Initiatives for Agricultural Cooperative Societies | 28 Dec 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Cooperation has taken a series of initiatives for the development of cooperative societies in agriculture including Multipurpose Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (MPACS).
What is MPACS?
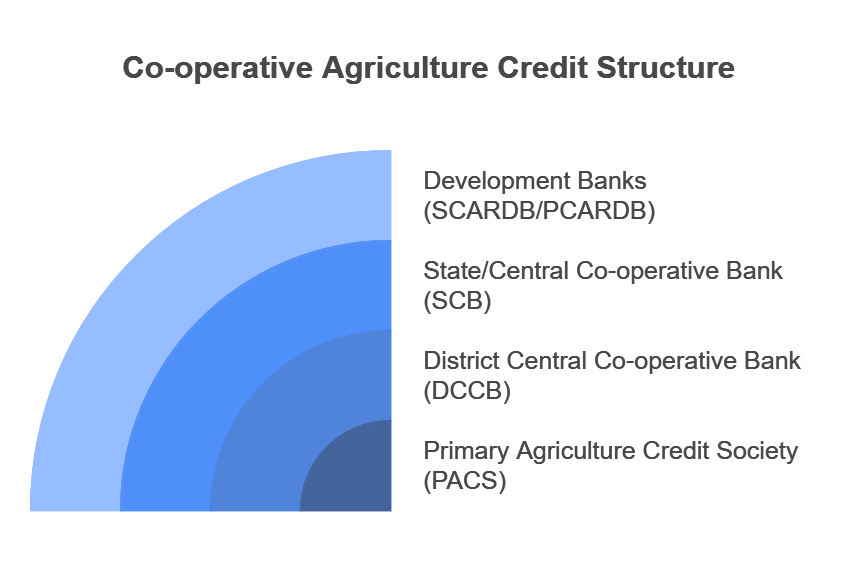
- About PACS: PACS are village-level cooperative credit societies that provide loans and collect repayments from rural agricultural borrowers.
- PACS are registered under the respective State Cooperative Societies Act of the state and are administered by the State Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS).
- Constitutional Backing: 97th Amendment Act, 2011 added the word cooperatives in Article 19(1)(c) under Part III of the Constitution.
- A new Article 43B was added in the Directive Principles of State Policy (Part IV) regarding the promotion of cooperative societies.
- About MPACS: MPACS provide a wide range of services beyond agricultural credit, addressing multiple needs of rural communities.
- It includes credit societies as well as dairy and fisheries cooperatives, and is engaged in 32 activities, including storage and distribution of manure, gas, fertilisers, and water, making them more versatile and effective.
What are the Recent Initiatives for Development of Cooperative Societies in Agriculture?
- Multipurpose PACS: 10,000 newly established Multipurpose Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (MPACS) were inaugurated along with Dairy and Fisheries Cooperative Societies.
- India has set a target of creating 2 lakh PACS in 5 years under a vision to have a presence of cooperatives in every panchayat across the country.
- National Organic Cooperative Limited (NOCL): Farmers were urged to connect with NOCL to increase their incomes through organic farming.
- NCOL is an umbrella organization for aggregation, procurement, certification, testing, branding and marketing of organic products of the co-operative sector.
- NOCL has been registered under the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act, 2002.
- NCOL is an umbrella organization for aggregation, procurement, certification, testing, branding and marketing of organic products of the co-operative sector.
- Mobile Rural Marts Initiative: It was launched in collaboration with NABARD, to provide essential items like pulses, rice, and wheat flour at affordable prices under the Bharat brand.
- The Bharat Brand offers essential goods to the middle class at subsidized prices.
- Micro-ATMs: Cooperative societies are being equipped with RuPay Kisan Credit Cards and Micro-ATMs to access low-cost loans, facilitating financial inclusion and support.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements:
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative
- Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)