Facts for UPSC Mains
Mahavir Jayanti
- 10 Apr 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Prime Minister inaugurated Navkar Mahamantra Divas to mark Mahavir Jayanti (10th April 2025), emphasizing that Lord Mahavir’s teachings of non-violence, truth, and compassion offer contemporary solutions to global challenges and align with the vision of ‘Viksit Bharat’.
What is the Historical Background of Mahavir Jayanti?
- About: Mahavir Jayanti, also known as Mahaveer Janma Kalyanak, is one of the significant religious festivals in Jainism.
- It celebrates the birth of Vardhamana Mahavira, the 24th and last Tirthankara of Jain tradition (succeeded the 23rd Tirthankara Parshvanatha), who is considered a great spiritual teacher and reformer.
- Mahavir Jayanti is celebrated on the 13th day of Chaitra month in the Hindu calendar, the date varies annually.
- Vardhamana Mahavira:
What is the Contemporary Relevance of Teachings of Lord Mahavira?
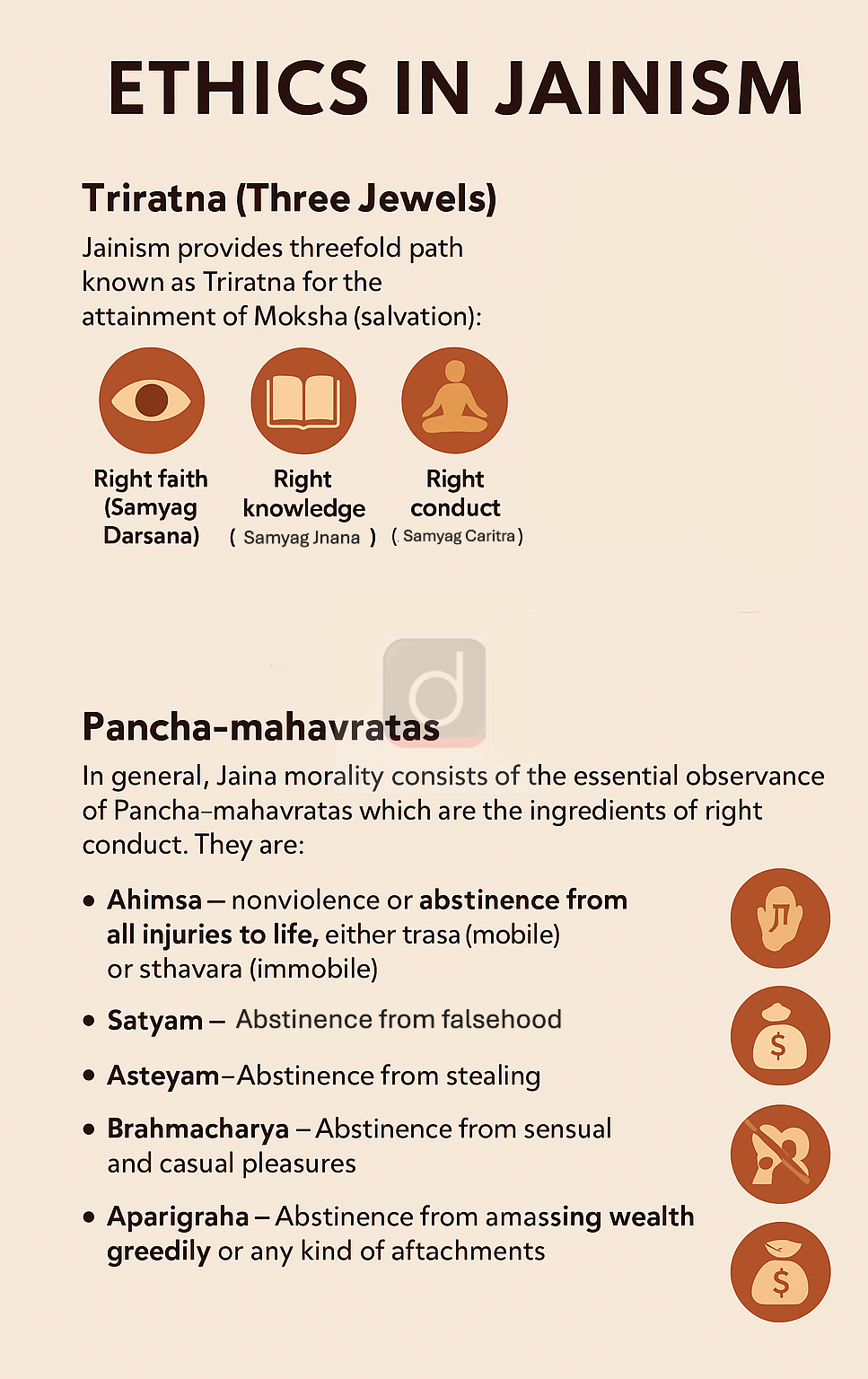
- Ahimsa (Nonviolence): Lord Mahavira’s teaching of Ahimsa advocates ending all forms of violence, including physical, verbal, and psychological, and promotes compassion towards all living beings.
- In today’s world, plagued by armed conflicts, terrorism, and nuclear threats, this principle calls for peaceful resolutions and compassionate dialogue.
- This principle is also echoed in the UN Charter, Gandhian ethics, and Sustainable Development Goal 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions), highlighting its global relevance and contemporary importance..
- Aparigraha (Non-possessiveness): Mahavira’s principle of detachment from material possessions encourages a sustainable lifestyle, fostering minimalism and curbing greed, values that align with Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) and and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) to address environmental degradation and climate change
- Anekantavada: It teaches that truth has many dimensions, promoting respect for diverse perspectives and helping reduce religious intolerance, racial discrimination, and societal divisions.
- It resonates with constitutional morality, freedom of thought and expression (Article 19), and secularism (Article 25) in the Indian Constitution.
- Satya (Truth) and Asteya (Non-stealing): Mahavira’s principles of honesty and respecting others' rights promote transparency and integrity in today’s world, combating corruption and unethical practices.
- These teachings guide the creation of ethical businesses that prioritize social responsibility.
- In business, Asteya promotes ethical sourcing, fair wages, and sustainability, aligning with fair trade principles and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) frameworks to combat exploitation in the global economy.
- Brahmacharya (Celibacy/ Self-restraint): Though interpreted in modern times as self-discipline, it helps address issues like substance addiction, mental health, and emotional instability.
What are the Key Facts About Jainism?Click here to Read: Jainism |
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the Contemporary Relevance of Teachings of Lord Mahavira. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to the religious practices in India, the “Sthanakvasi” sect belongs to (2018)
(a) Buddhism
(b) Jainism
(c) Vaishnavism
(d) Shaivism
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2017)
- Sautrantika and Sammitiya were the sects of Jainism.
- Sarvastivadin held that the constituents of phenomena were not wholly momentary, but existed forever in a latent form.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to the history of ancient India, which of the following was/were common to both Buddhism and Jainism? (2012)
- Avoidance of extremities of penance and enjoyment
- Indifference to the authority of the Vedas
- Denial of the efficacy of rituals
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Anekantavada is a core theory and philosophy of which one of the following? (2009)
(a) Buddhism
(b) Jainism
(c) Sikhism
(d) Vaishnavism
Ans: (b)