International Relations
Indo-China Disengagement at Hot Springs & Gogra Post
- 09 Sep 2022
- 7 min read
For Prelims: India-China Standoff, Pangong Tso Lake, Line of Actual Control, Hot Springs and Gogra Post, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), India-China Military Talks, Aksai Chin.
For Mains: India-China stand-off and disengagement.
Why in News?
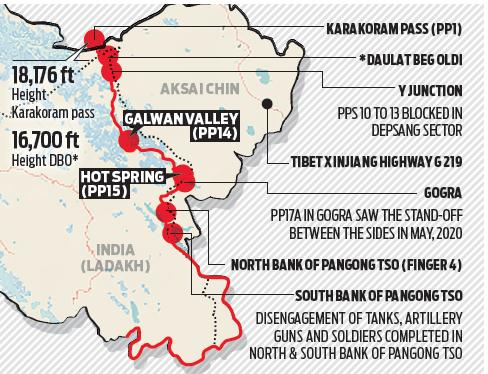
Recently, the Indian and Chinese troops have begun disengaging at Patrolling Pillar-15 (PP-15) in the Gogra-Hotspring region of Eastern Ladakh.
- Forces of the two countries have been locked in a confrontational position in the area since April 2020.
- The move comes ahead of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) summit in Uzbekistan.
Why are the Key Highlights about the Current Disengagement?
- Indian and Chinese armies have begun to disengage from Patrolling Point-15 in the Gogra-Hotsprings area of Eastern Ladakh, marking a step forward to end the standoff ongoing since May 2020.
- PP-15 is one of the 65 patrolling points in Ladakh along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- The disengagement has begun in a coordinated and planned way, which is conducive to peace and tranquility in the border areas.
- As per the understanding reached earlier on disengagement, a buffer zone is to be created at the friction points once troops are withdrawn by both sides and new patrolling norms are to be worked out after complete disengagement and de-escalation.
- The consensus about the disengagement was reached in the 16th round of India China Corps Commander Level Meeting.
- The 16th round of talks was held on July 17, 2022, at the Chushul border personnel meeting point on the Indian side.
- Since the stand-off began in May 2020, the two sides have so far held 16 rounds of talks with disengagement undertaken from both sides of Pangong Tso.
- With disengagement at PP-15, forces of the two countries have disengaged at all friction points in the region which included the North and South banks of the Pangong Tso, PP-14, PP-15 and PP-17A.
- The last disengagement between the forces of the two countries had been achieved at PP-17 A in August 2021 following the 12th Corp Commander Level meeting.
- The friction points that remain now are Demchok and Depsang, which China has constantly refused to accept, maintaining that they are not a part of the current stand-off.
What We Need to Know about the Hot Springs and Gogra Post?
- Location:
- Hot Springs is just north of the Chang Chenmo river and Gogra Post is east of the point where the river takes a hairpin bend coming southeast from Galwan Valley and turning southwest.
- The area is north of the Karakoram Range of mountains, which lies north of the Pangong Tso lake, and south east of Galwan Valley.
- Importance:
- The area lies close to Kongka Pass, one of the main passes, which, according to China, marks the boundary between India and China.
- India’s claim of the international boundary lies significantly east, as it includes the entire Aksai Chin area as well.
- Hot Springs and Gogra Post are close to the boundary between two of the most historically disturbed provinces (Xinjiang and Tibet) of China.
What should be the Way Forward?
- India must continue to press for complete disengagement and de-escalation from all friction areas.
- Also, the Corps Commander level talks should be continued as the relationship cannot go back to normal as long as the situation along the standoff continues.
- India should keep its stand firm over the restoration of the status quo and restoration along the LAC.
What is China’s fully solar-powered, semi-satellite drone?
- About:
- China’s first fully solar-powered Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) has successfully completed its maiden test flight with all onboard systems functioning optimally.
- The drone is a large machine powered entirely by solar panels with a wingspan of 164-ft.
- Named the Qimingxing-50, or Morning Star-50, this drone flies above 20-km altitude where there is stable airflow with no clouds.
- The High-Altitude, Long-Endurance (HALE) UAV can stay airborne for long durations.
- This helps these drones to make the maximum use of solar equipment to stay functional for extended durations.
- This drone is also referred to as ‘High Altitude Platform Stations’ or pseudo-satellites.
- Significance:
- It can operate without a break for months, even years.
- It is capable of carrying out satellite-like functions.
- If satellite services are not available for, say, time-sensitive operations or in case of wartime disruption, then near-space UAVs can step in to fill the operational gap.
- Morning Star-50’s long-endurance provides an added advantage to make this capability available over a longer period.
- It can undertake surveillance missions that require it to stay operational, watching over borders or oceans, for months.
- It can be used for monitoring forest fires, providing communication and environment relay.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)