead country for the energy sector. Myanmar trades mostly with Thailand and India in the BIMSTEC region.
- Mekong Ganga Cooperation:
- Myanmar is a member of the Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) since its inception in November 2000.
- MGC is an initiative by six countries – India and five ASEAN countries namely, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam – for cooperation in the fields of tourism, education, culture, transport and communication.
- SAARC:
- The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) was established with the signing of the SAARC Charter in Dhaka on 8th December 1985.
- SAARC comprises of eight Member States:
- Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- Myanmar was given the status of observer in SAARC in August 2008.
- ASEAN:
Why India Should be Concerned about the Meeting?
- China’s presence in Myanmar and growing bonds between China and Myanmar is an issue of deep concern for India as India shares 1600km of boundary with Myanmar
- Ever since the coup, China’s economic grip over Myanmar has become tighter with a special focus on projects critical for the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor.
- Moreover, the deadly attack on an Assam Rifles convoy near the Myanmar border in November 2021 was a reminder about the proclivity of China for creating trouble in the Northeast.
What Should be India’s Approach Moving Forward?
- Cultural Diplomacy:
- India’s cultural diplomacy through the lens of Buddhism can be leveraged for strengthening its ties with Myanmar.
- India’s “Buddhist Circuit” initiative, which seeks to double foreign tourist arrivals by connecting ancient Buddhist heritage sites across different states in India, should resonate with Buddhist-majority Myanmar.
- This could also build up India’s diplomatic reservoir of goodwill and trust with Buddhist-majority countries such as Myanmar.
- Resolving Rohingyas Issue:
- The quicker the Rohingya issue is resolved, the easier it will be for India to manage its relations with Myanmar and Bangladesh, focusing instead more on bilateral and subregional economic cooperation
- Other Measures:
- India should continue to engage with the present regime in Myanmar working towards mutual development of people of both the countries.
- It should support sharing experiences in constitutionalism and federalism to assist Myanmar in resolving the prevailing stalemate.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants?
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC) is an initiative by six countries – India and five ASEAN countries, namely, Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam for cooperation in tourism, culture, education, as well as transport and communications. It was launched in 2000 in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
- Both the Ganga and the Mekong are civilizational rivers and the MGC initiative aims to facilitate closer contacts among the people inhabiting these two major river basins.
- The MGC is also indicative of the cultural and commercial linkages among the member countries of the MGC down the centuries.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.