Marburg Virus Disease | 24 Dec 2024
Rwanda has successfully contained and declared its first-ever Marburg Virus Disease (MVD) outbreak officially over after a 42-day period without new cases.
- MVD is a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever caused by the Marburg virus, with high case fatality rates and no approved treatments currently available.
- Transmission: It is transmitted from fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus) to humans, and spreads through direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals.
- Symptoms: MVD starts with high fever, severe headache, and malaise.
- As it progresses, it can cause severe bleeding, shock, and multi-organ failure, with death occurring 8-9 days post-symptom onset.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis is confirmed through tests like RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction), and virus isolation, which require maximum biohazard containment.
- Treatment: No approved vaccine or antiviral treatments; supportive care, such as rehydration and symptom management, improves survival.
- Control: Key control measures include community engagement, safe burials, contact tracing, and infection control in healthcare settings.
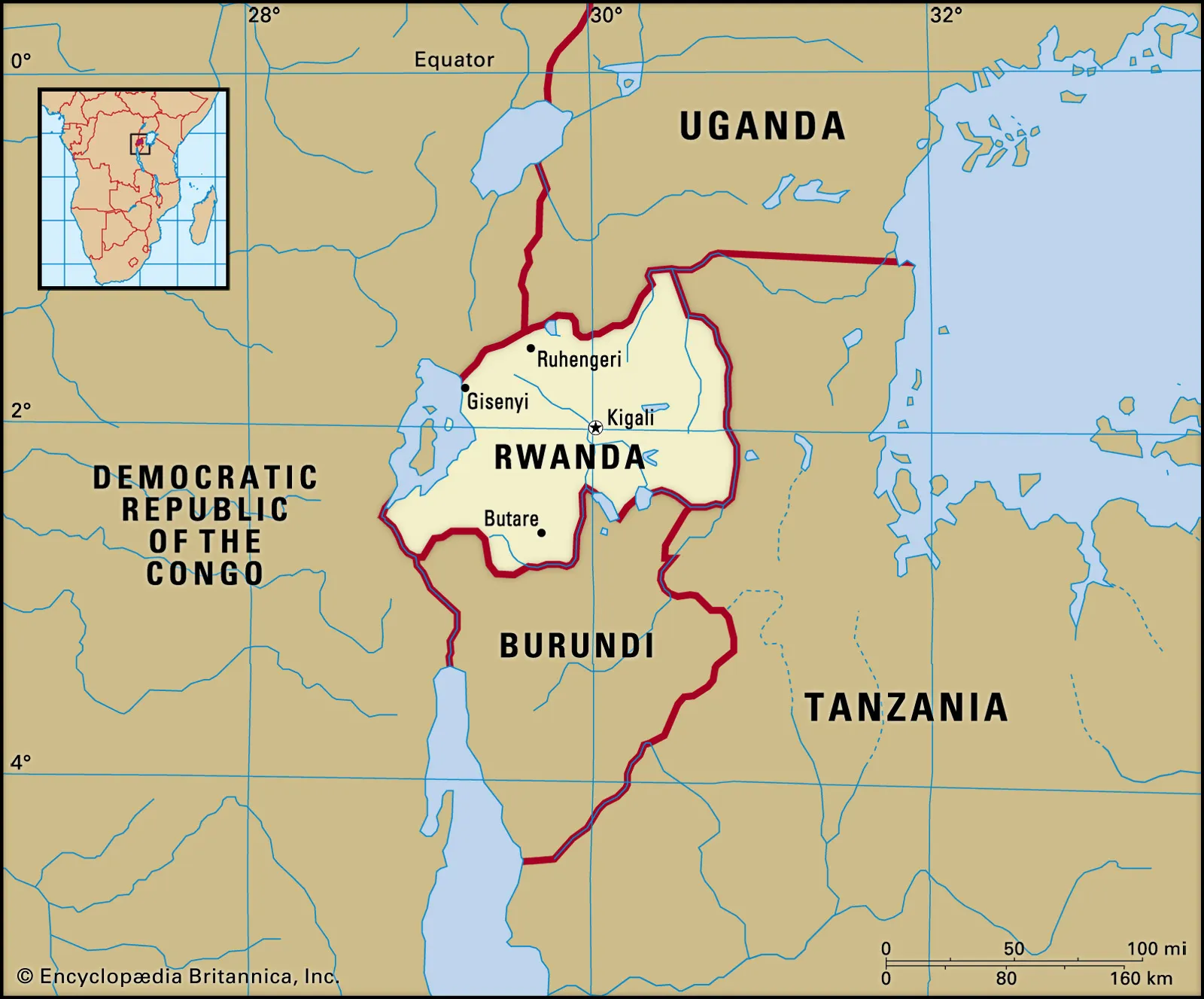
- Key Facts About Rwanda: It is a landlocked country in East-Central Africa, known as the "Land of a Thousand Hills." It shares borders with Burundi, Tanzania, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Kigali is the capital. The Nile and Congo rivers flow through Rwanda.
Read more: Marburg Virus