Langya Virus | 13 Aug 2022
Why in News?
Amid the Covid-19 and Monkeypox cases around, the new zoonotic Langya Henipavirus has raised concerns.
- The first case of the Langya virus was reported in 2019. The Langya virus has been classified among Biosafety Level 4 (BSL4) Pathogens.
What are the Biosafety levels?
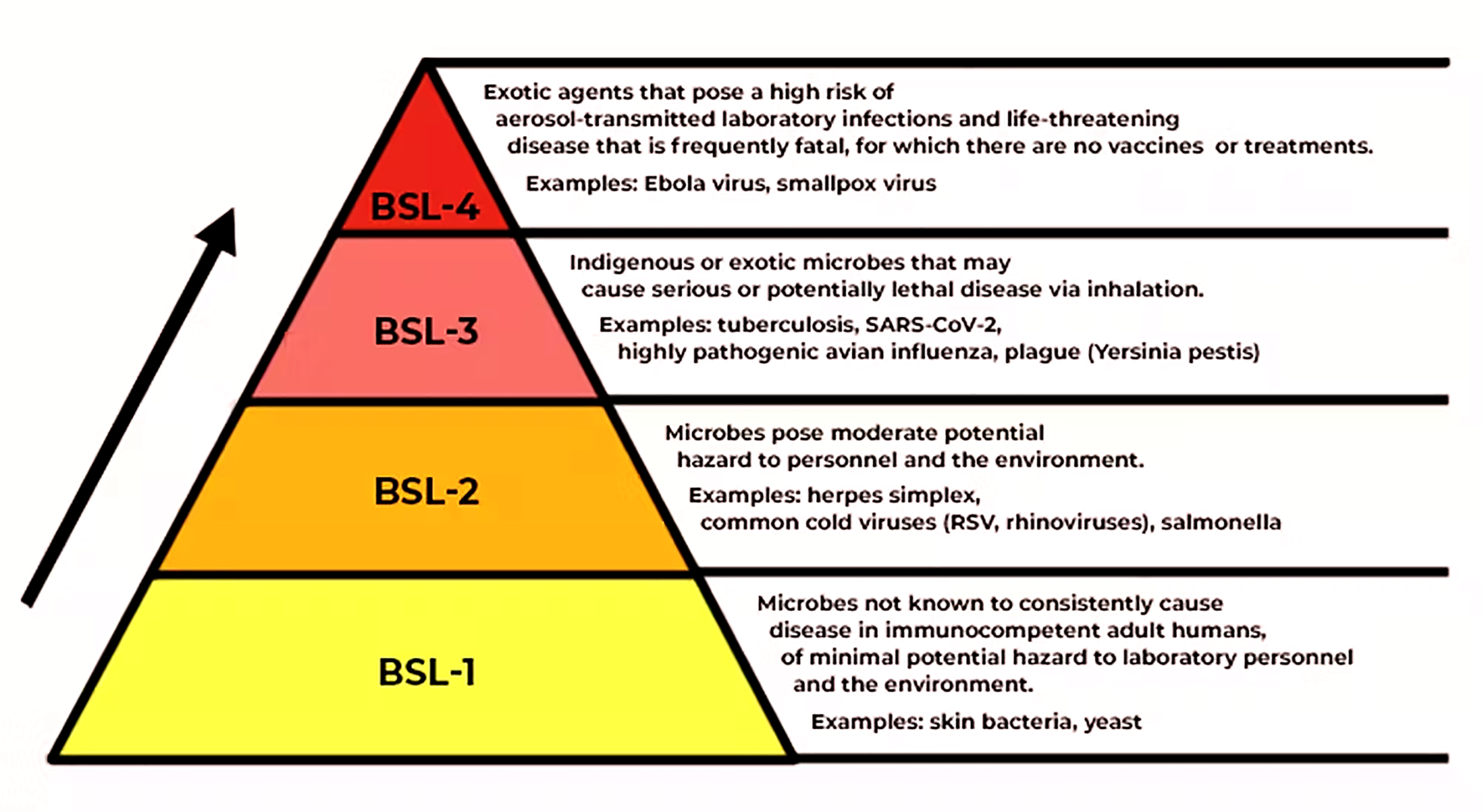
- BSL is used to identify the protective measures needed in a laboratory setting to protect workers, the environment, and the public.
- Activities and projects conducted in biological laboratories are categorized by biosafety level.
- The four biosafety levels are BSL-1, BSL-2, BSL-3, and BSL-4, with BSL-4 being the highest (maximum) level of containment.
What is Langya Virus?
- About:
- The Langya virus is a zoonotic virus which means it can be transmitted from animals to humans.
- Langya is part of the genus Henipavirus, which has a single-stranded RNA genome with a negative orientation.
- Unique features of henipaviruses Paramyxovirinae are their larger genomes, longer untranslated regions that are over 100 amino acids longer than any other known phosphoprotein in the family.
- It is an emerging cause of zoonosis in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Novel Langya Virus:
- The newly discovered Langya virus is a ‘phylogenetically distinct Henipavirus’.
- Other viruses of the type Henipavirus discovered earlier are the Mojiang, Ghanian, Cedar, Nipah, and Hendra.
- Of these, Nipah and Hendra are known to have caused fatal illnesses in humans.
- Langya’s genome organization is “identical to that of other Henipaviruses”, and that it is closely related to the “Mojiang Henipavirus, which was discovered in southern China.
- Symptoms:
- Fever, Fatigue, Cough, Nausea, Headache, Loss of appetite etc.
- Treatment:
- There are no licensed drugs or vaccines meant for humans.
How Impactful is Langya Virus?
- The Langya virus may potentially be fatal to humans in case of severe infections.
- Langya belongs to the same family of viruses as the deadly Nipah virus that is typically found in bats.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements:
- Adenoviruses have single-stranded DNA genomes whereas retroviruses have double-stranded DNA genomes.
- Common cold is sometimes caused by an adenovirus whereas AIDS is caused by a retrovirus.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Viruses that infect human hosts can be categorized as adenoviruses and retroviruses
- Adenovirus is a type of virus that has no envelope whereas retroviruses are characterized as enveloped viruses. Adenoviruses have double-stranded linear DNA and are associated with two major core proteins. A retrovirus is a virus that uses RNA as its genetic material. When a retrovirus infects a cell, it makes a DNA copy of its genome that is inserted into the DNA of the host cell. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Adenoviruses are common viruses that cause a range of illnesses. They can cause cold-like symptoms, fever, sore throat, bronchitis, pneumonia, diarrhoea, and pink eye (conjunctivitis). Whereas, retroviruses can cause several human diseases such as some forms of cancer and AIDS. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q. Among the following, which were frequently mentioned in the news for the outbreak of Ebola virus recently? (2015)
(a) Syria and Jordan
(b) Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia
(c) Philippines and Papua New Guinea
(d) Jamaica, Haiti and Surinam
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Ebola virus disease is a severe fatal illness in humans and non-human primates. The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission.
- The fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family are natural Ebola virus hosts.
- The Ebola virus is transmitted among humans through close and direct physical contact with infected bodily fluids, the most infectious being blood, faeces and vomit. The virus has also been detected in breast milk, urine and semen.
- Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia were in the news for the outbreak of Ebola virus. The most widespread outbreak of Ebola virus disease began in 2013 and continued until 2016, causing major loss of life and socio-economic disruption in the West African region, mainly in the countries of Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.
- The first cases were recorded in Guinea in December 2013. Later, the disease spread to neighbouring Liberia and Sierra Leone.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.