Important Facts For Prelims
Indoor Air Quality
- 14 Apr 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
Indoor air pollution is a growing concern in India, especially in urban areas where people spend 70–90% of their time indoors. Yet, discussions around Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) remain limited, with most policy focus still on outdoor pollution.
What is Indoor Air Quality?
- Definition: IAQ refers to the quality of air inside and around buildings, impacting the health and comfort of occupants.
- Common Indoor Air Pollutants:
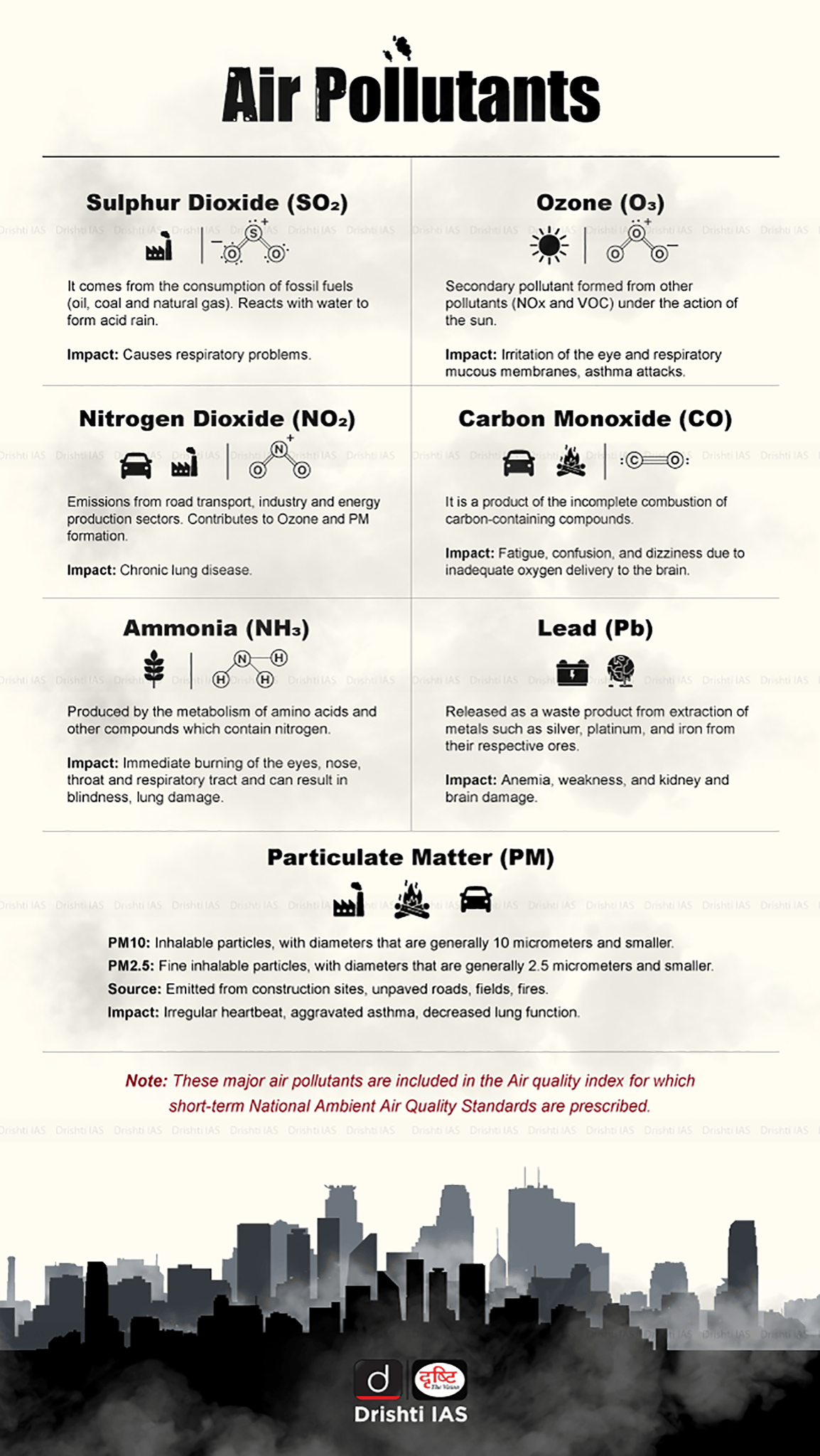
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A toxic odorless gas produced from incomplete combustion.
- Formaldehyde: Found in wood products, glues, paints, and furnishings; a known carcinogen.
- Asbestos: Found in older construction materials used for making fireproof or incombustible building components; exposure can lead to serious lung diseases.
- Radon: A radioactive gas that seeps from the ground into buildings.
- Lead: Found in old paints, plumbing, and ceramics.
- Mould: A microorganism and type of fungus that thrives in damp places, and humid environments.
- Pesticides: Used indoors for pest control, contributing to chemical exposure.
- Smoke: From cigarettes or cookstoves, carrying harmful toxins.
- Allergens: Dust mites, pet dander, and pollen trapped in carpets and furniture.
- Reasons for Deteriorating IAQ: Outdoor pollutants like Particulate Matter (PM2.5) enter poorly sealed or ventilated buildings through gaps in poorly insulated structures.
- Indoor activities such as cooking, smoking, use of incense sticks, and chemical cleaning.
- Overcrowded housing in Indian cities increases pollutant levels due to limited space for dispersion.
- The lack of public awareness and regulatory oversight on IAQ standards allows harmful practices and materials to persist unchecked.
- Impact: India recorded the highest average annual indoor PM2.5 levels (55.18 μg/m³), as revealed in Dyson’s Global study, followed by China, Turkey, UAE, and South Korea.
- Globally, household air pollution causes 3.2 million premature deaths annually (WHO), as pollutants from solid fuels and kerosene damage the lungs, impair immunity, and reduce blood oxygen levels.
- Poor ventilation can lead to carbon dioxide build-up, resulting in “sick building syndrome.”
- Indoor air pollution is linked to noncommunicable diseases such as stroke, heart disease, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer. Women and children bear the heaviest health burden.
What are the Solutions to Indoor Air Pollution?
- Air Purifiers: Use air purifiers equipped with High Efficiency Particulate Air filters to trap particulate matter like PM2.5 and other harmful pollutants.
- Use of Indoor Plants: Certain indoor plants, like spider plants and peace lilies, can help purify the air by absorbing pollutants like formaldehyde and benzene.
- Use Clean Fuels and Technologies: Switch to cleaner alternatives like solar, electricity, biogas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), natural gas, or alcohol fuels for cooking and heating.
- Low-VOC Materials: Reducing the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in building materials like paints, varnishes, and furnishings can significantly improve indoor air quality.
- Health-Focused Building Practices: Establish health-focused building construction guidelines in collaboration with the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), aligning with Eco-Niwas Samhita (ENS), to ensure suitability for healthy living.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the context of proposals to the use of hydrogen enriched CNG (H-CNG) as fuel for buses in public transport, consider the following statements: (2019)
- The main advantage of the use of H-CNG is the elimination of carbon monoxide emissions.
- H-CNG as fuel reduces carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon emissions.
- Hydrogen up to one-fifth by volume can be blended with CNG as fuel for buses.
- H-CNG makes the fuel less expensive than CNG.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into the atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)