Important Facts For Prelims
ISRO Tests Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell
- 11 Jan 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully tested a 100 W class Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) based Power System aboard the orbital platform, POEM3.
What are the Major Takaways from the Recent PEMFC Test?
- Technology Tested: ISRO tested a 100-watt class PEMFC, which converts hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, water, and heat. This technology offers several advantages over traditional power sources in space, including:
- High Efficiency: PEMFCs convert fuel directly into electricity, resulting in significantly higher efficiency compared to batteries.
- Clean Operation: PEMFCs produce only water as a byproduct, eliminating the need for complex waste management systems.
- The water produced by the PEMFC can be used for onboard consumption or for electrolysis to generate additional oxygen.
- Test Platform: The PEMFC was tested In orbital platform, POEM3, launched aboard PSLV-C58 on 1st January, 2024.
- POEM3 serves as a platform for testing new technologies in space under real-world conditions.
- Implications for Future Missions: The successful test of the PEMFC paves the way for several exciting possibilities for future space missions:
- Powering the Indian Space Station: The high efficiency and water production capabilities of PEMFCs make them ideal for powering the proposed Indian space station.
- Deep Space Exploration: PEMFCs can provide a reliable and sustainable source of power for long-duration missions to deep space destinations like Mars.
Note
ISRO also noted that it has qualified 10 Ah Silicon–Graphite anode based high energy density Li-ion cells as a low weight and low cost alternative to present cells being used.
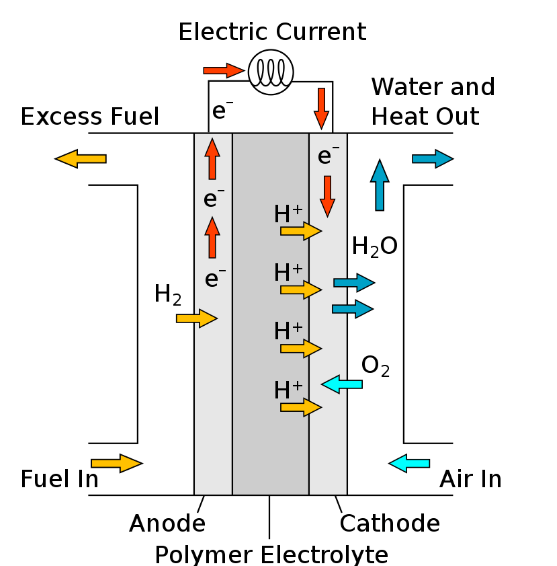
What is a Fuel Cell?
- About: A fuel cell is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (like hydrogen) and an oxidant (like oxygen) directly into electricity.
- Unlike batteries, which store chemical energy that gets converted to electrical energy, fuel cells continuously produce electricity as long as they are supplied with fuel and oxidant.
- Major Types of Fuel Cells:
- Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: They use a thin, solid polymer membrane as the electrolyte and are well-suited for portable applications.
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs): SOFCs use a ceramic electrolyte that can operate at high temperatures. They are highly efficient but are more expensive and complex than PEMFCs.
- Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFCs): AFCs use a liquid electrolyte made of potassium hydroxide (KOH). They are less efficient than PEMFCs and SOFCs but are less expensive and can be more tolerant of impurities in the fuel.
- Applications of Fuel Cells:
- Transportation: Fuel cells can be used to power electric vehicles, boats, and even airplanes.
- Fuel cells can also power space missions, providing electrical power for spacecraft, and a dependable energy source for long-duration missions.
- Highly efficient with zero emissions, making them ideal for space missions
- Portable Power: Fuel cells can be used to power laptop computers, cell phones, and other portable devices.
- Stationary Power: Fuel cells can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities.
- Transportation: Fuel cells can be used to power electric vehicles, boats, and even airplanes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce one of the following as “exhaust” (2010)
(a) NH3
(b) CH4
(c) H2O
(d) H2O2
Ans: (c)