Internal Security
India’s Strategy to Eliminate Naxalism
- 24 Mar 2025
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Operation Green Hunt, CoBRA, Greyhounds, Universal Service Obligation Fund Scheme, Maoism
For Mains: Left-Wing Extremism and internal security in India, Government strategies to eliminate Naxalism
Why in News?
The Union Home Minister announced that the central government is aggressively working towards a Naxal-free India, setting a target to eliminate Naxalism by 31st March 2026, ensuring that no citizen has to lose their life because of it.
What is India’s Strategy to Eliminate Naxalism?
- Development Programs: Under the Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution, Police and Public Order fall under the jurisdiction of state governments.
- However, to combat Left-Wing Extremism (LWE), the National Policy and Action Plan to Address LWE, 2015 was adopted, implementing a multi-pronged approach that combines security measures, development initiatives, and community rights protection.
- Road Connectivity Project for LWE-Affected Areas under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana II enhances road connectivity to improve access to remote areas and facilitate security operations.
- ROSHNI Scheme focuses on training and employment opportunities for rural youth in LWE-affected districts.
- Industrial Training Institutes and Skill Development Centers are established in LWE Districts.
- Around 130 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) were made functional in tribal blocks of LWE-affected districts to improve access to quality education.
- Under the Universal Service Obligation Fund Scheme (now Digital Bharat Nidhi), mobile towers are installed to improve communication in LWE-affected areas.
- Tribal Youth Exchange Programs under Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan to enhance outreach to tribal youth in LWE-affected districts.
- Security Operations: Large-scale operations like Operation Green Hunt deploy paramilitary forces to eliminate the Naxalite presence.
- Increased deployment of Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) and state police, along with specialized forces such as Commando Battalion for Resolute Action (CoBRA) and Greyhounds (Andhra Pradesh), strengthens counter-insurgency efforts in the Red Corridor for long-term security.
- Legal Framework: Laws such as the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA, 1967 ban Naxalite organizations.
- Additionally, the Forest Rights Act, 2006 secures tribal communities' rights over forest produce, while the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, (PESA) 1996 empowers tribal gram sabhas in governance and resource management.
- Surrender-cum-Rehabilitation Policy: Financial aid, vocational training, and social reintegration programs are provided for surrendered Naxals to facilitate their return to mainstream society.
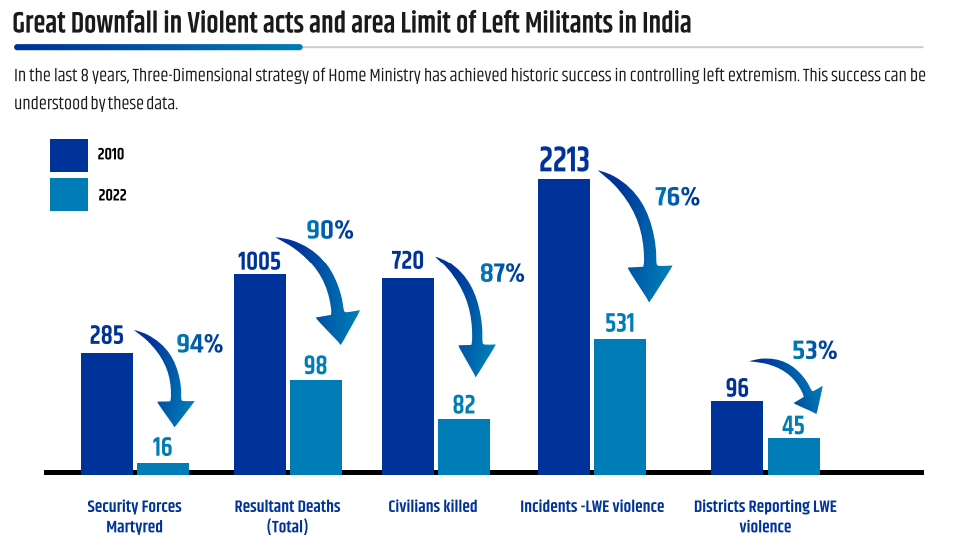
- Progress Made: The number of LWE-affected districts has reduced from 126 (2014) to just 12 (2024).
- Naxal-related incidents have significantly decreased from 16,463 (2004-2014) to 7,700 (2014-2024).
- Casualties among security forces due to Naxalism have declined by 73%, while civilian casualties have decreased by 70%.
- Fortified police stations have increased from 66 (2014) to 612 (2024).
What is Naxalism?
- About: Naxalism, a form of LWE inspired by Maoist ideology, seeks to overthrow the state through armed rebellion (violence and guerrilla warfare).
- The term Naxalism derives its name from the village Naxalbari in West Bengal, where an uprising of peasants occurred in 1967 against exploitative landlords.
- It has since evolved into a complex insurgency affecting several states across India.
- Causes for Naxalism:
- Landlessness and Exploitation: Unequal land distribution and exploitative practices by landlords, moneylenders, and middlemen fuel resentment in rural and tribal areas and led to growth of Naxalism.
- Poverty and Underdevelopment: Naxalite-affected regions lack basic amenities like healthcare, education, and employment opportunities, driving people towards extremism.
- Tribal Alienation: Displacement due to industrial and mining projects without proper rehabilitation creates anger and distrust towards the state, leading many to join Naxalite movements.
- State Neglect and Violence: A weak government presence, lack of basic services, and instances of police excesses, including custodial deaths, have further intensified grievances, strengthening the Naxalite insurgency.
- Indian Maoists: The Communist Party of India (Maoist) is the largest and most violent Maoist group in India. It was formed through the merger of two major Maoist factions: CPI (Marxist-Leninist) People’s War and the Maoist Communist Centre of India.
- The CPI (Maoist) and its organizations were banned under the UAPA, 1967.
- Geographic Spread: The Naxal movement is most active in the “Red Corridor,” spanning parts of several Indian states, including Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Maharashtra, and Bihar.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the factors that contributed to the rise of Naxalism in India and analyze the government’s approach to countering it. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q. The persisting drives of the government for development of large industries in backward areas have resulted in isolating the tribal population and the farmers who face multiple displacements. With Malkangiri and Naxalbari foci, discuss the corrective strategies needed to win the Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) doctrine that affected citizens back into the mainstream of social and economic growth. (2015)
Q. Article 244 of the Indian Constitution relates to administration of scheduled areas and tribal areas. Analyze the impact of non-implementation of the provisions of the Fifth schedule on the growth of Left-wing extremism. (2018)
Q. What are the determinants of left-wing extremism in the Eastern part of India? What strategy should the Government of India, civil administration and security forces adopt to counter the threat in the affected areas? (2020)