India's Role in Advancing Global DPI | 16 Jul 2024
Why in News?
India's increasing influence in the digital sphere has been globally acknowledged, particularly through its advancements in Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI).
- The recent Report of India’s G20 Task Force on DPI highlighted India's leadership in this domain and urged the country to proactively extend its digital solutions to the Global South.
Note: The Task Force was established in January 2023 to oversee India's G20 Presidency agenda on DPI and Financial Inclusion.
- It aims to boost productivity through digital technology adoption and support the government's digital economy policies.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Identifying a Global Body: The report recommends establishing a global-standard organisation to harness the DPI ecosystem across various regions.
- This entity should have a multinational presence and the expertise necessary to formulate policies and implement strategies effectively. Its goal would be to facilitate collaboration among nations, especially in the Global South.
- Integration of AI with DPI: Explore the integration of Artificial Intelligence to enhance DPI capabilities while ensuring ethical use and data privacy safeguards.
- The report suggests using open-source software and AI models to promote innovation and scalability in DPI, making it more accessible for private players.
- Implementing measures to protect user data is crucial for building trust in AI-enabled services.
- Addressing biases in AI algorithms ensures fair treatment for all users, Ensuring transparency in AI processes helps in gaining public confidence in digital services.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- Definition: DPI is described as a set of shared digital systems that should be secure and interoperable, and can be built on open standards and specifications to deliver and provide equitable access to public and/or private services at societal scale.
- DPI is governed by applicable legal frameworks and enabling rules to drive development, inclusion, innovation, trust, and competition, while respecting human rights and fundamental freedoms.
- Components of DPI:
- Technology: This comprises digital systems and applications (e.g., software codes, building blocks, protocols, standards) that are interoperable.
- Governance: Governance facilitates user adoption at scale by establishing trust in DPI. Governance frameworks may include:
- Rules of engagement governing stakeholder behavior.
- Cross-cutting and domain-specific norms, laws, and policies.
- Governance embedded into digital technologies.
- Accountable institutions for maintaining oversight on its design, deployment, and implementation.
- Community: Vibrant and inclusive community participation can enable value creation. This also comprises private sector and civil society actors who can collaborate to unleash innovation and unlock value.
- Foundational DPI:
- Identification: The ability for people and businesses to securely verify their identity, as well as complementary trust services such as electronic signatures and verifiable credentials.
- Payments: Easy and instant transfer of money between people, businesses, and governments.
- Data sharing: Seamless flow of personal data with consent, wherever applicable, across public and the private sectors, with safeguards for personal data protection as per applicable data governance frameworks.
- India’s DPI Examples and Achievements:
How is India Currently Engaging with Global DPI?
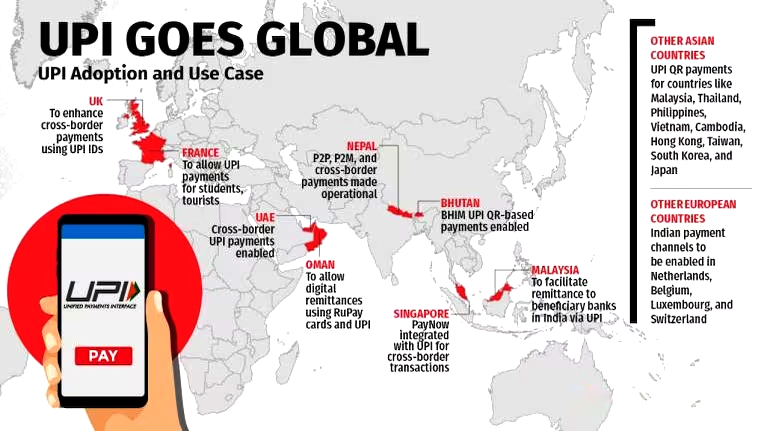
- Globalisation of UPI: The Reserve Bank of India is actively working with Indian missions abroad to globalise the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), having engaged with over 80 countries and established partnerships in more than 30 countries.
- Role of NPCI: The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) is pushing for UPI's international acceptance, highlighting India's commitment to digital finance globally.
Read more: Digital Public Infrastructure
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2020)
(a) Digital security infrastructure
(b) Food security infrastructure
(c) Health care and education infrastructure
(d) Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Ans: (a)
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a technology for authenticating users and devices in the digital world. Under this system, one or more trusted parties digitally sign documents certifying that a particular cryptographic key belongs to a particular user or device. The key can then be used as an identity for the user in digital networks.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.

