Mahanadi River | 18 Aug 2022
Why in News?
The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecast a heavy rainfall causing the flood situation in the Mahanadi River, Odisha.
- The low-pressure area is expected to form over the north Bay of Bengal and trigger heavy rainfall at a few places in Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
What is the India Meteorological Department (IMD)?
- IMD was established in 1875.
- It is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology.
What are the Key Points of Mahanadi River?
- About:
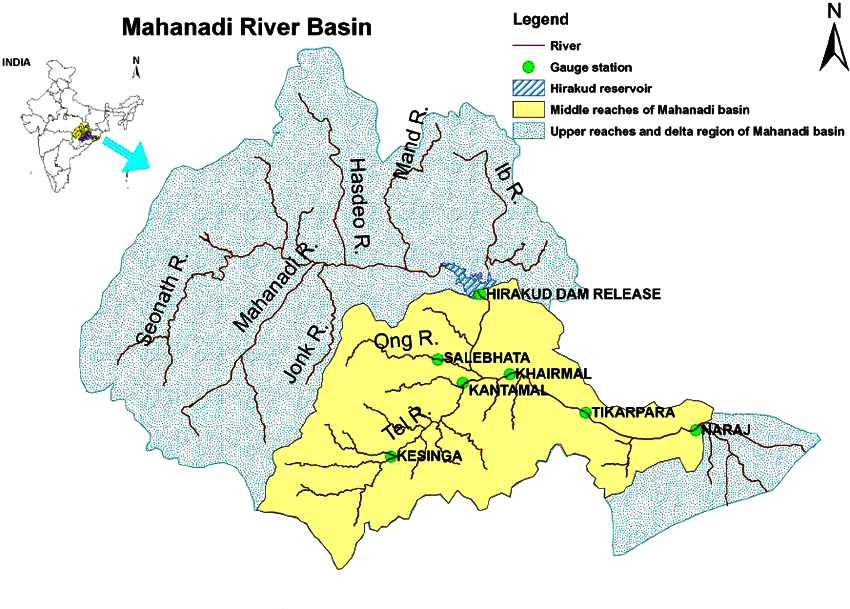
- The Mahanadi River system is the third largest of peninsular India after Godavari and Krishna, and the largest river of Odisha state.
- The catchment area of the river extends to Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Jharkhand and Maharashtra.
- Its basin is bounded by the Central India hills on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and east and by the Maikala range in the west.
- Source:
- It rises from a place near Sihawa, near Raipur in the state of Chhattisgarh to the south of Amarkantak.
- Major Tributaries:
- The Seonath, the Hasdeo, the Mand and the Ib joins Mahanadi from left whereas the Ong, the Tel and the Jonk joins it from right.
- Mahanadi River Dispute:
- The Central Government constituted Mahanadi Water Disputes Tribunal in 2018.
- Major Dams/Projects on Mahanadi:
- Hirakud Dam: This is the longest dam of India.
- Ravishankar Sagar, Dudhawa Reservoir, Sondur Reservoir, Hasdeo Bango and Tandula are other major projects.
- Urban Centres :
- Three important urban centres in the basin are Raipur, Durg and Cuttack.
- Industries:
- Mahanadi basin, because of its rich mineral resource and adequate power resource, has a favourable industrial climate.
- Iron and Steel plant at Bhilai
- Aluminium factories at Hirakud and Korba
- Paper mill near Cuttack
- Cement factory at Sundargarh.
- Other industries based primarily on agricultural produce are sugar and textile mills.
- Mining of coal, iron and manganese are other industrial activities.
- Mahanadi basin, because of its rich mineral resource and adequate power resource, has a favourable industrial climate.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following rivers: (2015)
- Vamsadhara
- lndravati
- Pranahita
- Pennar
Which of the above are tributaries of Godavari?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The Godavari River originates in Triambakeshwar, Maharashtra. It flows in the states of Maharashtra, Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, etc. It empties into the Bay of Bengal.
- Its left bank tributaries include Pranahita, Indravati (combined waters of Wainganga, Penganga, Wardha and Vainganga), Sabari etc., while its right bank tributaries include Pravara, Manjira, Maner, etc. Hence, 2 and 3 are correct.
- Vamsadhara river flows in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh and falls into the Bay of Bengal but it does not join the Godavari river. Hence, 1 is not correct.
- Pennar river flows in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh and falls into the Bay of Bengal. It also does not join the Godavari. Hence, 4 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. What do you understand by Run-of-river hydroelectricity project? How is it different from any other hydroelectricity project? (2013)
Q. The interlinking of rivers can provide viable solutions to the multi-dimensional inter-related problems of droughts, floods, and interrupted navigation. Critically examine. (2020)