International Relations
Iran-Israel Conflict
- 30 Apr 2024
- 15 min read
For Prelims: Iran, Israel, Middle East,1979 Islamic Revolution, Stuxnet, Gaza Strip, Red Sea Crisis, Israeli air defence system, OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries), Two State Solution, Gulf Cooperation Council, European Union, United Nations, Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
For Mains: Historical Background of Relations Between Iran and Israel, Key Events that Led to Iran’s Attack on Israel, Impact of Iran- Israel Conflict on India and World
Why in News?
The conflict between Israel and Iran has created a situation of turmoil affecting the security of the large Indian diaspora based in the Gulf region.
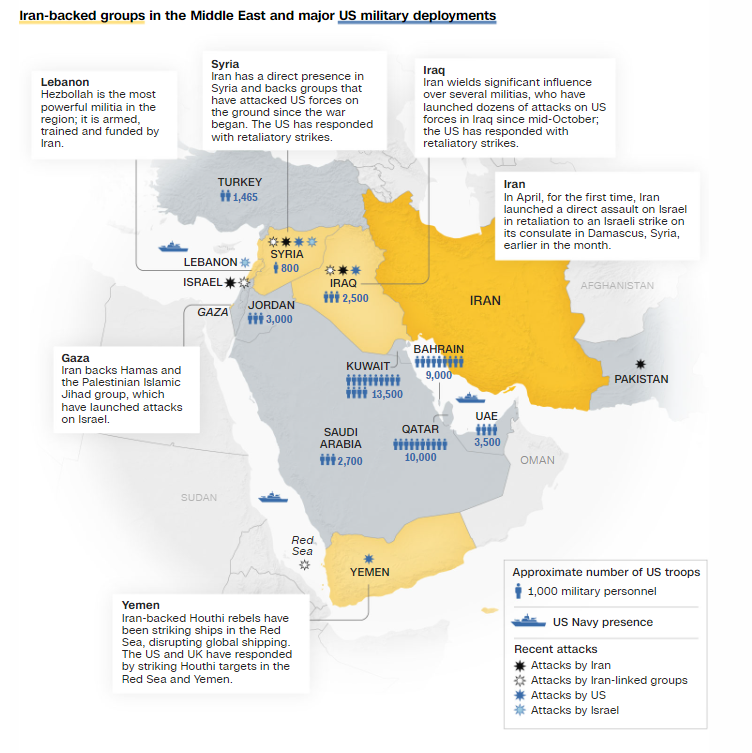
- Iran has launched significant attacks on Israel, deploying over 300 projectiles, including drones, cruise missiles, and ballistic missiles. This action was widely seen as retaliation for a deadly strike on Iran's consulate in Damascus, Syria.
- This has created the additional risk of piracy and hostage-taking in the Gulf region.
What are the Reasons for the Iran-Israel Conflict?
- Historical Context: Iran and Israel have had a tumultuous relationship since the Iranian Revolution of 1979, which transformed Iran from a close ally of Israel under the rule of the Shah to an Islamic Republic openly hostile towards Israel.
- Religious and Ideological Differences: Iran is an Islamic republic governed by Shia Islam, while Israel is a predominantly Jewish state.
- The religious and ideological differences between the two countries have contributed to mutual suspicion and animosity.
- Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: Iran has been a staunch supporter of Palestinian causes, including backing militant groups like Hamas and Hezbollah, which are considered terrorist organisations by Israel.
- Iran's support for these groups and its calls for the destruction of Israel have heightened tensions.
- Geopolitical Rivalry: Iran and Israel are regional rivals vying for influence in the Middle East. They have conflicting interests in various regional conflicts, including the civil wars in Syria and Yemen.
- Where Iran supports the Assad regime and Houthi rebels, respectively, while Israel opposes Iranian influence in these countries.
- Nuclear Program: Israel views Iran's nuclear program with great concern, fearing that Iran may develop nuclear weapons that could pose an existential threat to Israel's security.
- Israel has been a vocal critic of the Iran nuclear deal (Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action) and has taken measures, including covert operations, to disrupt Iran's nuclear activities.
- Proxy Conflicts: Iran and Israel have engaged in proxy conflicts through their support for opposing factions in neighbouring countries.
- Regional Power Dynamics: The balance of power in the Middle East is shaped by the competition between Iran and its allies on one side and Israel and its allies on the other.
- This competition has contributed to a cycle of tensions and conflicts in the region.
What are the Recent Events that have Given the Israel-Iran Rivalry a New Dimension?
- Withdrawal from Iran’s Nuclear Deal: In 2018, Israel praised the US decision to withdraw from the Iran nuclear deal Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), which it had lobbied against for years, considering it a significant move.
- Assassination of Iran’s Army General: In 2020, Israel supported the US drone strike in Baghdad that killed General Qassem Soleimani, a top Iranian military commander, prompting retaliatory missile attacks from Iran on Iraqi bases housing American troops.
- Hamas Missile Attack: In October 2023, Hamas, an Iran-backed group, launched a missile attack on Israel, prompting Israeli airstrikes on Gaza in response to perceived threats from Hamas operating in civilian areas.
- Houthi Group’s Red Sea Incident: Since November 2023, the Iran-backed Houthi group from Yemen has targeted several ships related to Israel and its allies in the Red Sea, triggering the 'Red Sea Crisis' and causing disruptions to supply chains.
- Airstrike on the Iranian Embassy and Iran’s Retaliation: Suspected Israeli airstrikes targeted the Iranian embassy compound in Syria, resulting in casualties and in retaliation Iran launched a missile attack on Israel in April 2024, marking a significant escalation in direct hostilities between the two nations.
What are the Implications of the Iran-Israel Conflict on India?
- Economic Implications:
- Conflict between Israel and oil-rich Iran could disrupt oil supply from the region, leading to a rise in oil prices globally.
- India imports around 2 million barrels of crude oil daily through the strategic Strait of Hormuz located at the mouth of the Persian Gulf. Any conflict or instability in the region would lead to supply shortages and increasing energy costs leading to inflation and constraining Economic Growth in India.
- Diaspora: Large Indian diaspora in West Asia, and particularly the Persian Gulf might be affected due to the tension in the region.
- Their safety will have to be a priority. India has in the past organised big evacuations- famously from Kuwait at the time of the first Gulf War, and more recently from Libya and Ukraine.
- Connectivity: The strategic connectivity interests of India might be affected. This includes the port of Chabahar in Iran, linking India to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- Shipping disruption in the Red Sea would affect the trade in the region.
- A disturbance here could lead to delays, increased shipping costs, and instability in global trade.
- Diplomatic Challenges for India:
- Over the decade, India has had good relations with Israel and has leveraged Israeli expertise in defence, technology and start-ups.
- The problem is that if the war effort intensifies, then India may have to take sides. That will not be a very comfortable situation to have. Of course, India can always take the middle path or the neutral stance, but that does not yield dividends any longer.
Efforts Taken to bring Peace between Israel and Its Neighbours
- Oslo Accords: The Oslo Accords in 1993, facilitated by the US, were a significant milestone in Israeli-Palestinian peace efforts, although the peace process has since stalled.
- Abraham Accord: The Abraham Accord was signed in 2020 between Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain and was mediated by the US.
- I2U2: I2U2 stands for India, Israel, USA and the UAE. It was formed in October 2021 following the Abraham Accords between Israel and the UAE, to deal with issues concerning maritime security, infrastructure and transport in the region.
- United Nations: The United Nations has been actively involved in efforts to resolve the Israel-Palestine conflict through its various agencies, including the UN Security Council and the UN General Assembly.
- The UN has repeatedly called for a two-state solution based on the pre-1967 borders, with East Jerusalem as the capital of Palestine.
- Arab Peace Initiative: Arab states have also played a role in peace efforts, particularly through the Arab Peace Initiative.
- This initiative, first proposed by Saudi Arabia in 2002 and later endorsed by the Arab League, offers Israel normalised relations with Arab states in exchange for a full withdrawal from the occupied territories and a just resolution to the Palestinian refugee issue.
- India's Role:
- Diplomatic Relation: India has historically maintained diplomatic relations with both Israel and various Arab states including Palestine.
- Two-State Solution: India has consistently advocated for a two-state solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, which envisions the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, based on the pre-1967 borders with East Jerusalem as the capital of Palestine.
- India's support for this solution aligns with the consensus view of many global leaders and organisations.
- India has participated in multilateral forums addressing Middle East issues, such as the United Nations General Assembly and the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM).
- Within these forums, India has voiced its support for peaceful resolution of conflicts in the region, including the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, and has called for dialogue and negotiations to achieve lasting peace.
- Humanitarian Assistance: India has provided humanitarian assistance to Palestinians through various channels, including contributions to UN agencies and support for development projects in Palestinian territories.
- This assistance aims to alleviate the humanitarian suffering of Palestinians and contribute to stability in the region.
Way Forward
- Sustainable Ceasefire and Two-State Solution:
- Israel should accept a sustainable ceasefire in Gaza as soon as possible, open the borders for international humanitarian aid to Gaza, and respect the UN resolutions to end the 70-year-old crisis by realising a two-state solution.
- The two-state solution is the only feasible way ahead for long-term security, peace and stability in the region.
- The solution would establish an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel- two states for two peoples.
- In theory, this would win Israel’s security and allow it to retain a Jewish demographic majority while granting the Palestinians a state.
- Dialogue and Diplomacy:
- Encouraging both countries to engage in direct talks facilitated by international mediators could help build trust and find common ground.
- Iran and Israel could engage in direct talks facilitated by a neutral third party, such as the European Union or the United Nations.
- Addressing Nuclear Proliferation Concerns:
- Iran could adhere to the terms of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) and allow international inspections of its nuclear facilities to ensure compliance with the agreement.
- In return, Israel could recognise Iran's right to peaceful nuclear energy and commit to refraining from military strikes against Iranian nuclear facilities.
- Regional Cooperation:
- Promoting cooperation between Iran and Israel within the framework of regional organizations, such as the Arab League or the Gulf Cooperation Council, could help address shared security concerns and foster stability in the Middle East.
- Long-Term Vision for the Middle East:
- Regional powers could work together to establish a comprehensive security architecture for the Middle East, including confidence-building measures, arms control agreements, and mechanisms for resolving conflicts peacefully.
- Addressing underlying issues, such as historical grievances, territorial disputes, and religious extremism, can help create an environment conducive to peace and reconciliation.
- Normalisation of Relations:
- Iran and Israel could take steps towards normalising diplomatic relations, such as exchanging ambassadors, reopening embassies, and facilitating people-to-people exchanges, similar to the peace agreements between Israel and some Arab states like the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What is India’s stake in the Iran-Israel conflict? Discuss why India does not want to escalate the tensions. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q 1. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Q. The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2018)
(a) China
(b) Israel
(c) Iraq
(d) Yemen
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q . “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)