International Relations
Insurgency in Balochistan
- 01 Apr 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Baloch Militancy, Liberation of Bangladesh, Taliban, Iran, Pakistan, Sunni Militant group, Jaish al-Adl, Terrorism.
For Mains: Reasons for Unrest in Balochistan, India’s Stand on Balochistan Issue, Impact on India of Balochistan Unrest, Pakistan and the Baloch Militancy, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Balochistan province of Pakistan is witnessing a resurgence of insurgency and unrest. The recent train hijacking by Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA) militants, demanding the release of their comrades, highlights the deteriorating security situation in the region.
Balochistan and History of Insurgency
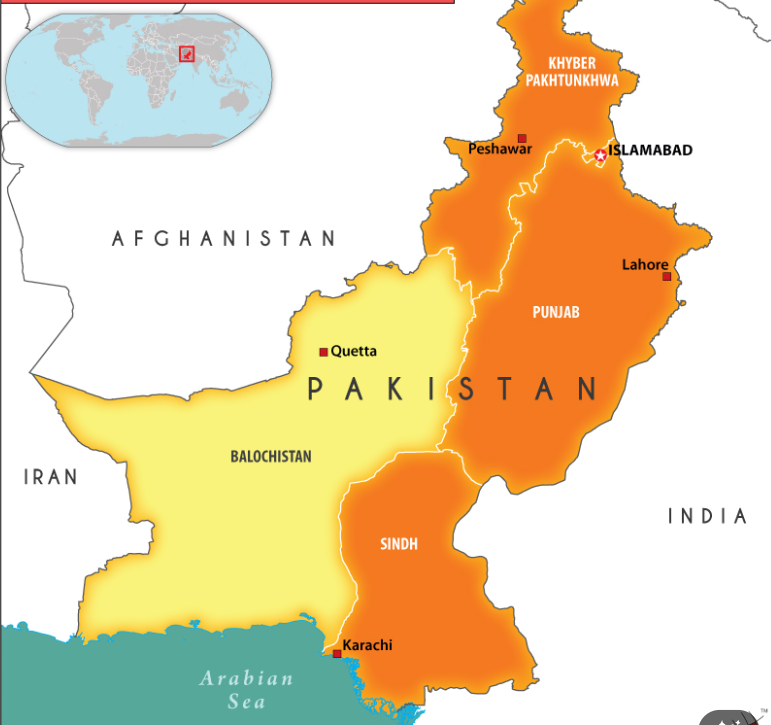
- Geography: Balochistan is Pakistan's southwestern province that borders Afghanistan, Iran, Punjab and Sindh (provinces of Pakistan), and the Arabian Sea.
- Demography: It covers 44% of the country's total land area but is home to only 5% of its population, predominantly inhabited by the Baloch, a Sunni Muslim ethnic group, who also have significant communities in Iran and Afghanistan.
- It is the largest and least populated province, rich in natural resources such as natural gas, coal, gold, and copper, but remains highly impoverished, with 70% of its population classified as multidimensionally poor.
- History of Insurgency: At the time of Partition of India (1947), Balochistan comprised 4 princely states: Kharan, Makaran, Las Bela, and Kalat, with Kalat opting for independence while the others joined Pakistan.
- Though Jinnah initially accepted Kalat’s sovereignty, British pressure led to its forced annexation in 1948 after isolating it strategically. Allegations of the Khan’s intent to join India further accelerated Pakistan’s actions.
- Resistance to Pakistani rule intensified over the years. The first major rebellion broke out in 1954 following Pakistan’s One-Unit policy, which merged Balochistan with West Pakistan in 1955, deepening resentment.
- In 1958, Khan of Kalat, Nawab Nauroz Khan, declared independence but was tricked into surrendering and imprisoned.
- A third rebellion in 1963 sought the withdrawal of Pakistani troops and recognition of Balochistan as a province (materialised in 1970).
- Inspired by Bangladesh’s 1971 independence, Baloch leaders demanded autonomy, but the Pakistan President dismissed the Balochistan government in 1973, triggering a 4-year insurgency.
- The fifth wave of conflict began in the mid-2000s, triggered by alleged military excesses. The insurgency continues, fueled by grievances over resource exploitation and political marginalization, with no resolution in sight.
- Amnesty International reports that over 10,000 Baloch have disappeared in Pakistan since 2011.
What are the Reasons for Conflict in Balochistan?
- Historical Grievances: Balochistan’s forced annexation by Pakistan in 1948 and the dismissal of its provincial government in 1973 deepened its alienation.
- The region lacks effective grievance redressal mechanisms, with Punjabi elites dominating bureaucracy and sidelining Baloch representation.
- Economic Exploitation: Despite abundant natural resources like gas, gold, and iron, Balochistan remains impoverished, with locals confined to low-skilled jobs due to poor education and infrastructure. It has Pakistan’s lowest literacy rate and worst Gender Parity Index (GPI).
- The Baloch nationalists view Chinese investments such as Gwadar Port and CPEC as benefiting Pakistan’s elite while marginalizing locals, fearing demographic changes and further exploitation.
- Human Rights Violations & Militarization: Enforced disappearances, extra-judicial killings, and fake encounters are frequently used as counter-insurgency tactics.
- The Commission of Inquiry on Enforced Disappearances constituted by Pakistan in 2011 recorded 2,752 cases, while civil society groups claim over 7,000 disappearances (2002–2024).
- Religious Extremism: Balochistan faces militant recruitment by groups like Al-Qaeda, Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), and sectarian outfits, with the Hazara Shia community frequently targeted by sectarian violence.
- Geopolitical Factors: Pakistan has alleged foreign support for militancy and separatist tendencies in Balochistan, citing instability in Afghanistan and certain terror groups from Iran as contributing factors.
What is India’s Stand on Balochistan Issue?
- India’s Cautious Approach: India denies involvement in Balochistan’s affairs and rejects Pakistan’s allegations of supporting Baloch militants, urging Pakistan to address its internal issues instead of blaming others.
- Diplomatic Stance: India’s stance on Balochistan is shaped by geopolitical considerations, regional stability, and its complex ties with Pakistan. India continues to raise the issue of minority rights and related concerns in Balochistan, in alignment with its democratic and secular values.
- In 2016, the Prime Minister raised Balochistan’s human rights situation in his Independence Day speech.
- Regional Stability: The unrest in Balochistan, coupled with China’s CPEC involvement, poses security challenges in South Asia.
- India balances its strategic interests while advocating for Baloch rights within international norms.
Conclusion
The Balochistan issue arises from historical grievances, economic exploitation, and political marginalization. Pakistan’s military approach has been ineffective, highlighting the need for political reforms and fair resource distribution. India views the situation strategically, considering its regional security impact.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the historical and geopolitical factors driving the Balochistan insurgency. How does the situation impact regional stability, and what should be India's strategic approach? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
(a) India’s trade with African countries will enormously increase.
(b) India’s relations with oil-producing Arab countries will be strengthened.
(c) India will not depend on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
(d) Pakistan will facilitate and protect the installation of a gas pipeline between Iraq and India.
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. In what ways would the ongoing U.S-Iran Nuclear Pact Controversy affect the national interest of India? How should India respond to this situation? (2018)
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)