Indian Economy
Inflation And Current Outlook of Indian Economy
- 29 Aug 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Inflation And Current Outlook of Indian Economy, Retail Inflation, Reserve Bank of India, Monetary Policy, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), Supply Chain.
For Mains: Inflation And Current Outlook of Indian Economy, Impact of Inflation on Na Economy.
Why in News?
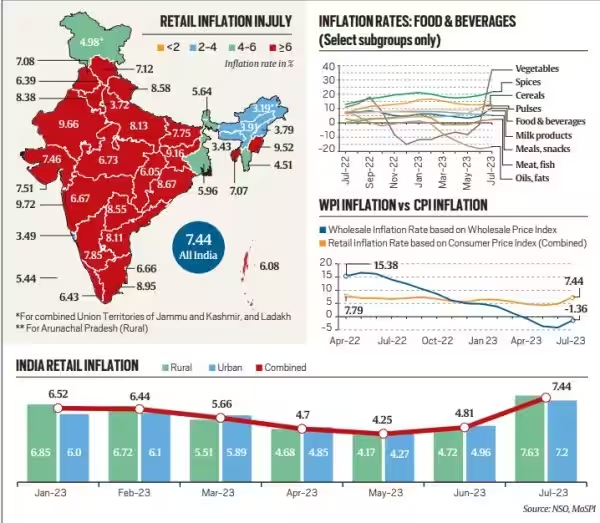
July 2023 witnessed a notable increase in Retail Inflation, reaching 7.44%, creating Goldilocks scenario for India, making investors and savers uncertain about the economic situation.
- A Goldilocks Scenario describes an ideal state for an economy whereby the economy is not expanding or contracting by too much. A Goldilocks economy has steady economic growth, preventing a recession, but not so much growth that inflation rises by too much.
What is the Current Economic Scenario of India and Projections?
- GDP Projection:
- The projected GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth for 2023-24 is 6.5%, while the benchmark Sensex index stands currently at 65,000 points.
- However, if inflation remains high, it could affect returns on stock market investments.
- Gold and bank deposit rates, on the other hand, are expected to remain stable in the coming months.
- The projected GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth for 2023-24 is 6.5%, while the benchmark Sensex index stands currently at 65,000 points.
- Inflation Projection:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) anticipates inflation to stay above 5% until the first quarter of 2024-25, potentially reaching 6.2% in the current quarter (July-Sept) 2023, exceeding the RBI's comfort level of 4%.
- Food Price Pressures:
- Food prices are expected to remain elevated for a few more months. July's data reveals a surge in vegetable prices (37.3%), along with inflation in cereals, pulses (both 13%), spices (21.6%), and milk (8.3%).
- It is expected that government interventions and fresh crop arrivals will eventually ease this pressure.
- Interest Rates and Monetary Policy:
- Due to the higher inflation projections, the possibility of a rate cut has been postponed to the next Fiscal Year (2024-25).
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is likely to maintain policy rates in the upcoming meeting, with the first rate cut potentially occurring in the following fiscal year.
- Market Outlook:
- Despite inflation and high interest rates, India's market has performed well.
- Supported by strong earnings prospects and stable macro conditions, India has outperformed other markets.
What is the Impact of Such Rising Inflation on the Indian Economy?
- Impact on Markets:
- When inflation is high, stock prices are undervalued, and the value of gold increases. Rising inflation reduces purchasing power, leading to lower real earnings.
- Additionally, higher inflation results in higher Interest Rates, affecting the cost of equity.
- The RBI's series of repo rate hikes since April 2022 has contributed to an overall increase in lending rates, affecting various types of loans.
- Income Redistribution:
- Inflation can impact different groups within society unevenly. Creditors may lose out, as the value of the money they receive from debtors decreases.
- Conversely, debtors could benefit by repaying loans with money that is worth less than when they borrowed it.
- International Competitiveness:
- High inflation in one country can lead to a decrease in its international competitiveness. If domestic prices rise faster than those in trading partner countries, the country's exports may become less attractive on the global market.
- Wage-Price Spiral:
- Inflation can sometimes trigger a cycle of rising wages and prices. Workers demand higher wages to keep up with rising costs, and businesses pass on those higher costs to consumers in the form of higher prices. This cycle can perpetuate inflation.
Way Forward
- Given the concerns about rising inflation, the government and the RBI need to work together to manage inflationary pressures. This could involve targeted measures to stabilize food prices, improve Supply Chain efficiency, and maintain a cautious monetary policy.
- The government should focus on maintaining a balanced budget, reducing unnecessary expenditure, and boosting revenue generation through reforms and measures that promote economic growth.
- The RBI should continue to adopt a vigilant and data-driven monetary policy approach. This may involve adjusting interest rates to manage inflation while also considering the impact on economic growth.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 With reference to Indian economy, demand-pull inflation can be caused/increased by which of the following?
- Expansionary policies
- Fiscal stimulus
- Inflation-indexing of wages
- Higher purchasing power
- Rising interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q.2 Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)