India’s E-commerce Market | 16 May 2024
For Prelims: e-Commerce, Foreign Direct Investment, Consumer Protection, Data Privacy, Intellectual Property, The Information Technology Act, Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021, Consumer Protection (E-Commerce) Rules 2020, Foreign Direct Investment Policy
For Mains: Need of E-Commerce export policy, Comparison of Indian E-Commerce Export Policy with Other Countries
Why in News?
According to a recent report by Invest India, an Investment Promotion and Facilitation Agency, India's E-Commerce Sector is projected to reach USD 325 billion by 2030.
- This will position India as the 3rd largest online retail market globally by scale.
What is the Status of the E-Commerce Sector in India?
- About: E-commerce, short for Electronic Commerce, encompasses the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet.
- It eliminates geographical barriers, allowing transactions to occur seamlessly across borders.
- It includes a wide range of activities, from online retailing to digital payments, and continues to evolve with advancements in technology and changes in consumer behaviour.
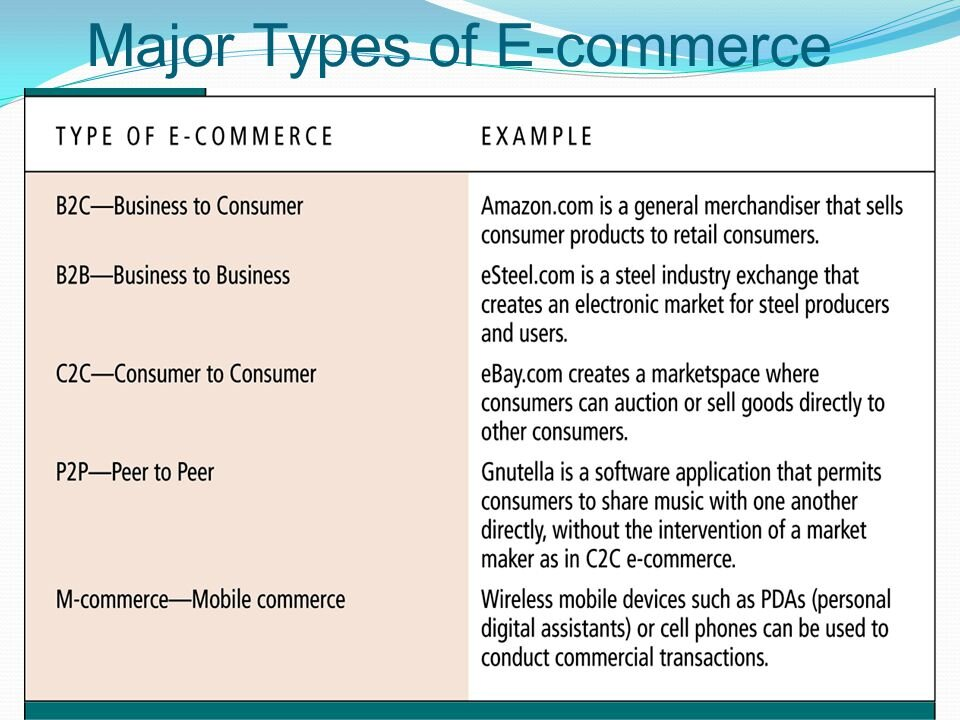
- Types:
- Key Statistics:
- Between 2019 and 2026, number of online shoppers in India will reach:
- 88 million in Rural India, showing a Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22% and
- 263 million in Urban India showing a CAGR of 15%.
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, Government e-marketplace (GeM) achieved its highest-ever Gross Merchandise Value of USD 2011 billion.
- As of 2023, the e-commerce sector in India is valued at USD 70 billion, constituting approximately 7% of the country’s total retail market.
- As of 2022, Top 3 countries in the e-commerce market are : China, USA and Japan.
- As of 2022, India ranked 7th in the e-commerce Market.
- Between 2019 and 2026, number of online shoppers in India will reach:
- Driving Factors:
- Smartphone and Digital Penetration: The rise in smartphone usage has been a significant catalyst for e-commerce growth in India. It has democratised access to online platforms.
- 1.18 billion people, representing over 80% of India's population, will have access to smartphones by 2026.
- The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has emerged as a significant player in digital transactions, facilitating transactions worth USD 1.5 trillion in 2022.
- Affordability of Cheap Internet: It plays a pivotal role in India's internet penetration.
- Now one gigabyte of data is priced at approximately USD 0.17 (Rs 13.5), which gives incentive to a substantial number of the population to opt for online activities
- India ranks 7th on the list of countries with cheapest mobile data.
- Also, internet penetration is expected to grow to 87% by 2025.
- Improved Logistics and Supply Chain: The growth of e-commerce in India has been supported by the development of efficient logistics and supply chain networks.
- Government initiatives such as the National Logistics Policy streamlines deliveries to the last mile, enhancing logistical efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Rising Middle-Class Population and Disposable Incomes: India's growing middle-class population and increasing disposable incomes have fueled the demand for e-commerce.
- According to the World Economic Forum, nearly 80% of households in 2030 will be middle-income in India.
- Convenience and Time-Saving: E-commerce offers consumers the convenience of shopping from the comfort of their homes or on-the-go, saving time and effort.
- Example: Food delivery platforms like Zomato and Swiggy have gained immense popularity due to the convenience they offer to consumers, allowing them to order meals without leaving their homes or offices.
- Wider Product Assortment and Competitive Pricing: E-commerce platforms provide consumers with a vast array of product choices and competitive pricing options, making it easier to find desired products at affordable rates.
- This has been a significant draw for consumers, particularly in smaller cities and rural areas where product availability and pricing can be limited.
- Rising Focus on Rural E-Commerce: Recent reports highlight the growing prominence of Rural-Centric E-Commerce.
- It expects a significant portion of demand to originate from tier 2-4 towns and rural areas by 2026.
- This trend is further reinforced by government initiatives and the emergence of quick commerce.
- Smartphone and Digital Penetration: The rise in smartphone usage has been a significant catalyst for e-commerce growth in India. It has democratised access to online platforms.
- Challenges:
- Counterfeit and Intellectual Property Infringement: Cases of counterfeit and substandard goods being sold on popular e-commerce platforms have been reported in India.
- It can undermine consumer trust and lead to legal and financial consequences for e-commerce companies.
- Infrastructural Challenges: Internet penetration remains relatively low in certain areas. Postal addresses are not standardised, affecting logistics.
- Due to lack of supply chain integration, high delivery charges, more time taken to deliver product
- Lack of Clear Regulatory Framework: Clear legislation is needed to regulate e-commerce practices domestically and internationally.
- The rise of social commerce, where consumers can make purchases directly through social media platforms, poses a potential challenge to the traditional regulatory framework.
- Technological Disruptions and Cybersecurity Threats: The e-commerce industry is susceptible to technological disruptions, such as the emergence of new business models, advancements in artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity threats like data breaches, hacking, and phishing attacks.
- Customers are sceptical of paying by credit card due to the increasing threat of fraud by hackers
- Counterfeit and Intellectual Property Infringement: Cases of counterfeit and substandard goods being sold on popular e-commerce platforms have been reported in India.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to the E-Commerce Sector in India?
- FDI Policy: 100% FDI is allowed in B2B e-commerce. Also, 100% FDI under the automatic route is permitted in the marketplace model of e-commerce.
- National E-Commerce Policy: The Indian government is set to introduce a national e-commerce policy that aims to create a favourable environment for the development of the sector and drive exports.
- Key Features:
- Aim: Establish a regulatory framework that facilitates ease of doing business in the sector.
- Boosting Exports: Recognizes India’s significant e-commerce export potential. Aims to capitalise on global cross-border e-commerce growth.
- Regulatory Body and FDI: Considers establishing a regulator for the e-commerce sector. Advocates for transparency in rules governing FDI.
- Addressing Trader Concerns: Clarifies issues related to deep discounts and preferences given to select sellers.
- Key Features:
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC): This initiative fosters an open-source e-commerce network that connects consumers, platforms, and retailers, promoting transparency and interoperability.
- It will provide equal opportunities for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) to thrive in digital commerce.
- The Consumer Protection (e-commerce) Rules, 2020. The Rules directed the e-commerce companies to display the country of origin alongside the product listings.
- In addition, the companies will also have to reveal parameters that go behind determining product listings on their platforms.
- Digital India initiative: The Digital India initiative has provided solid impetus to other government-led initiatives, including UMANG, Start Up India and Aatmanirbhar Bharat, which have great potential to translate into global success.
- India Stack: This initiative comprises a set of open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that enable government agencies, businesses, and developers to leverage digital infrastructure for various services, including e-commerce.
- BharatNet Project: Aims to provide internet connectivity in local bodies (Panchayats), increasing e-commerce reach in rural areas.
- Heavy investment is being made by the Government for rolling out a fibre network for 5G that will help boost e-commerce in India.
What Measures can be Adopted to Boost the E-Commerce Sector?
- Robust Infrastructure Development: Investing in improving logistical infrastructure, including transportation networks and warehousing facilities is needed to enhance last-mile delivery and reduce fulfilment costs.
- Utilising AI technology, data analytics and automation to optimise logistics and supply chain management.
- Strong Payment System: As E-commerce heavily relies on online payment, it is necessary to build a secure payment system to build trust and facilitate transactions.
- It is important to ensure that the payment gateway complies with the PCI DSS for security.
- The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to protect credit card data.
- It is required by all organisations that process, store, or transmit credit card information.
- It is important to ensure that the payment gateway complies with the PCI DSS for security.
- Regulatory Framework for E-commerce: It is needed to ensure that consumer rights are safeguarded through a clear framework, which includes accurate product descriptions, transparent pricing, fair return and exchange policies, and effective grievance redressal mechanisms.
- Creating Awareness: It is crucial to create awareness among people to promote and increase the growth of this industry.
- It can be done through several ways such as:
- Education and training can help in gaining a better understanding of the benefits and opportunities offered by e-commerce exports.
- Networking events which can serve as a platform for businesses and individuals to connect and share ideas.
- Marketing campaigns can also play a crucial role in creating awareness about e-commerce exports.
- It can be done through several ways such as:
|
Drishti Mains Question: The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) initiative is expected to make e-commerce more inclusive and accessible for consumers. Discuss. |