Biodiversity & Environment
International Day of Forests 2025
- 22 Mar 2025
- 11 min read
For Prelims: International Day of Forests, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Carbon Sequestration, National Afforestation Programme, Environment Protection Act of 1986, Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
For Mains: Significance of Forests for India, Issues Associated with Forests in India.
Why in News?
The International Day of Forests, also known as World Forests Day (WFD), is celebrated each year on 21st March to raise awareness about the importance of forests and trees for the survival of humanity and the planet.
- The theme for 2025 WFD is "Forests and Food".
International Day of Forests
- The International Day of Forests evolved from the "World Forestry Day" established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 1971.
- It was formally recognized by the United Nations General Assembly in 2012.
- It aims to raise awareness about forest conservation and sustainable management.
Note
- Definition of Forest in India: In T.N. Godavarman Thirumulpad vs the Union of India 1996 Case, the Supreme Court interpreted that the word “forest” must be understood according to its “dictionary meaning”.
- This description covers all statutorily recognised forests, whether designated as reserved, protected or otherwise.
What is the Significance of Forests?
- Ecological Significance:
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests absorb ~30% of global CO₂ emissions (from fossil fuel) annually (FAO, 2020) and store 861 gigatonnes of carbon, making them crucial for climate change mitigation.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Forests host 80% of terrestrial biodiversity (UNEP, 2021).
- India’s forests and tree cover (25.17% of total area, ISFR 2023) shelter species like tigers (3,167, NTCA 2022) and Asian elephants (~30,000, MoEFCC 2023).
- Water Security: Forests regulate hydrological cycles, recharge groundwater, and mitigate floods.
- Over 85% of major cities rely on forested watersheds for freshwater. In crises, forests provide up to 20% of rural family income and ensure food security.
- The Western Ghats in India sustain rivers that supply water to 245 million people.
- Economic and Livelihood Value:
- Global Dependence: 1.6 billion people (including 70 million indigenous communities) rely on forests for food, fuel, and medicine (World Bank, 2022).
- Employment: Over 30 million people in India depend on forestry activities for their livelihood, with MGNREGA supporting afforestation projects and rural livelihoods.
- Livestock Support: Forests sustain 30-40 million pastoralists and provide fodder for 4 billion livestock. Trees enhance rangelands by offering shade and protection, improving livestock productivity.
- Cultural Significance: Forests are culturally revered for regeneration, health, and longevity.
- India has 100,000+ sacred groves (e.g., Kavus in Kerala, Law Lyngdoh in Meghalaya), preserving biodiversity and rare flora like Myristica malabarica (Karnataka).
- Genetic Diversity: Forests safeguard wild relatives of crops (e.g., wild rice in Assam), essential for breeding climate-resilient varieties.
What is the Status of Forests in India?
- As per the India State of Forest Report (ISFR)-2023, forest and tree cover is 25.17% of its geographical area (GA), with forest cover at 21.76% and tree cover at 3.41%.
- The country's forest and tree cover has increased by 1,445.81 km² compared to 2021.
- The report said 19 states/UTs have above 33% of the geographical area under forest cover.
- India's forest carbon stock is estimated at 7,285.5 million tonnes, with an increase of 81.5 million tonnes compared to 2021.
- India's mangrove cover is 4,991.68 km² (0.15% of GA), with a 7.43 km² decline since 2021.
- Largest Forest Cover (Area wise): Madhya Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh.
- Highest % of Forest Cover: Lakshadweep (91.33%), Mizoram (85.34%), Andaman & Nicobar (81.62%).
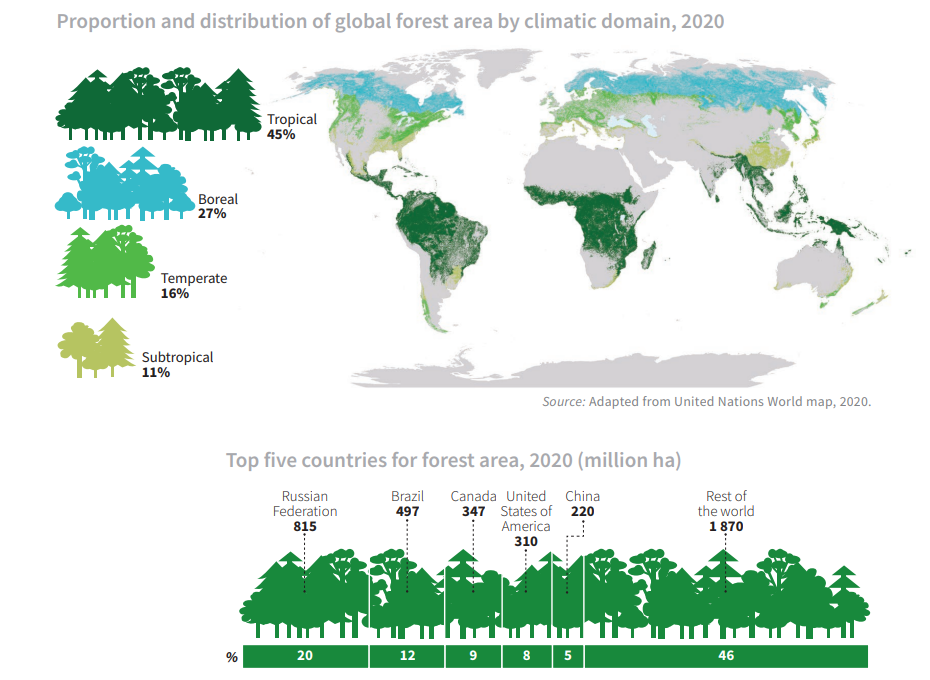
Global Forest Area (FAO 2020)
What are the Initiatives for Forest Conservation?
Global Initiatives
- REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation): A UNFCCC initiative incentivizing developing countries to reduce deforestation and enhance forest carbon stocks.
- The Bonn Challenge (2011): Launched by Germany and IUCN, aims to restore 150 million hectares by 2020 and 350 million hectares by 2030.
- New York Declaration on Forests (2014): A non-binding commitment to halve deforestation by 2020 and end it by 2030.
- The Paris Agreement (Art. 5): It urges conservation and enhancement of GHG sinks and reservoirs, including forests to combat climate change.
- FAO’s Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA): Provides comprehensive data on forest resources, trends, and conservation efforts globally.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): CBD is a key international agreement for forest conservation, aiming to conserve biodiversity, sustainably use its components, and share benefits from genetic resources.
India’s Initiatives
- Forest Conservation Act, 1980
- National Afforestation Programme
- Environment Protection Act of 1986
- Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA): Uses funds from diverted forest land projects for afforestation.
- Green India Mission (GIM): It is part of the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), launched in 2015-16 with the focus on biodiversity, water resources, and carbon sequestration.
- It aims to expand and improve 10 mha of forest/tree cover and boost livelihoods for 3 million households through forest-based income.
- Sub-Missions: Enhancing Forest Cover, Urban Greening and Agro-Forestry & Social Forestry.
- National Agroforestry Policy: It was launched in 2014 to promote agroforestry for climate resilience, environmental conservation, and economic benefits.
- It focuses on Quality Planting Material (QPM) through nurseries and tissue culture.
- ICAR-Central Agroforestry Research Institute (CAFRI) is the nodal agency, with support from state agricultural universities.
- Forest Fire Prevention & Management Scheme: It is a centrally sponsored scheme that supports states and UTs in preventing and controlling forest fires.
- National Action Plan on Forest Fire (2018) developed with World Bank, NDMA, and State Forest Departments.
- Forest Survey of India (FSI) uses remote sensing, GPS, GIS, and a satellite-based monitoring system for real-time fire alerts.
- PM Van Dhan Yojana (PMVDY): Enhance tribal livelihoods by adding value to Minor Forest Produce (MFPs) through skill training, infrastructure, and market linkages.
- Van Dhan Vikas Kendras (VDVKs): 300 members from 15 SHGs per Kendra for processing and marketing MFPs.
What are the Challenges in Forest Conservation?Click here to Read: Challenges in Forest Conservation What Measures can be Adopted to Enhance Forest Conservation in India?Click here to Read: Measures to Enhance Forest Conservation |
Conclusion
India's forest conservation efforts, through initiatives like the Green India Mission, Van Dhan Yojana, and Forest Fire Management, promote ecosystem restoration, climate resilience, and livelihood enhancement. On International Day of Forests 2025, reaffirming commitment to sustainable policies and community-driven conservation is vital for a greener and prosperous future.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the challenges of forest conservation in India and propose strategies for sustainable management in the context of climate change and development. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006? (2021)
(a) Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
(b) Ministry of Panchayati Raj
(c) Ministry of Rural Development
(d) Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Ans: (d)
Q2. A particular State in India has the following characteristics: (2012)
- It is located on the same latitude which passes through northern Rajasthan.
- It has over 80% of its area under forest cover.
- Over 12% of forest cover constitutes the Protected Area Network in this State.
Which one among the following States has all the above characteristics?
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Assam
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) Uttarakhand
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. “The most significant achievement of modern law in India is the constitutionalization of environmental problems by the Supreme Court.” Discuss this statement with the help of relevant case laws. (2022)