Maternity Leave for Surrogates | 26 Jun 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Government has notified an amendment to Central Civil Services (Leave) Rules, 1972 to grant maternity leave and other benefits to government employees in case of children born through surrogacy.
- This move aims to address the existing gap in the leave policies for government employees who opt for surrogacy.
What are the Provisions of Notified Amended Rules?
- Maternity Leave for Surrogate and Commissioning Mothers: It allows women government employees who have children through surrogacy to avail 180 days of maternity leave.
- This includes both the surrogate mother and the commissioning mother (the intended mother) with less than two surviving children.
- Paternity Leave for Commissioning Fathers: The new rules also grant 15 days of paternity leave to the "commissioning father" (the intended father) who is a male government servant with less than two surviving children.
- This leave can be availed within 6 months from the date of delivery of the child.
- Child Care Leave for Commissioning Mothers:
- Additionally, the commissioning mother with less than two surviving children is eligible for childcare leave, as per the existing provisions in the Central Civil Services (Leave) Rules.
What is Surrogacy and Related Regulation?
- About:
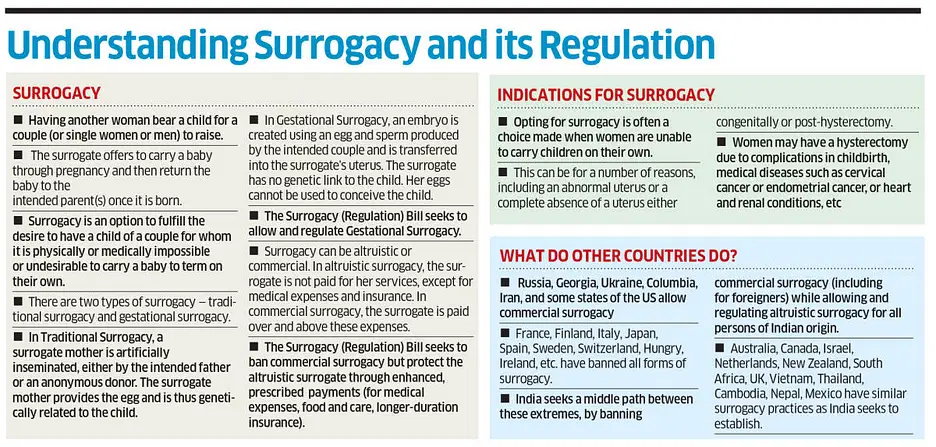
- It is a practice where a woman gives birth to a child for an intended couple with the intention to hand it over to them after the birth.
- It is permitted only for altruistic purposes or for couples who suffer from proven infertility or disease.
- Surrogacy is prohibited for commercial purposes such as sale, prostitution or any other forms of exploitation.
- A child born through surrogacy will be deemed to be the biological child of the couple.
- Abortion of such a fetus is allowed only with the consent of the surrogate mother and the authorities as per provisions of the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act 2021.
- Criteria:
- To avail of surrogacy, a couple should be married for at least 5 years, with the wife aged between 25-50 and the husband between 26-55.
- They should not have any living child unless the child has disabilities or a life-threatening illness.
- The couple must also have certificates of eligibility and essentiality, proving infertility and a court order for parentage and custody of the surrogate child. Additionally, the intended couple must provide insurance coverage for the surrogate mother for 16 months.
- Criteria for Surrogate Mother:
- She must be a close relative of the couple, a married woman with her own child, aged 25-35, and have only been a surrogate once.
- She also needs a certificate of medical and psychological fitness for surrogacy.
- Regulation:
- The National Surrogacy Board and State Surrogacy Boards are responsible for regulating surrogacy clinics and enforcing standards.
- The Act prohibits practices like commercial surrogacy, embryo selling, and exploitation or abandonment of surrogate mothers or children. Violations can lead to imprisonment for up to 10 years and a fine of Rs. 10 lakh.
Laws Related to Surrogacy:
Read more: Assisted Reproductive Technology, Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. In the context of recent advances in human reproductive technology, “Pronuclear Transfer” is used for (2020)
(a) fertilisation of egg in vitro by the donor sperm
(b) genetic modification of sperm producing cells
(c) development of stem cells into functional embryos
(d) prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring
Ans: (d)