Indian Navy Sheds Colonial Legacy | 25 May 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Navy has taken significant steps to shed its British colonial legacies by renaming traditional naval symbols and introducing new insignias.
- This transformation underscores India's efforts to redefine its naval identity to reflect its national heritage and aspirations better.
What are the Recent Changes in Nomenclature?
- New Nomenclature: To indigenize and reflect national pride, the Indian Navy has renamed ‘Jack’ to ‘National Flag’ and ‘Jackstaff’ to ‘National Flag Staff’.
- Old Terms and Their Origins: The terms 'Jack' and 'Jackstaff' are deeply rooted in British naval history and have been adopted by navies worldwide, including India, as remnants of British naval practices.
- ‘Jack’ typically refers to a flag, and the ‘Jackstaff’ is a short pole from which this flag is flown, positioned at the bow of a ship.
- Regulatory Framework and Legal Amendments: The change in nomenclature was formalised through an amendment to the "Regulations for the Navy (Ceremonial, Conditions and Service and Miscellaneous Regulation) 1963", leveraging the powers granted by the Naval Act of 1957.
What are Other Symbolic Changes Across the Armed Forces?
- Changes in Naval Insignia: In September 2022, the Indian Navy adopted a new naval ensign, discarding the British-inspired George's Cross for a design that includes a blue octagon with twin golden borders, the national emblem, and the motto ‘Satyamev Jayate’.
- This insignia draws inspiration from the seal of Shivaji Maharaj, symbolising the Navy's reach in all eight directions (four cardinal and four intercardinal).
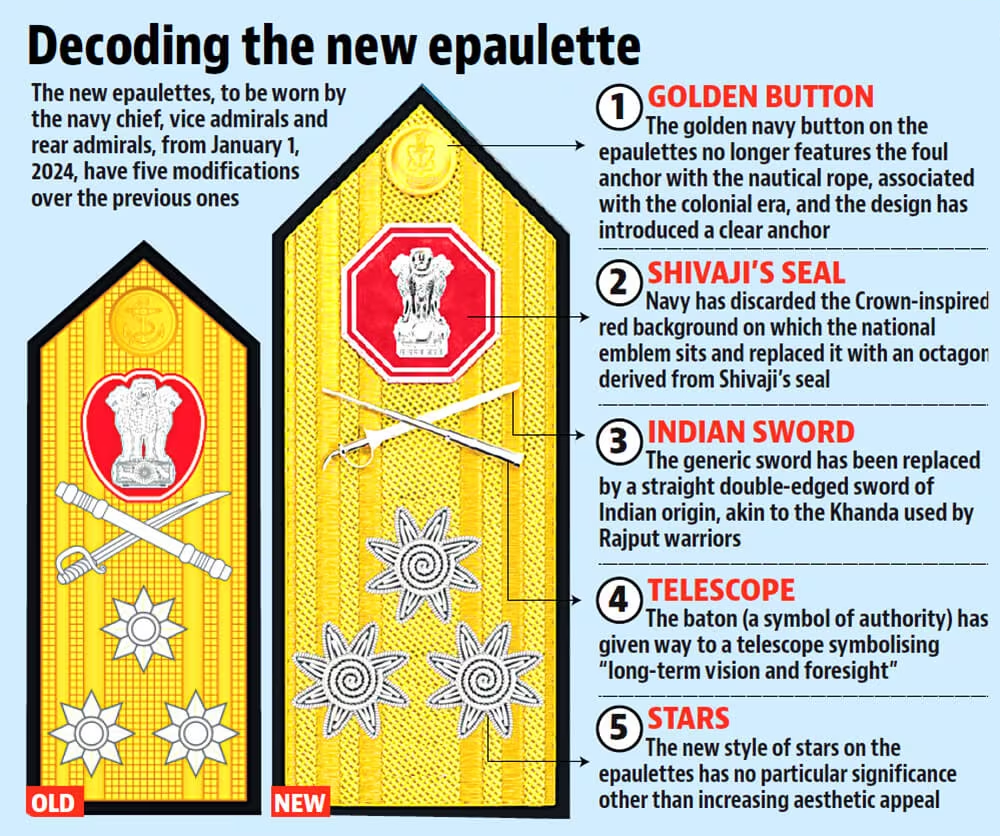
- Change in Epaulettes of Naval Officers: The Indian Navy also unveiled new senior officers' epaulettes inspired by Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's seal, symbolising a break from colonial legacies and a celebration of India's maritime heritage, with five modifications from the previous design for the navy chief, vice admirals, and rear admirals.
- New Dress Code in Messes: The Indian Navy has embraced its heritage by introducing the Kurta-Pyjama in naval messes, with senior officers among the first to don the traditional attire.
- Changes in Indian Army: The Indian Army has also started phasing out traditional practices such as horse-drawn buggies at events, retirement ceremonies, and pipe bands at dinners.
- Significance:
- Renaming and redesigning naval symbols indicate both distance from colonial ties and reasserting Indian sovereignty and maritime heritage.
- These steps align with India's Prime Minister's "Panch Pran" pledges for the nation's development by its 100th year of independence.
National Flag
- The design of the Indian tricolour is largely attributed to Pingali Venkayya, an Indian freedom fighter.
- Arguably the first national flag of India is said to have been hoisted on 7th August 1906, in Kolkata at the Parsee Bagan Square (Green Park).
- The National Flag is rectangular with a length-to-width ratio of 3:2.
- According to Article 51A (a), it shall be the duty of every citizen of India to abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag, and the National Anthem.
- A person who is convicted for the following offences under the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act of 1971 is disqualified to contest in the elections to the Parliament and state legislature for 6 years.
- Offence of insulting the National Flag
- Offence of insulting the Constitution of India
- Offence of preventing the singing of the National Anthem
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the National Flag of India according to the Flag Code of India, 2002: (2023)
Statement-I: One of the standard sizes of the National Flag of India is 600 mm x 400 mm.
Statement-II: The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the Flag shall be 3 : 2.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement- II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement- I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement- II is correct
Ans: (d)
Q. Department of Border Management is a Department of which one of the following Union Ministries? (2008)
(a) Ministry of Defence
(b) Ministry of Home Affairs
(c) Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport and Highways
(d) Ministry of Environment and Forests
Ans: (b)