Magnetars and Related AstroSat's Discovery | 27 Dec 2023
Why in News?
AstroSat, India’s first multi-wavelength space-based observatory, has detected bright sub-second X-ray bursts from a new and unique neutron star with an ultrahigh magnetic field (magnetar).
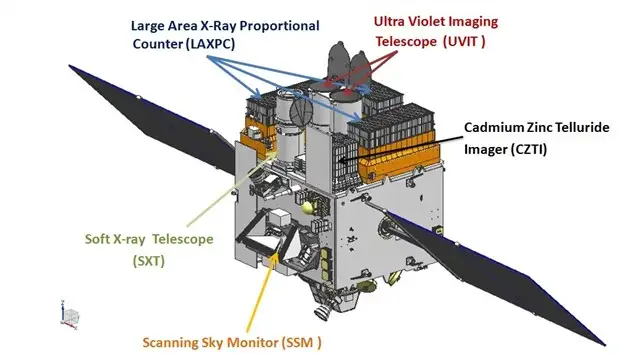
- Scientists performed the timing and spectral analysis of this magnetar using two instruments onboard AstroSat: the Large Area X-Ray Proportional Counter (LAXPC) and Soft X-Ray telescope (SXT).
What are Magnetars?
- Magnetars are neutron stars having an ultrahigh magnetic field that are much stronger than the terrestrial magnetic field (over one quadrillion times stronger than the magnetic field of Earth).
- High-energy electromagnetic radiation emitted by magnetars results from the decay of their powerful magnetic fields.
- They display strong temporal variability, typically including a slow rotation, a rapid spin-down, bright but short bursts going on up to months-long outbursts.
- One such magnetar, called SGR J1830-0645, was discovered in October 2020 by NASA's Swift spacecraft.
- It is relatively young (about 24,000 years) and an isolated neutron star.
Note
A neutron star is a dense and compact stellar object that forms from the remnants of a massive star's core after a supernova explosion. These stars are among the densest objects known in the universe, packing an immense mass into a relatively small size.
- The discovery of pulsars in 1967 provided the first evidence of the existence of neutron stars. Pulsars are neutron stars that emit pulses of radiation once per rotation
What is AstroSat?
- About: AstroSat is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- It was launched in September, 2015 onboard PSLV-C30 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- Mission operations center at ISTRAC Bengaluru manages the task of operating AstroSat.
- Payload:
- Major Scientific Observations of AstroSat:
- Spotted stars forming in gas streams, offering insights into how galaxy clusters behave.
- It found over 75,000 young stars in the Andromeda Galaxy's bulge, a first discovery.
- Black holes in a binary system were seen spinning almost as fast as possible by LAXPC and SXT payloads.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
(a) ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
(b) ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
(c) Possibility of intergalactic space travel through ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
(d) It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’
Ans: (b)