International Relations
India-Uzbekistan Relations
- 01 Aug 2022
- 8 min read
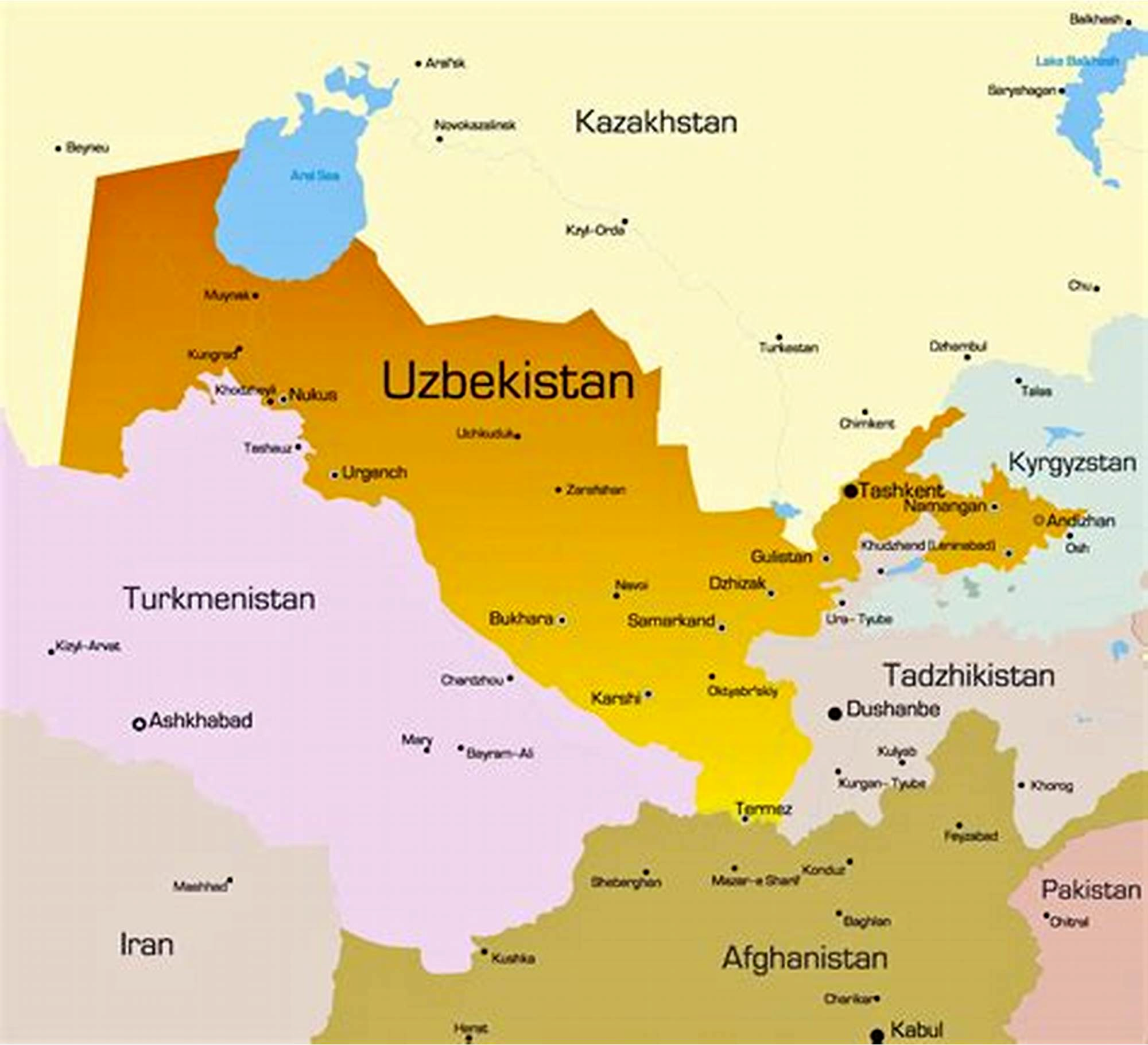
For Prelims: Map of Uzbekistan and neighbouring countries
For Mains: India-Uzbekistan Relations, International Treaties and Agreements
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister for Commerce & Industry attended the 13th Session of the India-Uzbekistan Inter-Governmental Commission.
- Further, he highlighted India-Uzbekistan relations as key to India’s vision of integrated extended neighbourhood.
- IGC meeting is an important platform to deliberate on ideas, discuss issues & strengthen bilateral relations especially in the field of trade & investment.
What are the Key Highlights of the Session?
- Minister Highlighted:
- That there is a need to take the relationship forward in newer areas like technology, digital payment solutions, and investment in start-ups.
- The need for an integrated approach for regional connectivity and cooperation.
- Further, there are seven emerging areas of cooperation between both nations namely Digital Payments, Space Cooperation, Agri and Dairy, Pharma, Gems and Jewellery, MSME, and Inter-regional cooperation.
How has been India-Uzbekistan Relations?
- About:
- India and Uzbekistan have a long history of cooperation.
- After Uzbekistan's independence, India was one of the first countries to acknowledge its state sovereignty.
- Bilateral relations now encompass a wider canvas, including political and strategic issues, defense and security, trade and investment, energy, agriculture, S&T, education, and people-to-people ties.
- Initiatives:
- Defense Cooperation:
- The first-ever joint military exercise held between India and Uzbekistan was named Dustlik.
- India has also assisted in setting up an India Room at the Armed Forces Academy of Uzbekistan in Tashkent.
- The first-ever joint military exercise held between India and Uzbekistan was named Dustlik.
- Security Cooperation:
- India and Uzbekistan share common perspectives on a number of security issues, including terrorism, trans-national organized crime, illegal trafficking, smuggling, etc.
- The main focus of engagement in this sphere has been to provide assistance to Uzbek security agencies through training and capacity building.
- Trade:
- It has increased from USD 247 million in 2019-20 to USD 342 million in 2021-22, a growth of 38.5%.
- Investments:
- Indian investments by Indian companies include those in the field of pharmaceuticals, amusement parks, automobile components, and the hospitality industry.
- Amity University and Sharda University have opened campuses in Tashkent and Andijan respectively.
- Indian institutions like iCreate are actively cooperating with Uzbek counterparts for promoting a start-up ecosystem in Uzbekistan and training entrepreneurs in setting up incubators.
- Tourism:
- The Uzbek government has extended the e-Visa facility to Indian tourists.
- Uzbekistan has also emerged as a significant source of medical tourism with about 8,000 Uzbeks annually seeking medical treatment in India.
- Solar Power:
- Uzbekistan has expressed interest in joining the International Solar Alliance.
- There is interest in Indian participation in the development of the solar power sector through competitive bidding.
- Defense Cooperation:
- Bilateral Mechanism:
- National Coordination Committees: India and Uzbekistan have set up National Coordination Committees to oversee the implementation of mutually agreed projects and initiatives.
- Multilateral Initiatives:
- India-Central Asia Business Council: The dialogue brought together Business Councils of all five Central Asian countries to take the trade and investment partnership forward with a special focus on energy, pharmaceuticals, automotive, agro-processing, education, and urban infrastructure, transport, civil aviation, IT and tourism.
- India- Central Asia Dialogue: It enables the issues of further strengthening ties between India and the countries of Central Asia in the spheres of politics, economics, digitalization, and cultural and humanitarian direction.
What are the Challenges in India-Uzbekistan Relations?
- There is a very low amount of trade and commerce between the two countries.
- Lack of connectivity, as Uzbekistan is a landlocked country, and the air connectivity is not up to the mark.
- China has made in-roads with Belt and Road Initiative in all the central Asian countries including Uzbekistan.
Way Forward
- Indian companies can take advantage of Uzbekistan’s various trade agreements and implement joint beneficial investment projects in the area to tap the economic and trade potential of the two countries.
- There is a need for increased convergence between the two countries.
- Uzbekistan should join the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC). With both Iran and India as members of INSTC, the addition of Uzbekistan will move things, especially connectivity, in the proper direction.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following has/have shrunk immensely/ dried up in the recent past due to human activities? (2018)
- Aral Sea
- Black Sea
- Lake Baikal
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Aral Sea: It lies between Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. It has been shrinking steadily since the 1960s after its tributaries were diverted by Soviet irrigation projects. By 2007, the lake had declined to 10% of its original size and had split into four separate lakes. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Black Sea: It is also known as the Euxine Sea. It is one of the major water bodies and a famous inland sea in the world. The countries sharing a border with the Black Sea include Romania, Turkey, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Russia, and Georgia. There has been no dramatic shrinkage of the Black Sea in the recent past. Hence, 2 is not correct.
- Lake Baikal: Located in Siberian Russia, this UNESCO World Heritage site has not undergone any dramatic shrinkage in the recent past. One of the most recognizable shifts affecting Lake Baikal is the rapidly increasing number of Spirogyra, a diverse form of algae. Hence, 3 is not correct. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. A number of outside powers have entrenched themselves in Central Asia, which is a zone of interest to India. Discuss the implications, in this context, of India’s joining the Ashgabat Agreement (2018)