International Relations
Infrastructure Developments Around Pangong Tso
- 07 Jul 2023
- 7 min read
For Prelims: India-China Standoff, Pangong Tso Lake, Line of Actual Control
For Mains: Infrastructure Developments along India-China border, Background of India-China Standoff.
Why in News?
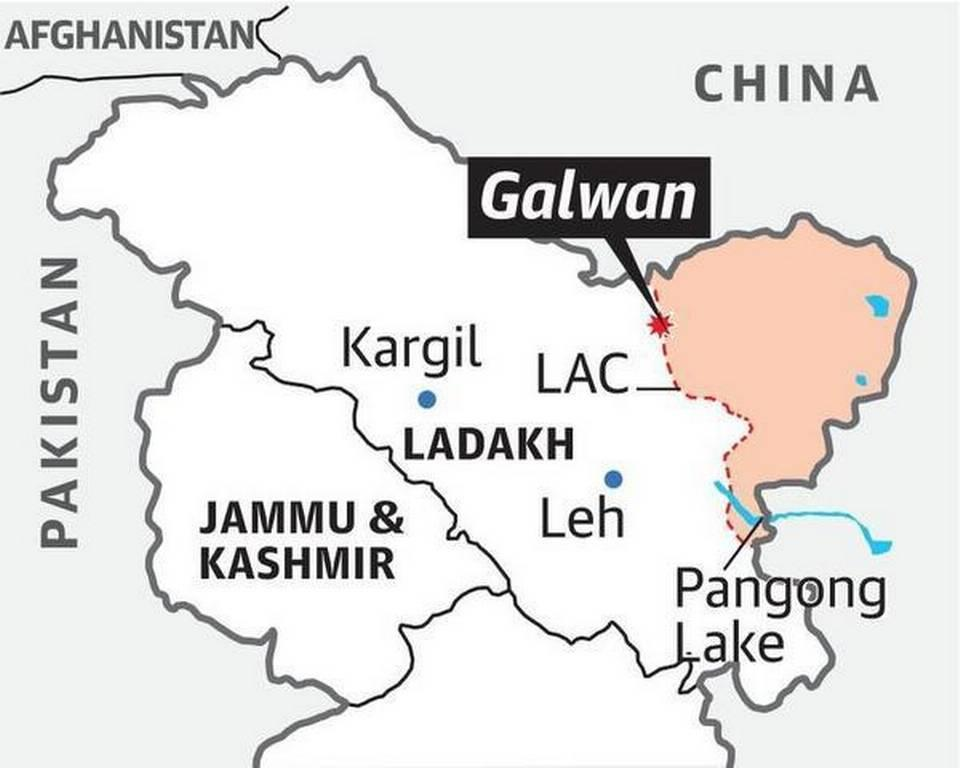
Three years after the violent clash between Indian and Chinese forces in Galwan, there is significant infrastructure development taking place in the India-China border region.
- These infrastructure developments are occurring on both sides since the standoff even as the two await the 19th round of Corps Commander level talks to find a resolution to their dispute in the region.
What are the Infrastructure Developments Around the Border Region?
- China's Infrastructure Efforts:
- Construction of a bridge across the Pangong Tso, connecting the north and south banks, is in progress.
- Large-scale construction activity, including road connectivity towards Shandong village, is observed on the Chinese side.
- A 22 km-long tunnel is being constructed along the G-0177 expressway, connecting to the vital G-216 highway in Tibet.
- India's Infrastructure Projects:
- India is building a black-topped road on the north bank of the Pangong Tso, towards Finger 4.
- Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is nearing completion of key infrastructure projects such as the Sela, Nechipu, and Sela-Chhabrela tunnels, enhancing all-weather connectivity along the LAC.
- Construction work on an alternate axis to the critical Darbuk-Skyok-Daulat Beg Oldie road is advancing through the Saser La.
- India-China Border Roads (ICBR) intiative was also started to improve the mobility of the Indian forces and the connectivity of the border areas. It has three phases: ICBR-I (73 roads), ICBR-II (104 roads) and ICBR-III (37 roads).
- The capital budget of the BRO, which does most of the ICBR work, has increased by 43% to Rs 5,000 crore in 2023-24.
- Nearly 70% of these roads under ICBR-III would be built in Arunachal Pradesh.
- The Sela Tunnel Road project is the most prominent project to connect Arunachal Pradesh via a network of roads. It will be the world’s longest bi-lane tunnel at altitude above 13,000 ft built.
- The Vibrant Villages Programme, a Centrally sponsored scheme, was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- It aims to provide comprehensive development of villages on the border with China and improve the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
- The program will improve infrastructure in states like Himachal Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh. Under the program, residential and tourist centers will be constructed.
What is the Implication of These Infrastructure Developmental Projects?
- Positive:
- Enhanced border infrastructure strengthens India's defense capabilities and improves its ability to patrol and secure the border.
- Improved connectivity benefits local communities, boosts regional development, and generates economic opportunities.
- The improved infrastructure allows India to maintain a stronger strategic position in the region, potentially deterring any aggressive moves from China.
- Negative:
- Infrastructure developments may contribute to ongoing border disputes and heighten tensions.
- It raises concerns within both India and China about improved connectivity and defense capabilities in the region of the other country.
- Perception of India's (or China’s) assertiveness could influence bilateral negotiations and relations.
Pangong Tso Lake:
- Characteristics:
- Pangong Tso is a 135-km long landlocked lake located at an altitude of over 14,000 feet i.e., 4350 m above sea level.
- The lake, a glacial melt, has mountain spurs of the Chang Chenmo range jetting down, referred to as fingers.
- It is one of the highest altitude lakes in the world that is filled with saline water.
- However, even though it is a saline water lake, Pangong Tso freezes completely.
- The brackish water of this region has very low micro-vegetation.
- No aquatic life or fish, except crustaceans during winters are found.
- It is one of the highest altitude lakes in the world that is filled with saline water.
- Pangong Tso is popular for its changing colour abilit; its colour changes from shades of blue to green to red.
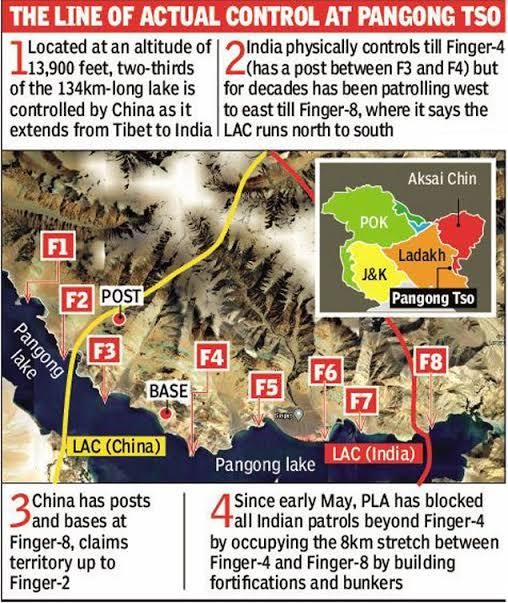
- The Fingers of Pangong Tso:
- The Pangong Tso is a lake located in eastern Ladakh, and it has a unique shape resembling a boomerang, stretching for about 135 kilometers.
- The lake is characterized by mountain spurs that protrude into the water, known as "fingers".
- The fingers of Pangong Tso are numbered from 1 to 8, with Finger 1 being the closest to the eastern end of the lake and Finger 8 the farthest.
- India and China have differing perceptions of the Line of Actual Control (LAC), which serves as the de facto border between the two countries.
- The Pangong Tso is a lake located in eastern Ladakh, and it has a unique shape resembling a boomerang, stretching for about 135 kilometers.
- India and China’s Share:
- Indian and China have around one-third and two-thirds of Pangong Tso Lake respectively.
- India has around 45 km of Pangong Tso under its control. The eastern end of Pangong Tso lies in Tibet
- Border Dispute at Pangong Tso:
- India claims control over the lake until Finger 4 but believes its territory extends up to Finger 8.
- The north bank, where the fingers are located, has been the center of clashes and tensions between the two countries.
- Indian troops are stationed near Finger 3, while the Chinese have a base east of Finger 8, claiming territory up to Finger 2.
- India claims control over the lake until Finger 4 but believes its territory extends up to Finger 8.