Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) | 08 Oct 2022
For Prelims: Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Chabahar Port, International North-South Transit Corridor (INSTC), Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
For Mains: Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India's Interests, JCPOA and its Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, the US imposed sanctions against a Mumbai based petrochemical company, Tibalaji Petrochem Pvt Ltd. as it was accused of selling Iranian petroleum products.
- It is the first Indian entity to face the US designation under unilateral sanctions passed in 2018-19, after the US walked out of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
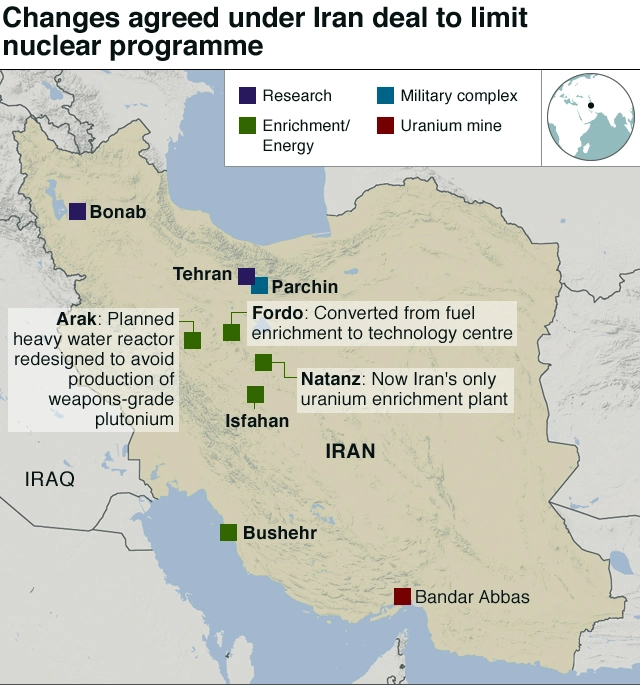
What was the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)?
- The deal is also known as 2015 Iran Nuclear Deal.
- The JCPOA was the result of prolonged negotiations from 2013 and 2015 between Iran and P5+1 (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, the United States + Germany).
- Under the deal, Iran agreed to significantly cut its stores of centrifuges, enriched uranium and heavy-water, all key components for nuclear weapons.
- Iran also agreed to implement a protocol that would allow inspectors from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to access its nuclear sites to ensure Iran would not be able to develop nuclear weapons in secret.
- While the West agreed to lift sanctions related to Iran’s nuclear proliferation, other sanctions addressing alleged abuses of human rights and Iran’s ballistic missile programme remained in place.
- The US committed to lifting sanctions on oil exports, but continued to restrict financial transactions, which have deterred international trade with Iran.
- Nonetheless, Iran’s economy, after suffering years of recessions, currency depreciation, and inflation, stabilized significantly after the deal took effect, and its exports skyrocketed.
- After US abandoned the deal in 2018 and reinstated banking and oil sanctions, Iran ramped up its nuclear programme in earnest, returning to approximately 97% of its pre-2015 nuclear capabilities.
What Happened After the US Pulled Out of the Deal?
- In April 2020, the US announced its intention to snap back sanctions. However, the other partners objected to the move, stating that since the US was no longer part of the deal, it could not unilaterally reimpose sanctions.
- Initially following the withdrawal, several countries continued to import Iranian oil under waivers granted by the Trump administration. A year later, the US ended the waivers to much international criticism and, by doing so, significantly curbed Iran’s oil exports.
- The other powers, in an attempt to keep the deal alive, launched a barter system known as Instrument in Support of Trade Excahanges (INSTEX) to facilitate transactions with Iran outside the US banking system. However, INSTEX only covered food and medicine, which were already exempt from US sanctions.
- In January 2020, after the US assassinated the top Iranian general Qasem Soleimani, Iran announced that it would no longer limit its uranium enrichment.
- In September 2022, Iran and International Atomic Energy Agency officials held a round of talks to discuss the possibility of Iran’s agreement to reallow inspectors back to Iran for oversight over reactors.
- The U.S. and Iran have also exchanged their stands indirectly via the European Union for a “final draft” on rejoining the JCPOA.
What is the significance of JCPOA for India?
- Enhance Regional Connectivity:
- Removing sanctions may revive India’s interest in the Chabahar port, Bandar Abbas port, and other plans for regional connectivity.
- This would further help India to neutralize the Chinese presence in Gwadar port, Pakistan.
- Apart from Chabahar, India’s interest in the International North-South Transit Corridor (INSTC), which runs through Iran, and will improve connectivity with five Central Asian republics, may also get a boost.
- Energy Security:
- Due to the pressure linked to the US Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA), India has to bring down oil imports to zero.
- Restoration of ties between the US and Iran will help India to procure cheap Iranian oil and aid in energy security.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(b) Saudi Arabia
(c) Oman
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is an alliance of 6 countries in the Arabian Peninsula – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Iran is not a member of the GCC.
- It was established in 1981 to promote economic, security, cultural and social cooperation between the members and holds a summit every year to discuss cooperation and regional affairs. Therefore, option A is the correct answer.