Local Bubbles | 14 Jan 2023
Why in News?
Recently, new research on a giant cosmic cavity that surrounds the solar system could reveal the universe’s secrets, including questions about the origins of stars.
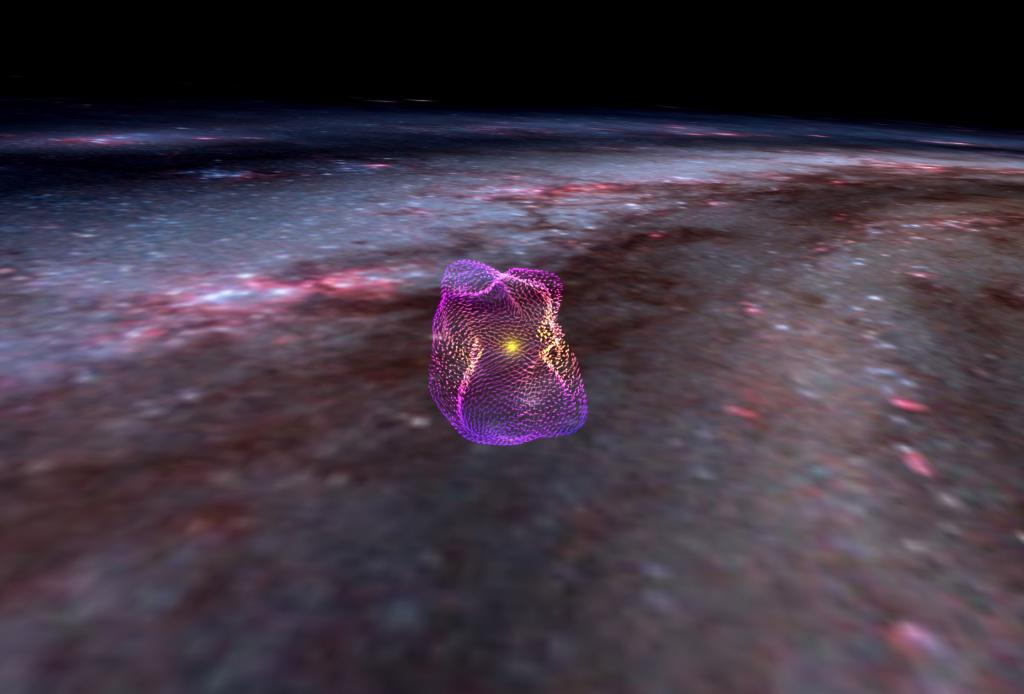
- Researchers from the Center for Astrophysics (CfA) | Harvard & Smithsonian have generated a 3D magnetic map of the cavity called Local Bubble.
What are Local Bubbles?
- The Local Bubble is a 1,000-light-year-wide cavity or a superbubble. Other superbubbles also exist in the Milky Way.
- The Local Bubble is a large, low-density region in the interstellar medium (ISM) of our galaxy, the Milky Way.
- The interstellar medium is the material which fills the space between the stars.
- It's a cavity that is thought to have been created by a series of supernovae explosions that occurred about 30 to 50 million years ago.
What is a Supernova?
- A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion that occurs at the end of the life of a massive star.
- It is caused by the collapse of the core of the star, which can trigger a massive release of energy.
- Supernovae are also important for the enrichment of the interstellar medium with heavy elements and for the propagation of cosmic rays.
- There are two main types of supernovae:
- Type I:
- It is a supernova caused by the thermonuclear explosion of a white dwarf star that is part of a binary system.
- The white dwarf accretes material from its companion star, and when its mass exceeds a certain limit, it becomes unstable and detonates.
- Type II:
- It is caused by the gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star.
- When a star has exhausted the nuclear fuel in its core, its outer layers collapse inward, and the core becomes incredibly hot and dense.
- This causes a huge release of energy, which causes the star to explode.
- The explosion is so powerful that it can outshine an entire galaxy for a brief period of time, and the explosion debris can cause the formation of nebulae, dust and heavy elements.
- Type I:
How 3D Map of a Gigantic Cavity of Local Bubbles Observed?
- They used Gaia and Planck space based observatories launched by the European Space Agency (ESA).
- Gaia was used to identify the location and local concentration of cosmic dust.
- This helped them trace the boundaries of the Local Bubble.
- Planck provided information on the magnetic alignment of cosmic dust.
- This alignment can indicate the orientation of the magnetic field acting on the dust particles, allowing the researchers to generate a 3D magnetic field orientation on the surface of the Local Bubble.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
(a) ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
(b) ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
(c) Possibility of inter-galactic space travel through ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
(d) It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’
Ans: (b)